
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Niacin is needed or not for the proper functioning of the ETC has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Electron transport chain is a sequence of biochemical reactions in which electrons and hydrogen atoms from the citric acid cycle are transferred to various intermediate carriers and finally reacts with molecular oxygen to form a water molecule. There are four complexes associated with the electron transport chain that is present in the inner mitochondrial membrane. The four complexes that help in the electron transfer in the electron transport chain are:
Complex I: NADH-coenzyme Q reductase.
Complex II: Succinate-coenzyme Q reductase.
Complex III: Coenzyme Q-cytochrome c reductase.
Complex IV: Cytochrome c oxidase.
An overview of the electron transport chain is as follows:
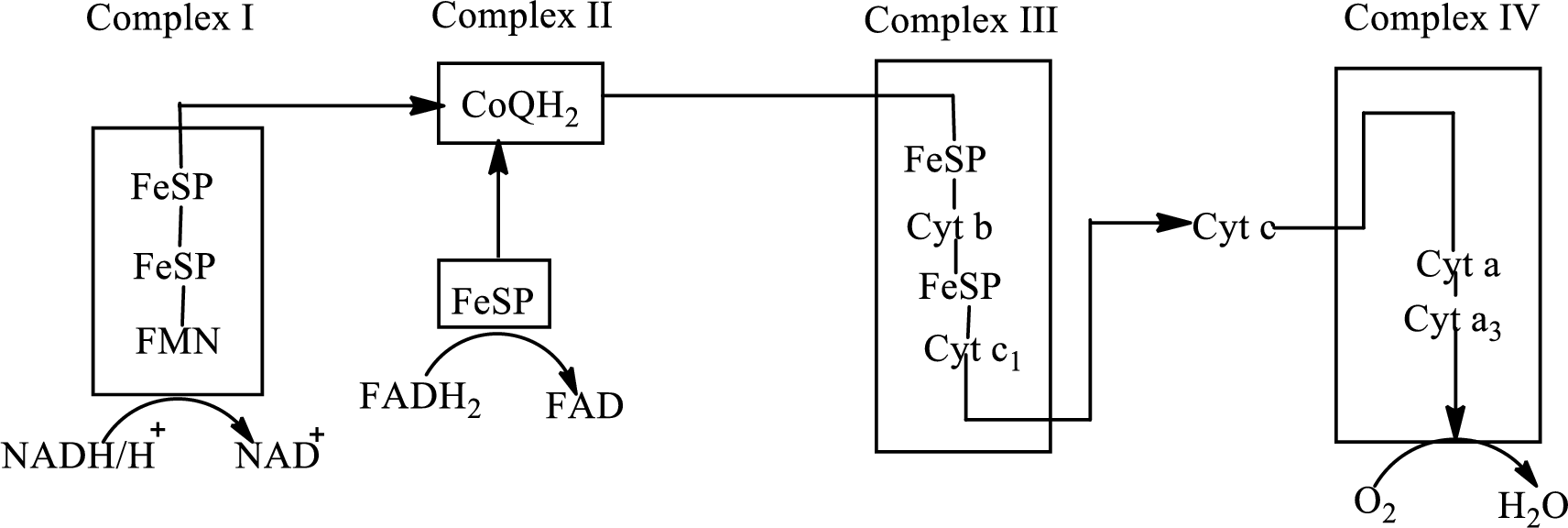
The B-vitamins consist of a group of vitamins that are water soluble and acts as precursors for enzyme cofactors.
(b)
Interpretation:
Biotin is needed or not for the proper functioning of the ETC has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Electron transport chain is a sequence of biochemical reactions in which electrons and hydrogen atoms from the citric acid cycle are transferred to various intermediate carriers and finally reacts with molecular oxygen to form a water molecule. There are four complexes associated with the electron transport chain that is present in the inner mitochondrial membrane. The four complexes that help in the electron transfer in the electron transport chain are:
Complex I: NADH-coenzyme Q reductase.
Complex II: Succinate-coenzyme Q reductase.
Complex III: Coenzyme Q-cytochrome c reductase.
Complex IV: Cytochrome c oxidase.
