
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The steps required to obtain the pure samples of the given compound from the starting material are to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The rearrangement in which acyl azides (RCO−N3) undergoes a reaction to form the
Answer to Problem 23.60AP
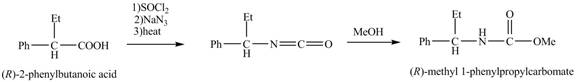
The reaction route for the synthesis of the given product is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The separation of enantiomers occurs in three steps.
In the first step, the two enantiomers, (±)-2- phenylbutanoic acid are reacted with (R)- form of 1- phenylpropane -1- amine to give the diasteromeric salts. Then the diasteromeric salts are separated by the process of fractional crystallization with the help of suitable solvent and the precipitates of isomers are obtained. At last, the precipitates get separated when treated with dilute HCl.
The separation of the two enantiomers is shown below.
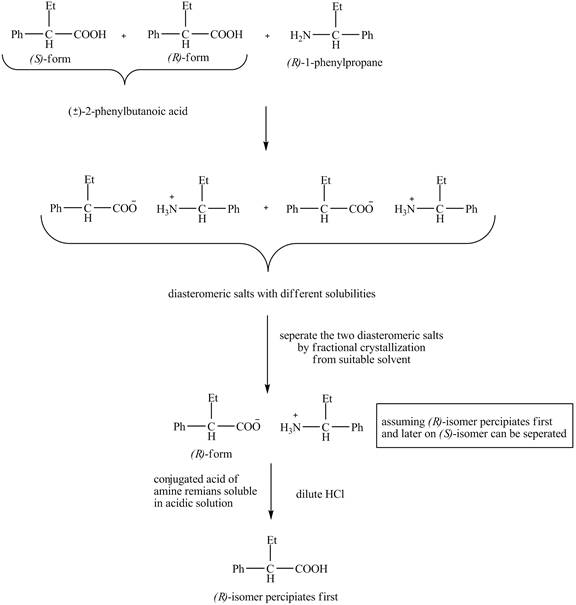
Figure 1
The formation of the given product follows the curtius rearrangement. The reaction follows a concerted mechanism, a reaction in which the bond formation and bond dissociation occurs in a single step.
The (R)- form of 2- phenylbutanoic acid obtained by the separation method is heated with NaN3 in presence on thionyl chloride to form the isocyanate. Then the reaction of the isocynate with MeOH results in the formation of the desired product, (R)- methyl 1- phenylpropylcarbamate.
The reaction for the formation of (R)- methyl 1- phenylpropylcarbamate is shown below.
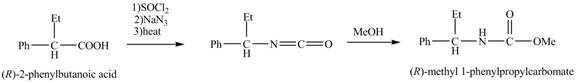
Figure 2
The desired product, (R)- methyl 1- phenylpropylcarbamate is formed by the curtius reacrrangent as shown in Figure 2.
(b)
Interpretation:
The steps required to obtain the pure samples of the given compound from the starting material are to be stated.
Concept introduction:
An ester is formed by the reaction of carboxylic with alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst. This reaction is known as Esterification.
Ester is the
Answer to Problem 23.60AP
The reaction route for the synthesis of the given product is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
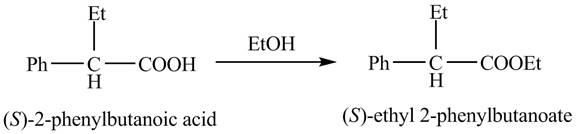
The (S)- isomer of the 2- phenylbutanoic acid is obtained by the enantiomer separation steps. The (S)-2- phenylbutanoic acid on treatment with ethanol gives the desired ester, (S)- ethyl 2- phenylbutanoate.
The reaction of the formation of (S)- ethyl 2- phenylbutanoate is shown below.
