
Physics (5th Edition)
5th Edition
ISBN: 9780321976444
Author: James S. Walker
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 20, Problem 39PCE
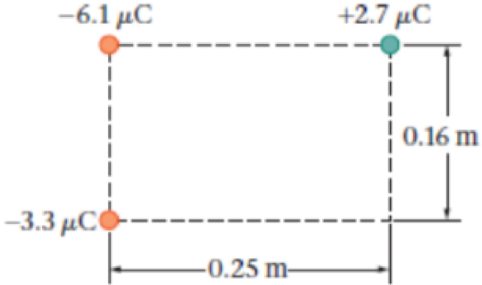
How much work must be done to move the three charges in Figure 20-32 infinitely far from one another?
Figure 20-32
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Problem 16:
A +38 μC point charge is placed 36 cm from an identical
+38 μC charge. A -1.5 μC charge is moved from point A
to point B as shown in Fig. 17-47. What is the change in
potential energy?
B
14 cm
12 cm
24 cm
FIGURE 17-47
38 μC
38 μC
Problem 81.
A
A +38 µC point charge is placed 36 cm from an identical
+38 µC charge. A –1.5 µC charge is moved from point A
to point B as shown in Fig. 17–47. What is the change in
potential energy?
В
14 cm
FIGURE 17-47
38 μC
12 cm
24 cm
38 μC
Problem 81.
A
103 In Fig. 24-72, two particles of
charges qi and q2 are fixed to an x
axis. If a third particle, of charge
+6.0 µC, is brought from an infinite
distance to point P, the three-parti-
cle system has the same electric potential energy as the original
two-particle system. What is the charge ratio qılq2?
|-d--1.5d-|
Figure 24-72 Problem 103.
Chapter 20 Solutions
Physics (5th Edition)
Ch. 20.1 - The electric potential in system A changes...Ch. 20.2 - Particle A accelerates from rest through a...Ch. 20.3 - The following systems consist or a point charge at...Ch. 20.4 - Figure 20-14 shows a series of equipotential...Ch. 20.5 - Two parallel-plate capacitors are identical,...Ch. 20.6 - The following systems consist of a capacitor for...Ch. 20 - In one region of space the electric potential has...Ch. 20 - If the electric field is zero in some region of...Ch. 20 - Sketch the equipotential surface that goes through...Ch. 20 - How much work is required to move a charge from...
Ch. 20 - It is known that the electric potential is...Ch. 20 - Explain why equipotentials are always...Ch. 20 - Two charges are at locations that have the same...Ch. 20 - A capacitor is connected to a battery and fully...Ch. 20 - On which of the following quantities does the...Ch. 20 - We say that a capacitor stores charge, yet the...Ch. 20 - An electron is released from rest in a region of...Ch. 20 - A uniform electric field of magnitude 3.8 105 N/C...Ch. 20 - A uniform electric field of magnitude 6.8 105 N/C...Ch. 20 - BIO Electric Potential Across a Cell Membrane In a...Ch. 20 - An old-fashioned computer monitor accelerates...Ch. 20 - A parallel-plate capacitor has plates separated by...Ch. 20 - When an ion accelerates through a potential...Ch. 20 - The Electric Potential of the Earth The Earth has...Ch. 20 - A uniform electric field with a magnitude of 6860...Ch. 20 - Predict/Calculate A spark plug in a car has...Ch. 20 - A uniform electric field with a magnitude of 1200...Ch. 20 - A Charged Battery A typical 12-V car battery can...Ch. 20 - BIO Predict/Calculate The Sodium Pump Living cells...Ch. 20 - Predict/Calculate The electric potential of a...Ch. 20 - Points A and B have electric potentials of 332 V...Ch. 20 - Predict/Explain An electron is released from rest...Ch. 20 - Calculate the speed of (a) a proton and (b) an...Ch. 20 - Ion Thrusters NASAs Deep Space 1 and Dawn...Ch. 20 - Find the potential difference required to...Ch. 20 - Predict/Calculate A particle with a mass of 3.8 g...Ch. 20 - Conduction Electrons In the microscopic view of...Ch. 20 - A proton has an initial speed of 5.5 105 m/s. (a)...Ch. 20 - In