An overview of the electron transport chain is as follows:
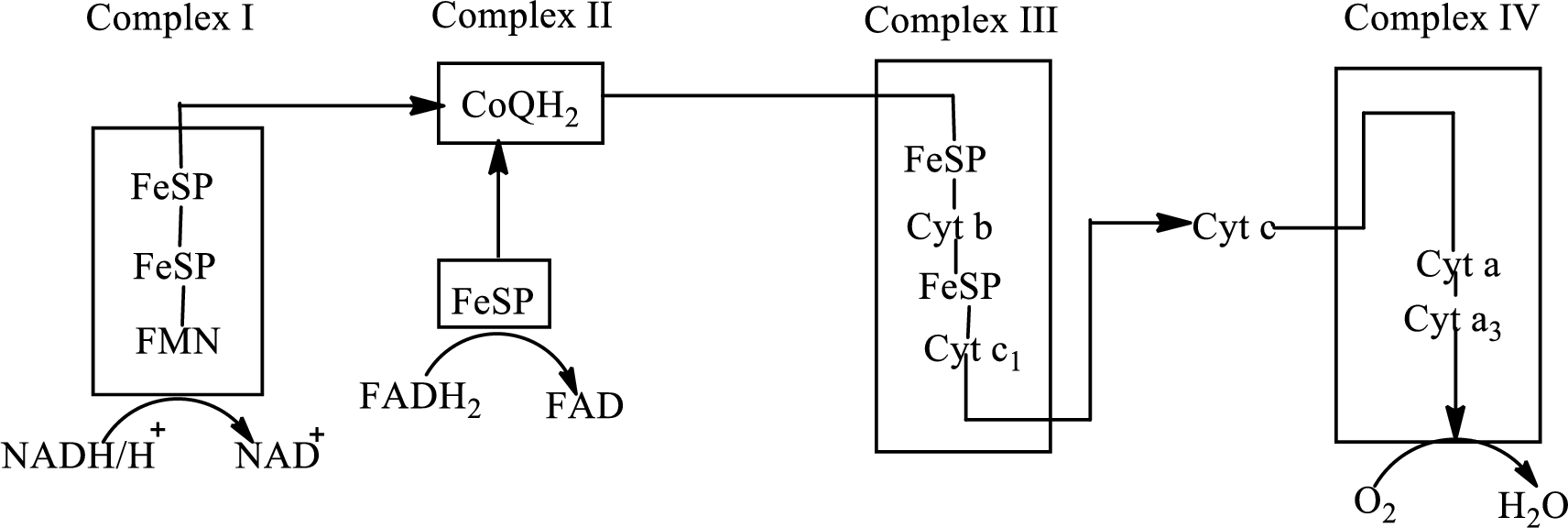
The B-vitamins consist of a group of vitamins that are water soluble and acts as precursors for enzyme cofactors.
(c)
Interpretation:
Pantothenic acid is needed or not for the proper functioning of the ETC has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Electron transport chain is a sequence of biochemical reactions in which electrons and hydrogen atoms from the citric acid cycle are transferred to various intermediate carriers and finally reacts with molecular oxygen to form a water molecule. There are four complexes associated with the electron transport chain that is present in the inner mitochondrial membrane. The four complexes that help in the electron transfer in the electron transport chain are:
Complex I: NADH-coenzyme Q reductase.
Complex II: Succinate-coenzyme Q reductase.
Complex III: Coenzyme Q-cytochrome c reductase.
Complex IV: Cytochrome c oxidase.
