
Concept explainers
Determine the x and y components of each of die forces shown.
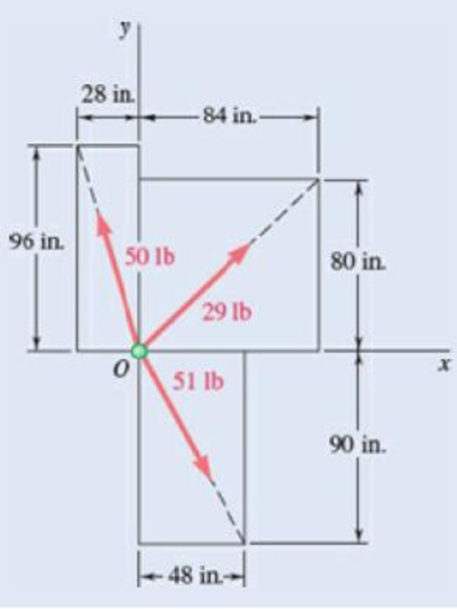
Fig. P2.22
To determine the x and y components of the forces shown in figure P2.22.
Answer to Problem 2.22P
The x component of the
The x component of the
The x component of the
Explanation of Solution
Refer figure P2.22.
The simplified diagram of the figure P2.22 is shown in figure 1 below. Figure 1 shows all the three components of force and the corresponding position vectors and their magnitudes. Position vectors
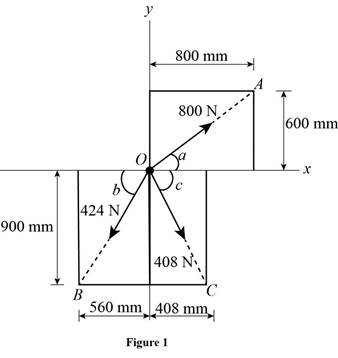
Let
Write the equation to find the magnitude of position vector
Here,
Write the equation to find the magnitude of position vector
Here,
Write the equation to find the magnitude of position vector
Here,
Let
Write the equation to find the x component of the
Here,
Here,
Similarly write the equation to find the y component of
Here,
Rewrite the equation of y component of
Here,
Write the equation to find the x component of the
Here,
Here,
Similarly write the equation to find the y component of
Here,
Here,
Write the equation to find the x component of the
Here,
Here,
Similarly write the equation to find the y component of
Here,
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, The x component of the
The x component of the
The x component of the
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
EBK VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STA
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies. Eight steel cables (with equal distance to each other) are supporting a circular heavy moulding of diameter 3m from an overhead point. If the moulding weighs 5 kN/m and the attachment point is 4m above it, determine the following: a. Calculate the tension of the cable. b. Determine the diameter of the wire if the allowable stress is 125 MPa. c. If the diameter of the cable is 10 mm, find the deflection of the steel cable. d. If the diameter of the cable is 10 mm, find the vertical displacement of the molder.arrow_forward4.11 (A/B). Two bars, one of steel, the other of aluminium alloy, are each of 75 mm width and are rigidly joined together to form a rectangular bar 75 mm wide and of depth (t, +tah where t,= thickness of steel bar and = thickness of alloy bar. Determine the ratio of t, to t, in order that the neutral axis of the compound bar is coincident with the junction of the two bars. (E, - 210 GN/m; E,- 70 GN/m?.) If such a beam is 50 mm deep determine the maximum bending moment the beam can withstand if the maximum stresses in the steel and alloy are limited to 135 MN/m' and 37 MN/m respectively. [0.577; 1.47 kN m.]arrow_forwardThe rectangular plate shown weighs 80 lb and is supported by three vertical wires. Determine the weight and location of the lightest block that should be placed on the plate if the tensions in the three wires are to be equal.arrow_forward
- 2.23 The rigid bars AB and CD are supported by pins at A and D. The vertical rods are made of aluminum and bronze. Determine the vertical displacement of the point where the force P = 10 kips is applied. Neglect the weights of the members. %3Darrow_forwardDetermine the internal forces and moments acting at sections 1, 2, and 3 in the member shown (Fig. 3)arrow_forward425 |lb PROBLEM 2.11 30° A steel tank is to be positioned in an excavation. Knowing that a = 20°, determine by trigonometry (a) the required magnitude of the force P if the resultant R of the two forces applied at 4 is to be vertical, (b) the corresponding magnitude of R.arrow_forward
- Problem 3.7 The simple structure shown in Fig 3.35 is called a cantilever beam and is one of the fundamental mechanical elements in engineering. A cantilever beam is fixed at one end and free at the other. In Fig. 3.35, the fixed and free ends of the beam are identified as points A and C, respectively. Point B correspondks to the center of gravity of in the beam. Assume that the beam shown has a weight W = 100 N and a length /=1m. A force with magnitude F= 150 N is applied at the free-end of the beam in a direction that makes an angle 0- 45" with the hon zontal. Determine the magnitude and direction of the net moment developed at the fixed-end of the be am, Pr Fig arm the f (a) I th WE ex ind Answer, MA 56 N-m (ccw). Fig. 3.35 A cantuleverlam Fig. 3.37 IPro ype here to searcharrow_forward1.3 (A). Define the terms shear stress and shear strain, illustrating your answer by means of a simple sketch. (Two circular bars.) one of brass and the other of steel, are to be loaded by a shear load of 30 kN. Determine(the necessary diametet of the bars (a) in single shear, (b) in double shear, if the shear stress in the two materials must not exceed 50 MN/m and 100 MN/m respectively. Ans: [27.6, 19.5, 19.5, 13.8mm.]arrow_forwardPulleys A and B are mounted on bracket CDEF The tension on each side of the two belts is as shown. Replace the four forces with a single equivalent force, and determine where its line of action intersects the bottom edge of the bracket.arrow_forward
- 3.6 Two forces, each of magnitude P, are applied to the wrench. The diameter of the steel shaft AB is 20 mm. Determine the largest allowable value of P if the shear stress in the shaft is not to exceed 120 MPa and its angle of twist is limited to 7°. Use G= 80 GPa for steel. 300 mm B 500 mm FIG. P3.6arrow_forward5.86 The cast iron inverted T-section supports two concentrated loads of magni- tude P. The working stresses are 48 MPa in tension, 140 MPa in compression, and 30 MPa in shear. (a) Show that the neutral axis of the cross section is located at d = 48.75 mm and that the moment of inertia of the cross-sectional area about this axis is I = 11.918 x 106 mm“. (b) Find the maximum allowable value of P. 1.0 m 1.0 m 15 mm 3 m 150 mm NA- d 15 mm 150 mm FIG. P5.86arrow_forwardThe 20 × 20-in. square plate shown weighs 56 lb and is supported by three vertical wires. Determine the weight and location of the lightest block that should be placed on the plate if the tensions in the three wires are to be equal.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





