
Applied Statics and Strength of Materials (6th Edition)
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780133840544
Author: George F. Limbrunner, Craig D'Allaird, Leonard Spiegel
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 21, Problem 21.4P
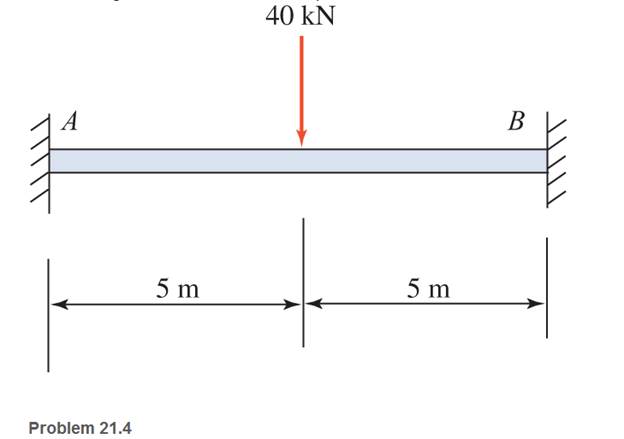
Draw complete shear and moment diagrams for the fixed beams shown.
Select the lightest structural steel
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Please draw by deriving SF and BM equations for each sections.Draw a labelled diagram mentioning valus at key points.
Thank you
QUESTION 3
If the allowable bending stresses for a beam in one application is 6 kip/in2 in tension. The cross-section of the beam is W8 x 40.
If the beam is 10 foot long and simply supported and has a concentrated load applied at x = 3 ft as shown below.
• Generate the shear force and bending moment diagram in terms of P;
• Based on the allowable maximum bending moment you just obtained above, calculate/ input the mazimm allowable value of the load P:
please, pay attention to units, and calculate your answer to 1 decimal place..
3 ft
7 ft
kip.
NU
Fixed
end
Y
4.25 KN.m
0.3m
5KN
100 KN
100 KN
0.4 m
3.0 KN.m
5 KN
200 KN
200KN
0.1 m
x
Calculate the reactions at the fixed support and draw the axial load, torque, shear force and
bending moment diagrams for the beam. Include equations and calculations. The stainless steel
beam has a circular cross section and diameter of 7 centemeters.
Chapter 21 Solutions
Applied Statics and Strength of Materials (6th Edition)
Ch. 21 - Prob. 21.1PCh. 21 - Prob. 21.2PCh. 21 - Use the method of superposition to determine the...Ch. 21 - Draw complete shear and moment diagrams for the...Ch. 21 - Draw complete shear and moment diagrams for the...Ch. 21 - Draw complete shear and moment diagrams for the...Ch. 21 - Determine the reactions for the beam shown.Ch. 21 - Prob. 21.8PCh. 21 - 21.9 Select a southern pine timber beam () for the...Ch. 21 - For the continuous beams shown, find moments at...
Ch. 21 - For the continuous beams shown, find moments at...Ch. 21 - For the continuous beams shown, find moments at...Ch. 21 - Prob. 21.13SPCh. 21 - Prob. 21.14SPCh. 21 - Prob. 21.15SPCh. 21 - Prob. 21.16SPCh. 21 - Prob. 21.17SPCh. 21 - Prob. 21.18SPCh. 21 - Prob. 21.19SPCh. 21 - Prob. 21.20SPCh. 21 - For these problems, use any appropriate method of...Ch. 21 - For these problems, use any appropriate method of...Ch. 21 - Prob. 21.23SPCh. 21 - For these problems, use any appropriate method of...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- i need it asap please thank you.arrow_forwardFor the beam shown, derive the expressions for V and M, and draw the shear force and bending moment diagrams. Calculate the shear force V and bending moment M at a cross section located 0.5 m from the fixed support. Neglect the weight of the beam. (Show complete calculation and step by step process. Show free body diagram)arrow_forwardSolve in neatly and cleanly the detail solutionarrow_forward
- Please answer Part 3, thank you PART 1 Use the graphical method to construct the shear-force and bending-moment diagrams for the beam shown. Let a= 6 m, b = 3 m, PB = 70 kN, Pc= 100 kN, and PE= 30 kN. Construct the shear-force and bending-moment diagrams on paper and use the results to answer the questions in the subsequent parts of this GO exercise. Calculate the reaction forces Ay and Dy acting on the beam. Positive values for the reactions are indicated by the directions of the red arrows shown on the free-body diagram below. (Note: Since Ax= 0, it has been omitted from the free-body diagram.) Answer: Ay = 50 kN Dy= 150 kN PART 2 Determine the shear force acting at each of the following locations: (a) x = 3m (b)x= 9 m (c)x = 13.5 m (d)x= 18 m When entering your answers, use the shear force sign convention. Answers: (a) V= 50 kN (b) V= -20 kN (c) V= -120 kN (d)V= 30 kN PART 3 (PLEASE ANSWER, THANK YOU) Determine the bending moment acting at each of the…arrow_forwardproblemarrow_forwardQuestion is for review, not for gradearrow_forward
- Determine the reactions and draw the shear and bending moment diagrams for the beams shown in Figs. using the method of consistent deformations. Select the reaction at the roller support to be the redundantarrow_forwardConsider Beam 1 is simply supported, draw the free body diagram and the shear force and bending moment diagrams.arrow_forward7arrow_forward
- Figure 1 below shows a 5 m length of beam with a pinned support at A and roller support at E. The beam carries three concentrated loads of 10 kN, 5 kN and 15 kN at B, C and D, respectively. а. Show the Free Body Diagram (FBD) of the beam then determine the reaction force. b. Calculate the shear force, V. Draw Shear Force Diagram (SFD). Calculate the bending moment, M. Draw the Bending Moment Diagram (BMD). 10 kN 5 kN 15 kN A E B C D 1m 1m 1 m 2 m Figure 1 C.arrow_forwardAn overhanging beam is loaded as indicated. In order to accommodate communication cables to be installed later the beam is manufactured with two circular channels running through its length. The beam has a weight of q = 300 N/m. Calculate (a) the value and position of the maximum bending moment and sketch the relevant bending moment and shear force diagrams, (b) the position of the neutral axis, and (c) the maximum compressive and tension stress in the beam due to the bending. 2m 3 KN 3m B Bm 1 KN 100 mm 100 mm 20 mm H 30 mmarrow_forwardPLEASE ANSWER THIS URGENT. I WILL SURELY UPVOTE!!!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Types of Manufacturing Process | Manufacturing Processes; Author: Magic Marks;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=koULXptaBTs;License: Standard Youtube License