Engineering Mechanics: Statics & Dynamics (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780133915426
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 21.6, Problem 63P
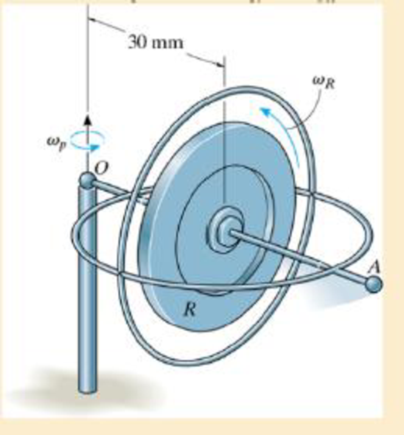
The toy gyroscope consists of a rotor R which is attached to the frame of negligible mass. If it is observed that the frame is precessing about the pivot point O at ωp = 2 rad/s, determine the angular velocity ωR of the rotor. The stem OA moves in the horizontal plane. The rotor has a mass of 200 g and a radius of gyration kOA = 20 mm about OA.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
5. Determine the transfer function of G(s) = 01(s)/T₁(s) and 02(s)/T₁ for the mechanical system
shown in Figure Q5. (Hints: assume zero initial condition)
T₁(t) 01(t)
102(1)
Ол
N1
D1
D2
No. 1790220000
N2
Figure Q5
K2
A spring package with two springs and an external force, 200N. The short spring has a loin of 35 mm. Constantly looking for spring for short spring so that total compression is 35 mm (d). Known values: Long spring: Short spring:C=3.98 N/mm Lo=65mmLo=87.4mmF=c·fTotal compression is same for both spring. 200 = (3.98(c1) × 35) + (c₂ × 35)
200 = 139.3 + 35c₂
200 - 139.3 = 35c₂
60.7 = 35c₂
c₂ = 60.7/35
Short spring (c₂) = 1.73 N/mm
According to my study book, the correct answer is 4.82N/mm
What is wrong with the calculating?
What is the reason for this composition?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Statics & Dynamics (14th Edition)
Ch. 21.1 - Show that the sum of the moments of inertia of a...Ch. 21.1 - Prob. 2PCh. 21.1 - Prob. 3PCh. 21.1 - Determine the moments of inertia Ix and Iy of the...Ch. 21.1 - Prob. 5PCh. 21.1 - Determine by direct integration the product of...Ch. 21.1 - Prob. 7PCh. 21.1 - Prob. 8PCh. 21.1 - Prob. 9PCh. 21.1 - Prob. 10P
Ch. 21.1 - Prob. 11PCh. 21.1 - Determine the moment of inertia Ixx of the...Ch. 21.1 - Prob. 13PCh. 21.1 - Prob. 14PCh. 21.1 - Prob. 15PCh. 21.1 - Prob. 16PCh. 21.1 - The bent rod has a weight of 1.5 lb/ft. Locate the...Ch. 21.1 - Prob. 18PCh. 21.1 - Prob. 19PCh. 21.1 - Prob. 20PCh. 21.1 - Prob. 21PCh. 21.3 - If a body contains no planes of symmetry, the...Ch. 21.3 - Prob. 23PCh. 21.3 - The 15-kg circular disk spins about its axle with...Ch. 21.3 - Prob. 25PCh. 21.3 - Prob. 26PCh. 21.3 - Prob. 27PCh. 21.3 - Prob. 28PCh. 21.3 - Prob. 29PCh. 21.3 - Prob. 30PCh. 21.3 - Prob. 31PCh. 21.3 - The 2-kg thin disk is connected to the slender rod...Ch. 21.3 - Prob. 33PCh. 21.3 - Prob. 34PCh. 21.3 - The 200-kg satellite has its center of mass at...Ch. 21.3 - Prob. 36PCh. 21.3 - Prob. 37PCh. 21.3 - Determine the kinetic energy of the 7-kg disk and...Ch. 21.3 - Prob. 39PCh. 21.3 - Prob. 40PCh. 21.4 - Prob. 41PCh. 21.4 - Prob. 42PCh. 21.4 - Prob. 43PCh. 21.4 - Prob. 44PCh. 21.4 - Prob. 45PCh. 21.4 - The assembly is supported by journal bearings at A...Ch. 21.4 - Prob. 47PCh. 21.4 - Prob. 48PCh. 21.4 - Prob. 49PCh. 21.4 - Prob. 50PCh. 21.4 - Prob. 51PCh. 21.4 - Prob. 52PCh. 21.4 - Prob. 53PCh. 21.4 - Prob. 54PCh. 21.4 - Prob. 55PCh. 21.4 - Prob. 56PCh. 21.4 - The blades of a wind turbine spin about the shaft...Ch. 21.4 - Prob. 58PCh. 21.4 - The thin rod has a mass of 0.8 kg and a total...Ch. 21.4 - Show that the angular velocity of a body, in terms...Ch. 21.4 - A thin rod is initially coincident with the Z axis...Ch. 21.6 - The gyroscope consists of a uniform 450-g disk D...Ch. 21.6 - The toy gyroscope consists of a rotor R which is...Ch. 21.6 - The top consists of a thin disk that has a weight...Ch. 21.6 - Solve Prob. 2164 when =90.Ch. 21.6 - Prob. 66PCh. 21.6 - Prob. 67PCh. 21.6 - Prob. 68PCh. 21.6 - Prob. 69PCh. 21.6 - Prob. 70PCh. 21.6 - Prob. 71PCh. 21.6 - Prob. 72PCh. 21.6 - Prob. 73PCh. 21.6 - Prob. 74PCh. 21.6 - Prob. 75PCh. 21.6 - Prob. 76PCh. 21.6 - Prob. 77PCh. 21.6 - Prob. 