An overview of the electron transport chain is as follows:
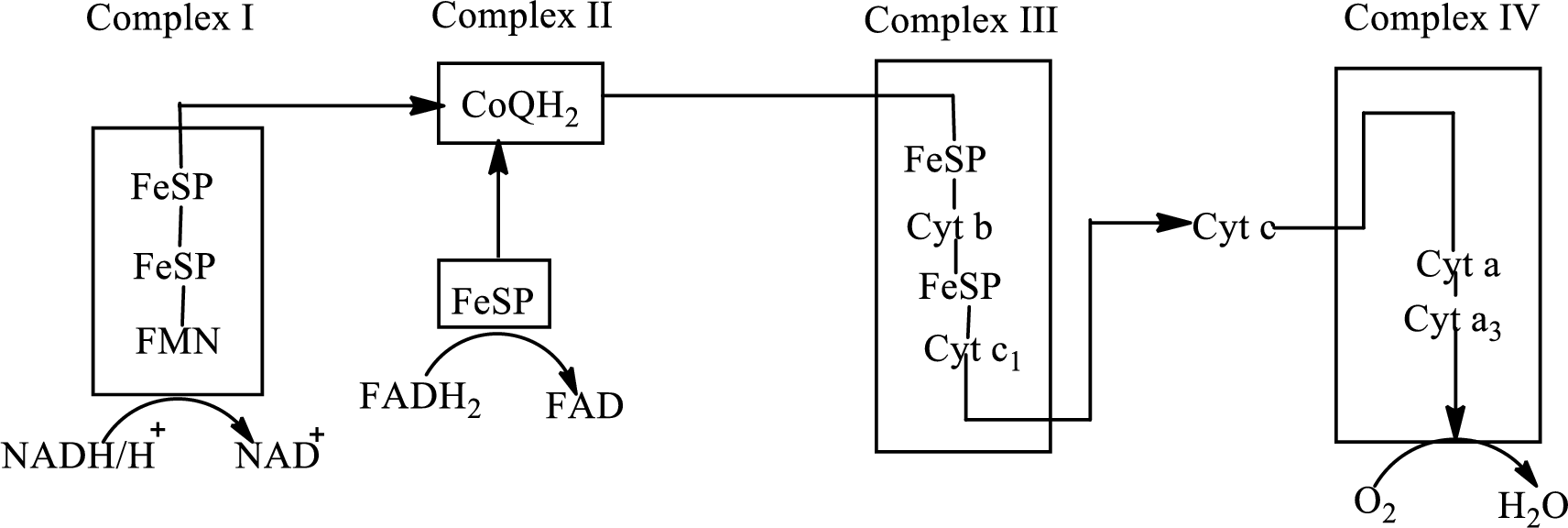
The B-vitamins consist of a group of vitamins that are water soluble and acts as precursors for enzyme cofactors.
(d)
Interpretation:
Vitamin B6 is needed or not for the proper functioning of the ETC has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Electron transport chain is a sequence of biochemical reactions in which electrons and hydrogen atoms from the citric acid cycle are transferred to various intermediate carriers and finally reacts with molecular oxygen to form a water molecule. There are four complexes associated with the electron transport chain that is present in the inner mitochondrial membrane. The four complexes that help in the electron transfer in the electron transport chain are:
Complex I: NADH-coenzyme Q reductase.
Complex II: Succinate-coenzyme Q reductase.
Complex III: Coenzyme Q-cytochrome c reductase.
Complex IV: Cytochrome c oxidase.
An overview of the electron transport chain is as follows:
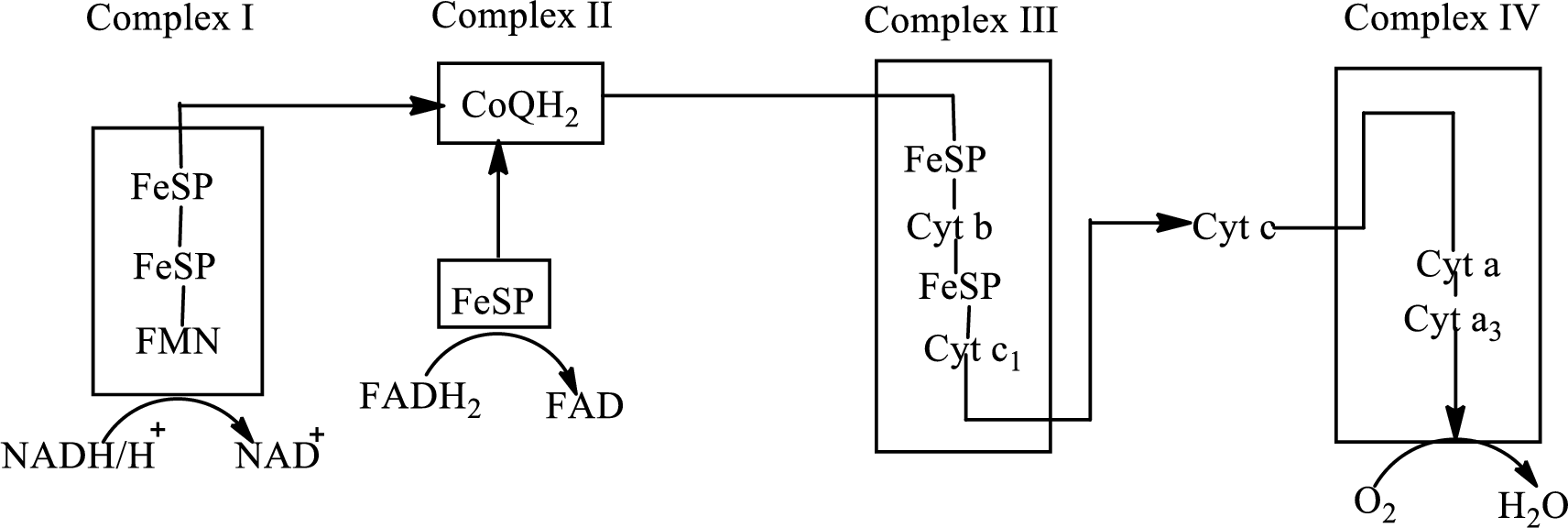
The B-vitamins consist of a group of vitamins that are water soluble and acts as precursors for enzyme cofactors.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 23 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
- Question about general transcription factors and their relationship to polymerasesarrow_forwardIdentify the indicated structure?arrow_forwardrewrite: Problem 1 (Mental Health): The survivor victim is dealing with acute stress and symptoms of a post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) due to their traumatic experience during the January 2025 wildfire. Goal 1: To alleviate the client's overall level, frequency, and intensity of anxiety and PTSD symptoms so that daily functioning remains unimpaired. Objective 1: The client will learn and regularly use at least two anxieties management techniques to reduce anxiety symptoms to less than three episodes per week. Intervention 1: The therapist will provide psychoeducation about anxiety and PTSD, including their symptoms and triggers. The therapist will also teach and assist the client in adopting relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises and progressive muscle relaxation, to better manage anxiety and lessen PTSD symptoms.arrow_forward