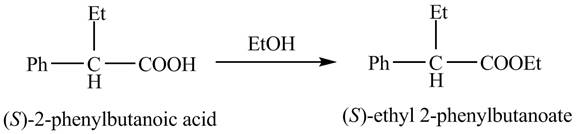
Figure 3
The formation of (S)- ethyl 2- phenylbutanoate follows the esterification reaction and the reaction is shown in Figure 3.
(c)
Interpretation:
The steps required to obtain the pure samples of the given compound from the starting material are to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Hofmann rearrangement reaction is the conversion reaction of the primary amide to a primary amine with the loss of one carbon chain. The reaction requires basic conditions. The reaction of sodium hydroxide with bromine forms sodium hypobromite as an intermediate in situ.
Answer to Problem 23.60AP
The reaction route for the synthesis of the given product is shown below.
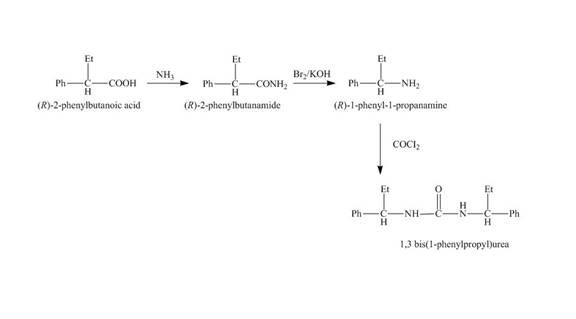
Explanation of Solution
The isomer, (R)-2- phenylbutanoic acid reacts with ammonia and the amide group is introduced followed by the reaction with Br2 and KOH to give the amine with the loss of one carbon chain. Then, the reaction of amine with phosgene (COCl2) forms the desired product.
The reaction of the formation of (R,R)-1,3- bis (1-phenylpropyl) urea is shown below.
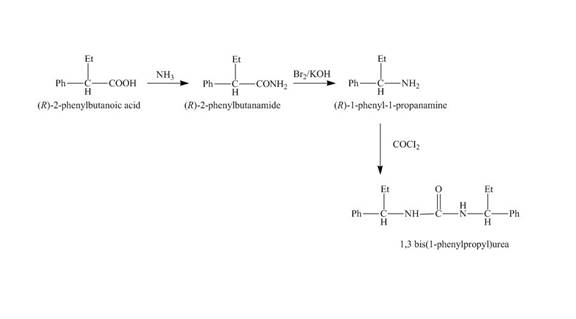
Figure 4
The formation of (R,R)-1,3- bis (1-phenylpropyl) urea is shown in Figure 4.
(d)
Interpretation:
The steps required to obtain the pure samples of the given compound from the starting material are to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Hofmann rearrangement reaction is the conversion reaction of the primary amide to a primary amine with the loss of one carbon chain. The reaction requires basic conditions. The reaction of sodium hydroxide with bromine forms sodium hypobromite as an intermediate in situ.
Answer to Problem 23.60AP
The reaction route for the synthesis of the given product is shown below.
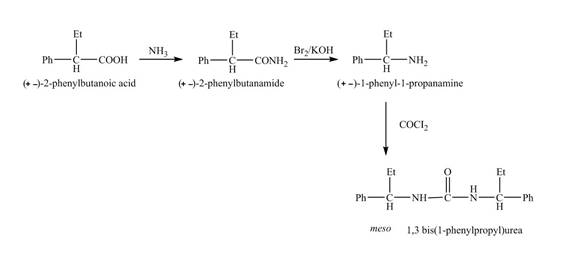
Explanation of Solution
The isomer, (+−)-2- phenylbutanoic acid reacts with ammonia and the amide group is introduced followed by the reaction with Br2 and KOH to give the amine with the loss of one carbon chain. Then, the reaction of amine with phosgene (COCl2) forms the desired product.
The reaction of the formation of (meso)-1,3- bis (1-phenylpropyl) urea is shown below.

Figure 5
The formation of (meso)-1,3- bis (1-phenylpropyl) urea is shown in Figure 5.