78P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Homework: ANOVA Table for followed design B AB Dr -1 -1 1 (15.18,12) 1 -1 -1 (45.48.51) -1 1 -1 (25,28,19) 1 1 (75.75,81)arrow_forward20. [Ans. 9; 71.8 mm] A semi-elliptical laminated spring is made of 50 mm wide and 3 mm thick plates. The length between the supports is 650 mm and the width of the band is 60 mm. The spring has two full length leaves and five graduated leaves. If the spring carries a central load of 1600 N, find: 1. Maximum stress in full length and graduated leaves for an initial condition of no stress in the leaves. 2. The maximum stress if the initial stress is provided to cause equal stress when loaded. [Ans. 590 MPa ; 390 MPa ; 450 MPa ; 54 mm] 3. The deflection in parts (1) and (2).arrow_forwardQ6/ A helical square section spring is set inside another, the outer spring having a free length of 35 mm greater than the inner spring. The dimensions of each spring are as follows: Mean diameter (mm) Side of square section (mm) Active turns Outer Inner Spring Spring 120 70 8 7 20 15 Determine the (1) Maximum deflection of the two springs and (2) Equivalent spring rate of the two springs after sufficient load has been applied to deflect the outer spring 60 mm. Use G = 83 GN/m².arrow_forward
- Q2/ The bumper springs of a railway carriage are to be made of rectangular section wire. The ratio of the longer side of the wire to its shorter side is 1.5, and the ratio of mean diameter of spring to the longer side of wire is nearly equal to 6. Three such springs are required to bring to rest a carriage weighing 25 kN moving with a velocity of 75 m/min with a maximum deflection of 200 mm. Determine the sides of the rectangular section of the wire and the mean diameter of coils when the shorter side is parallel to the axis of the spring. The allowable shear stress is not to exceed 300 MPa and G = 84 kN/mm². Q6/ A belicalarrow_forward11. A load of 2 kN is dropped axially on a close coiled helical spring, from a height of 250 mm. The spring has 20 effective turns, and it is made of 25 mm diameter wire. The spring index is 8. Find the maximum shear stress induced in the spring and the amount of compression produced. The modulus of rigidity for the material of the spring wire is 84 kN/mm². [Ans. 287 MPa; 290 mm]arrow_forwardWhat is the reason for this composition?arrow_forward
- Homework: ANOVA Table for followed design B AB Dr -1 -1 1 (15.18,12) 1 -1 -1 (45.48.51) -1 1 -1 (25,28,19) 1 1 (75.75,81)arrow_forwardS B Pin 6 mm Garrow_forwardMid-Term Exam 2024/2025 Post graduate/Applied Mechanics- Metallurgy Q1/ State the type of fault in the following case, and state the structure in which it will appear. АВСАВСВАСВАСАВСАВСarrow_forward
- الثانية Babakt Momentum equation for Boundary Layer S SS -Txfriction dray Momentum equation for Boundary Layer What laws are important for resolving issues 2 How to draw. 3 What's Point about this.arrow_forwardR αι g The system given on the left, consists of three pulleys and the depicted vertical ropes. Given: ri J₁, m1 R = 2r; απ r2, J2, m₂ m1; m2; M3 J1 J2 J3 J3, m3 a) Determine the radii 2 and 3.arrow_forwardB: Solid rotating shaft used in the boat with high speed shown in Figure. The amount of power transmitted at the greatest torque is 224 kW with 130 r.p.m. Used DE-Goodman theory to determine the shaft diameter. Take the shaft material is annealed AISI 1030, the endurance limit of 18.86 kpsi and a factor of safety 1. Which criterion is more conservative? Note: all dimensions in mm. 1 AA Motor 300 Thrust Bearing Sprocket 100 9750 เอarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Dynamics - Lesson 1: Introduction and Constant Acceleration Equations; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7aMiZ3b0Ieg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY