
Concept explainers
The required current in the top wire in the given figure to produce a field of zero at the point equidistant from the wires, provided currents in the bottom two wires are both 10.0 A into the page.
Answer to Problem 71PE
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Current carrying wire is placed at the vertices of an equilateral triangle of side 10.0 cm=
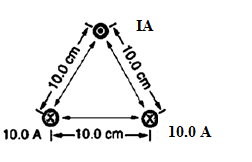
Formula used:
Magnetic field due to a long current carrying wire at perpendicular distance
Where
Calculation:
Label the wires at the vertices of triangle as P, Q and R.The equidistant point from all the three wires is centroid of the triangle. Let call the centroid point as O.
The perpendicular distance from the three wires to centroid of the triangle is
Let the current in P wire be
(Note the value of
Direction of fields at the centroid is shown by blue arrow in the figure below.
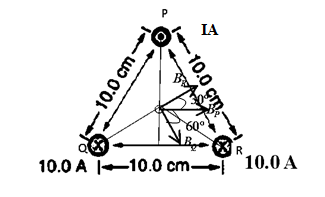
The resultant of vector
Now the net magnetic field at the centroid is
We want zero field at centroid. So,
Or
We are getting negative sign because what we have assumed the direction of current in wire P is not right to get zero field at centroid. So the new direction of current in top wire is to be into the page and its magnitude is
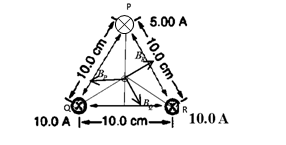
Conclusion:
Current in the top wire to produce a field of zero at the point equidistant from the wires is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
COLLEGE PHYSICS
- A solenoid 10.0 cm in diameter and 75.0 cm long is made from copper wire of diameter 0.100 cm, with very thin insulation. The wire is wound onto a cardboard tube in a single layer, with adjacent turns touching each other. What power must be delivered to the solenoid if it is to produce a field of 8.00 mT at its center?arrow_forwardCheck Your Understanding A straight, flexible length of copper wire is immersed in a magnetic field that is directed into the page, (a) If the wire's arrent runs in the +x-direction, which way will the wire bend? (b) Which way will the wire bend if the current nms in the -x-direction?arrow_forwardA current of 1.2 A is flowing in a coaxial cable whose outer radius is five times its inner radius. What is the magnetic field energy stored in a 3.0-m length of the cable?arrow_forward
- A hollow copper tube carries a current along its length. Why is B = 0 inside the tube? Is B nonzero outside the tube?arrow_forward(a) What is the speed of a supersonic aircraft with a 17.0-m wingspan, if it experiences a 1.60V Hall voltage between its wing lips when in level flight over the north magnetic pole, where the Earth's field strength is 8.00105T ? (b) Explain why very little current flows as a result of this Hall voltage.arrow_forward(a) A physicist performing a sensitive measurement wants to limit the magnetic force on a moving charge in her equipment to less than 1.001012N. What is the greatest the charge can be if it moves at a maximum speed of 30.0 m/s in the Earth’s field? (b) Discuss whether it would be difficult to limit the charge to less than the value found in (a) by competing it with typical static electricity and noting that static is often absent.arrow_forward
- Figure 22.30 (Quick Quiz 22.6) Four closed paths around three current-carrying wires. Rank the magnitudes of Bds for the closed paths a through d in Figure 22.30, from greatest to least.arrow_forwardIn a long, .straight, vertical lightning stroke, electrons move downward and positive ions move upward and constitute a current of magnitude 20.0 kA. At a location 50.0 m east of the middle of the stroke, a free electron drifts through the air toward the west with a speed of 300 m/s. (a) Make a sketch showing the various vectors involved. Ignore the effect of the Earth's magnetic field. (b) Find the vector force the lightning stroke exerts on the electron. (c) Find the radius of the electrons path. (d) Is it a good approximation to model the electron as moving in a uniform field? Explain your answer. (e) If it does not collide with any obstacles, how many revolutions will the electron complete during the 60.0-s duration of the lightning stroke?arrow_forwardTwo concentric circular wines with different diameters carry currents in tire same direction. Describe the force cm the inner wire.arrow_forward
- A proton having an initial velocity of 20.0iMm/s enters a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.300 T with a direction perpendicular to the protons velocity. It leaves the field-filled region with velocity 20.0jMm/s. Determine (a) the direction of the magnetic field. (b) the radius of curvature of the protons path while in the field, (c) the distance the proton traveled in the field, and (d) the time interval during which the proton is in the field.arrow_forward(a) A physicist performing a sensitive measurement wants to limit the magnetic force on a moving charge in her equipment to less than 1.001012N. What is the greatest the charge can be if it moves at a maximum speed of 30.0 m/s in Earth's field? (b) Discuss whether it would be difficult to limit the charge to less than the value found in (a) by comparing it with typical static electricity' and noting that static is often absent,arrow_forwardTwo straight, parallel, superconducting wires 4.5 mm apart carry equal currents of 15,000 A in opposite directions. What force, per unit length, does each wire exert on the other?arrow_forward
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