Figure 20-29, q1 = +1.8 nC and q2 = 2.1 nC, and...Ch. 20 - In Figure 20-29, it is given that, q1 = +Q. (a)...Ch. 20 - CE The charge q1 in Figure 20-29 has the value +Q....Ch. 20 - CE It is given that the electric potential is zero...Ch. 20 - The electric potential 1.6 m from a point charge q...Ch. 20 - A point charge of 9.2 C is at the origin. What is...Ch. 20 - The Bohr Atom The hydrogen atom consists of one...Ch. 20 - How far must the point charges q1 = +6.22 C and q2...Ch. 20 - Four different arrangements of point charges are...Ch. 20 - Predict/Calculate Point charges +4.1 C and 2.2C...Ch. 20 - In Figure 20-31, the charge q = 4.11 10-9C. (a)...Ch. 20 - Predict/Calculate In Figure 20-31, the charge q =...Ch. 20 - A charge of 4.07C is held fixed at the origin. A...Ch. 20 - Predict/Calculate A charge of 20.2 C is held fixed...Ch. 20 - A charge of 2.505 C is located at (3.055 m, 4.501...Ch. 20 - Predict/Calculate Figure 20-32 shows three charges...Ch. 20 - How much work must be done to move the three...Ch. 20 - (a) Find the electric potential at point P in...Ch. 20 - A square of side a has a charge +Q at each corner....Ch. 20 - A square of side a has charges +Q and Q...Ch. 20 - Predict/Explain (a) is the electric potential at...Ch. 20 - Predict/Explain Imagine sketching a large number...Ch. 20 - Two point charges are on the x axis. Charge 1 is...Ch. 20 - Figure 20-35 shows a series of equipotentials in a...Ch. 20 - Predict/Calculate Consider a region in space where...Ch. 20 - A given system has the equipotential surfaces...Ch. 20 - A given system has the equipotential surfaces...Ch. 20 - A 0.75-F capacitor is connected to a 9.0-V...Ch. 20 - It is desired that 7.7 C of charge be stored on...Ch. 20 - To operate a given flash lamp requires a charge of...Ch. 20 - Planet Capacitor It can be shown that the...Ch. 20 - A parallel-plate capacitor is made from two...Ch. 20 - A parallel-plate capacitor is constructed with...Ch. 20 - Predict/Calculate A parallel-plate capacitor has...Ch. 20 - Predict/Calculate A 72-nF parallel-plate capacitor...Ch. 20 - Predict/Calculate Consider a parallel-plate...Ch. 20 - A parallel-plate capacitor has plates of area 3.75...Ch. 20 - Predict/Calculate A parallel-plate capacitor...Ch. 20 - Suppose that after walking across a carpeted floor...Ch. 20 - (a) What plate area is required for an air-filled,...Ch. 20 - Lightning As a crude model for lightning, consider...Ch. 20 - A parallel-plate capacitor is made from two...Ch. 20 - Calculate the work done by a 9.0-V battery as it...Ch. 20 - BIO Defibrillator An automatic external...Ch. 20 - BIOPredict/Calculate Cell Membranes The membrane...Ch. 20 - A capacitor with plate area 0.0440 m2 and plate...Ch. 20 - Find the electric energy density between the...Ch. 20 - What electric field strength would store 17.5 J of...Ch. 20 - An electronic flash unit for a camera contains a...Ch. 20 - A parallel-plate capacitor has plates with an area...Ch. 20 - CE Predict/Explain A proton is released from rest...Ch. 20 - CE The plates of a parallel-plate capacitor have...Ch. 20 - CE A parallel-plate capacitor is connected to a...Ch. 20 - CE The plates of a parallel-plate capacitor have...Ch. 20 - CE A parallel-plate capacitor is connected to a...Ch. 20 - Find the difference in electric potential, V = VB ...Ch. 20 - A 0.32-F capacitor is charged by a 1.5-V battery....Ch. 20 - A charge of 22.5 C is located at (4.40 m, 6.22 m),...Ch. 20 - The Bohr Model In the Bohr model of the hydrogen...Ch. 