
LL A&P TEXT- LAB MANUAL/MASTERING ACCES
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780134493985
Author: MARIEB & HOEHN
Publisher: PEARSON C
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 21.7, Problem 20CYU
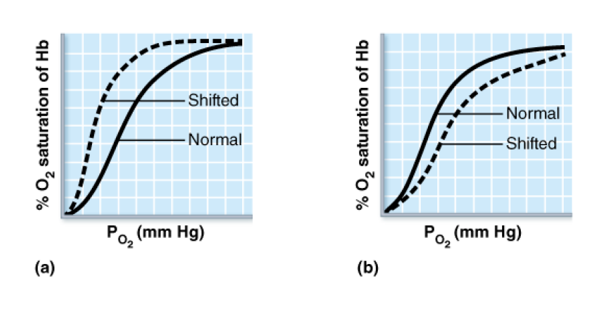
The dotted lines in the two graphs below represent a shift in the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve. Which shift would allow more oxygen delivery to the tissues? [Hint: Ask yourself which curve allows Hb to “let go” of more
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
After spending a day or more at high altitude (with an oxygen partial pressure of 75 torr), the concentration of 2,3- bisphosphoglycerate (2,3-BPG) in red blood cells increases. What effect would an increased concentration of 2,3-BPG have on the oxygen-binding curve for hemoglobin? Why would this adaptation be beneficial for functioning well at high altitude?
Name 3 conditions (ex: pO2) in which the oxygen dissociation curve will shift to the left. Additionally, when there is such a shift to the left, does that mean that hemoglobin's affinity for O2 has increased or decreased?
In the text, we learned that BPG is abundantly present in erythrocytes to greatly reduce the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen. When 2,3-BPG binds to deoxyhemoglobin, it acts to stabilize the low oxygen affinity state (T state) of the oxygen carrier. What would happen to hemoglobin if the BPG were removed? Would our body still be able to efficiently deliver oxygen to the tissues?
Chapter 21 Solutions
LL A&P TEXT- LAB MANUAL/MASTERING ACCES
Ch. 21.1 - Prob. 1CYUCh. 21.1 - Which part of the pharynx houses the pharyngeal...Ch. 21.2 - Which structure seals the larynx when we swallow?Ch. 21.2 - Which structural features of the trachea allow it...Ch. 21.2 - What features of the alveoli and their respiratory...Ch. 21.2 - A 3-year-old boy is brought to the emergency...Ch. 21.3 - The lungs are perfused by two different...Ch. 21.3 - Prob. 8CYUCh. 21.4 - What is the driving force for pulmonary...Ch. 21.4 - What causes the intrapulmonary pressure to...
Ch. 21.4 - What causes the partial vacuum (negative pressure)...Ch. 21.4 - Premature infants often lack adequate surfactant....Ch. 21.5 - Explain why slow, deep breaths ventilate the...Ch. 21.5 - Prob. 14CYUCh. 21.6 - You are given a sealed container of water and air....Ch. 21.6 - PO2 in the alveoli is about 56 mm Hg lower than in...Ch. 21.6 - Suppose a patient is receiving oxygen by mask. Are...Ch. 21.7 - Prob. 18CYUCh. 21.7 - What is the relationship between CO2 and pH in the...Ch. 21.7 - The dotted lines in the two graphs below represent...Ch. 21.8 - Which brain stem respiratory area is thought to...Ch. 21.8 - Prob. 22CYUCh. 21.9 - An injured soccer player arrives by ambulance in...Ch. 21.9 - Prob. 24CYUCh. 21.10 - What distinguishes the obstruction in asthma from...Ch. 21 - Cutting the phrenic nerves will result in (a) air...Ch. 21 - Which of the following laryngeal cartilages is/are...Ch. 21 - Prob. 3MCCh. 21 - The detergent-like substance that keeps the...Ch. 21 - Which of the following determines the direction of...Ch. 21 - When the inspiratory muscles contract, (a) the...Ch. 21 - The nutrient blood supply of the lungs is provided...Ch. 21 - Oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged in the...Ch. 21 - Which of the following would not normally be...Ch. 21 - Most oxygen carried in the blood is (a) in...Ch. 21 - Which of the following has the greatest...Ch. 21 - In mouth-to-mouth artificial respiration, the...Ch. 21 - Prob. 13MCCh. 21 - Prob. 14MCCh. 21 - Damage to which of the following would most likely...Ch. 21 - Prob. 16MCCh. 21 - Trace the route of air from the nares to an...Ch. 21 - (a) Why is it important that the trachea is...Ch. 21 - Briefly explain the anatomical reason why most men...Ch. 21 - The lungs are mostly passageways and elastic...Ch. 21 - Describe the functional relationships between...Ch. 21 - Discuss how airway resistance, lung compliance,...Ch. 21 - (a) Differentiate clearly between minute...Ch. 21 - Prob. 24SAQCh. 21 - (a) Define hyperventilation. (b) If you...Ch. 21 - Prob. 1CCSCh. 21 - Prob. 2CCSCh. 21 - Barbara Joley was in the bus that was hit...Ch. 21 - Barbara Joley was in the bus that was hit...Ch. 21 - Prob. 5CCSCh. 21 - Prob. 6CCSCh. 21 - Prob. 7CCS
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Explain what a partial pressure gradient is and how such gradients figure in gas exchange.arrow_forwardHow does hemoglobin help maintain the oxygen partial pressure gradient during gas transport in the body?arrow_forwardTalk about the factors that can move the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve TO THE RIGHT. What factors move the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve TO THE LEFT? What does this mean, exactly?arrow_forward