- O Macmillan Learning You have 0.100 M solutions of acetic acid (pKa = 4.76) and sodium acetate. If you wanted to prepare 1.00 L of 0.100 M acetate buffer of pH 4.00, how many milliliters of acetic acid and sodium acetate would you add? acetic acid: mL sodium acetate: mLarrow_forwardHow does the cost of food affect the nutritional choices people make?arrow_forwardBiopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics:Two-Compartment Model Zero-Order Absorption Questions SHOW ALL WORK, including equation used, variables used and each step to your solution, report your regression lines and axes names (with units if appropriate) :Calculate a-q a) B1, b) B2, c) hybrid rate constant (1) d) hybrid rate constant (2) e) t1/2,dist f) t1/2,elim g) k10 h) k12 i) k21 j) initial concentration (C0) k) central compartment volume (V1) l) steady-state volume (Vss) m) clearance (CL) AUC (0→10 min) using trapezoidal rule n) AUC (20→30 min) using trapezoidal rule o) AUCtail (AUC360→∞) p) total AUC (using short cut method) q) volume from AUC (VAUC)arrow_forward
- What are some external influences that keep people from making healthy eating decisions?arrow_forwardWhat type of structure(s) would you expect to see in peripheral membrane proteins? (mark all that apply) A. Amphipathic alpha helix (one side is hydrophilic and one side is hydrophobic) B. A hydrophobic beta barrel C. A hydrophobic alpha helix D. A chemical group attached to the protein that can anchor it to the membranearrow_forwardTemporal flexibility (the ability to change over time) of actin structures within a cell is maintained by… A. The growth/shrinkage cycle B. Periodic catastrophe C. GTP hydrolysis D. Treadmilling E. None of the abovearrow_forward
- During in vitro polymerization of actin and microtubule filaments from their subunits, what causes the initial delay in filament growth? A.Nucleation B.Reaching homeostasis C.Nucleotide exchange D.ATP or GTP hydrolysis E.Treadmillingarrow_forwardYou expect to find which of the following in the Microtubule Organizing Center (MTOC)...(mark all that apply) A. Gamma tubulin B. XMAP215 C. Centrioles D. Kinesin-13arrow_forwardThe actin-nucleating protein formin has flexible “arms” containing binding sites that help recruit subunits in order to enhance microfilament polymerization. What protein binds these sites? A.Thymosin B.Profilin C.Cofilin D.Actin E.Tropomodulinarrow_forward
- Essentials of Pharmacology for Health ProfessionsNursingISBN:9781305441620Author:WOODROWPublisher:Cengage
 Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira...Health & NutritionISBN:9781305634350Author:Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. SchroederPublisher:Cengage Learning
Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira...Health & NutritionISBN:9781305634350Author:Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. SchroederPublisher:Cengage Learning