(e)
Interpretation:
The steps required to obtain the pure samples of the given compound from the starting material are to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Hofmann rearrangement reaction is the conversion reaction of the primary amide to a primary amine with the loss of one carbon chain. The reaction requires basic conditions. The reaction of sodium hydroxide with bromine forms sodium hypobromite as an intermediate in situ.
Answer to Problem 23.60AP
The reaction route for the synthesis of the given product is shown below.
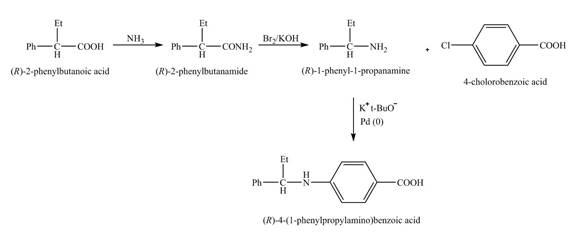
Explanation of Solution
The isomer, (R)-2- phenylbutanoic acid reacts with ammonia and the amide group is introduced followed by the reaction with Br2 and KOH to give the amine. The amine formed is reacted with 4- chlorobenzoic acid in presence of the Buchwald catalyst and a base to get the desired product,
The reaction of the formation of (R)-4-(1-phenylpropylamino) benzoic acid is shown below.
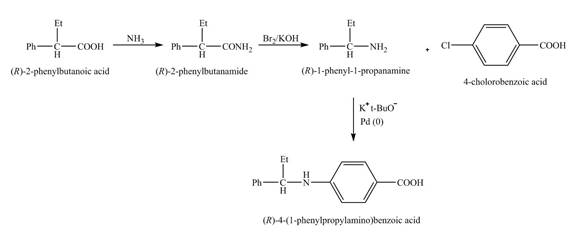
Figure 6
The formation of (R)-4-(1-phenylpropylamino) benzoic acid follows Hofmann rearrangement reaction as shown in Figure 6.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Predict the major organic product(s), if any, of the following reactions. Assume all reagents are in excess unless otherwise indicated.arrow_forwardHow many signals would you expect to find in the 1 H NMR spectrum of each given compound? Part 1 of 2 2 Part 2 of 2 HO 5 ☑ Х IIIIII***** §arrow_forwardA carbonyl compound has a molecular ion with a m/z of 86. The mass spectra of this compound also has a base peak with a m/z of 57. Draw the correct structure of this molecule. Drawingarrow_forward
- Can you draw this using Lewis dot structures and full structures in the same way they are so that I can better visualize them and then determine resonance?arrow_forwardSynthesize the following compound from cyclohexanol, ethanol, and any other needed reagentsarrow_forwardFor a titration of 20.00 mL of 0.0500 M H2SO4 with 0.100 M KOH, calculate the pH at each of the following volume of KOH used in the titration: 1) before the titration begin; 2) 10.00 mL; 3) 20.00 mL; 4) 30.00 mL. Ka2 = 1.20×10-2 for H2SO4.arrow_forward
- Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s) Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps Problem 73 of 10 Drawing Amows ro HO Donearrow_forward12. Synthesize the following target molecules (TMs) using the specified starting materials. .CI a) HO3S SM TM b) HO- SMarrow_forwardFor a titration of 20.00 mL of 0.0500 M H2SO4 with 0.100 M KOH, calculate the pH at each of the following volume of KOH used in the titration: 1) before the titration begin; 2) 10.00 mL; 3) 20.00 mL; 4) 30.00 mL. Ka2 = 1.20×10-2 for H2SO4.arrow_forward
- Write the systematic name of each organic molecule: structure name show work. don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forwardShow work with explanation needed. Don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forwardA Elschboard Part of SpeechT-D Alt Leaming App app.aktiv.com Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided resonance structures, draw the curved electron- pushing arrows to show the interconversion between resonance hybrid contributors. Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. Include all lone pairs and formal charges in the structures. Problem 45 of 10 I Select to Add Arrows N Please selarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