- Referring to the loading and unloading of oxygen from hemoglobin (as illustrated in the figure), which of the following statements is correct? Oxygen Dissociation Curve.png Group of answer choices When a person in ventilating at rest, 75% of hemoglobin is still oxyhemoglobin The percent saturation of hemoglobin is higher at higher partial pressures of oxygen A decrease in the pH of the blood would promote unloading oxygen from the hemoglobin All of these are correctarrow_forwardIn addition to O2 binding, changes in other chemical conditions can result in changes in hemoglobin structure and function. Increases in blood H+ result in oxygen binding curves for hemoglobin that are shifted to the right. The effect of H+ can be understood in terms of the equilibrium:H-Hb+ + O2 → Hb-O2 + H+How does the difference in pH in the lungs and tissues help hemoglobin do its job of delivering oxygen? Use the equilibrium equation in your argument.arrow_forwardBelow is the equation that represents O2 binding to hemoglobin. Hb+4O2⇌Hb(O2)According to Le Chatelier’s principle, which form of the hemoglobin (Hb or Hb(O2)4) is predominant in the lungs where the partial pressure of oxygen is high? Explain. I need help answering thisarrow_forward
- Suppose you visit the Dalai Lama in Dharamsala, India (elevation 1460 m),and you begin to ponder the “big questions,” such as “What is the fractionalsaturation of the Dalai Lama’s hemoglobin?”(a) Assuming the Dalai Lama’s hemoglobin has a Hill coefficient = 3.2,and a P50 = 31 mm Hg, calculate the change in fractional O2 saturationof his hemoglobin going from his lungs (where PO2 = 85 mm Hg) to hiscapillaries (where PO2 = 25 mm Hg).(b) Why do you suppose the Dalai Lama’s hemoglobin has a P50 higher thannormal (where “normal” = 27 mm Hg)?arrow_forward(b) The diagram on the right illustrates the change in the p50 (partial pressure of O2 required to achieve 50% saturation) of hemoglobin and the 2,3-bis-phosphoglycerate (BPG) concentration in the erythrocytes of a person who spent 6 days hik- ing in the Andes Mountains of Peru. As the hiker climbs to higher and higher altitudes, the atmos- pheric pressure, including the partial pressure of O2, decreases. Yet the p50 increases, making it less favorable to achieve saturation of the hemo- globin. Explain. Pso (torr) Sea level 34 33- 32 31 30- 29 28 27 26 4530 m above- sea level (c) If individuals with the following mutant hemo- globins accompanied the hiker, evaluate the degree of respiratory distress that they would experience despite the increased erythrocyte BPG concentration. (In the ta- ble of mutants on the right, the mutation His(143)Asp, for instance, means that the His residue that occurs at se- quence position 143 on the ß-chain has been substituted by Asp.) Describe the…arrow_forwardGraph the relationship between hemoglobin–O2 saturation and the partial pressure of O2 in the blood. What is the functional significance of the shape of the O2–hemoglobin dissociation curve? What factors affect the shape of the curve?arrow_forward
- When oxygenated blood (Hemoglobin nearly 100% saturated), reaches resting systemic tissues, what percentage of the available oxygen is unloaded from hemoglobin? 100%, 75%, 50%, or 25%?arrow_forwardO E-If answers (1), (2), (3) and (4) are TRUE Which of the following is NOT true about the liver lobule? * (1) Bile canaliculi transport bile towards the bile ducts located at the corners of the liver lobule. (2) Sinusoidal capillaries drain into the central vein. (3) Liver lobules are capable of producing plasma proteins such as albumin. (4) The portal arteriole takes blood to the liver lobule, while the portal venule takes blood away from the liver lobule. O A - If answers (1), (2) and (3) are TRUE B - If answers (1) and (3) are TRUE O C- If answers (2) and (4) are TRUE O D- If only answer (4) is TRUE O E- If answers (1), (2), (3) and (4) are TRUE Which of the following is NOT true with regards the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve? * 27°C ere to searcharrow_forwardExplain the mechanism through which the hemoglobin oxygen dissociation curve changes in exercising tissues relative to those tissues at rest. How does this change affect the amount of oxygen delivered to exercising tissues?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning

Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305112100
Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...
Biology
ISBN:9781285866932
Author:Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:Cengage Learning
The Cell Membrane; Author: The Organic Chemistry Tutor;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AsffT7XIXbA;License: Standard youtube license