20 - Predict/Calculate A +1.2-C charge and a 1.2-C...Ch. 20 - How much work is required to bring three protons,...Ch. 20 - A point charge Q = +87.1 C is held fixed at the...Ch. 20 - Electron Escape Speed An electron is at rest just...Ch. 20 - Quark Model of the Neutron According to the quark...Ch. 20 - A parallel-plate capacitor is charged to an...Ch. 20 - Predict/Calculate The three charges shown in...Ch. 20 - (a) In Figure 20-36 we see that the electric...Ch. 20 - BIO Predict/Calculate Electric Catfish The...Ch. 20 - Regenerative Braking Many electric cars can...Ch. 20 - Predict/Calculate Computer Keyboards Many computer...Ch. 20 - Predict/Calculate A point charge of mass 0.081 kg...Ch. 20 - BIO Cell Membranes and Dielectrics Many cells in...Ch. 20 - BIO Mitochondrial Membrane Every cell in the body...Ch. 20 - Long, long ago, on a planet far, far away, a...Ch. 20 - Rutherfords Planetary Model of the Atom In 1911,...Ch. 20 - Predict/Calculate (a) One of the Q charges in...Ch. 20 - Figure 20-38 shows a charge q = +6.77 C with a...Ch. 20 - The electric potential a distance r from a point...Ch. 20 - When the potential difference between the plates...Ch. 20 - The electric potential a distance r from a point...Ch. 20 - BIO The Electric Eel Of the many unique and...Ch. 20 - As a rough approximation, consider an electric eel...Ch. 20 - In terms of the parallel-plate model of the...Ch. 20 - How much energy is stored by an electric eel when...Ch. 20 - Predict/Calculate Referring to Example 20-9...Ch. 20 - Referring to Example 20-9 Suppose we can change...Ch. 20 - Predict/Calculate Referring to Example 20-9...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
41. (II) A 0.40-kg cord is stretched between two supports, 8.7 m apart. When one support is struck by a hammer,...
Physics: Principles with Applications
What focal length should you specify if you want a magnifying glass with angular magnification 3.2?
Essential University Physics: Volume 2 (3rd Edition)
Space radiation shielding. One of the hazards facing humans in space is space radiation: high-energy charged pa...
College Physics (10th Edition)
Suppose that you are viewing a soccer game from a helicopter above the playing field. Two soccer players simult...
University Physics Volume 1
3. What is free-fall, and why does it make you weightless? Briefly describe why astronauts are weightless in th...
The Cosmic Perspective
Find the speed of a satellite in geostationary orbit.
Essential University Physics (3rd Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A particle with charge 1.60 1019 C enters midway between two charged plates, one positive and the other negative. The initial velocity of the particle is parallel to the plates and along the midline between them (Fig. P26.48). A potential difference of 300.0 V is maintained between the two charged plates. If the lengths of the plates are 10.0 cm and they are separated by 2.00 cm, find the greatest initial velocity for which the particle will not be able to exit the region between the plates. The mass of the particle is 12.0 1024 kg. FIGURE P26.48arrow_forwardTwo particles each with charge +2.00 C are located on the x axis. One is at x = 1.00 m, and the other is at x = 1.00 m. (a) Determine the electric potential on the y axis at y = 0.500 m. (b) Calculate the change in electric potential energy of the system as a third charged particle of 3.00 C is brought from infinitely far away to a position on the y axis at y = 0.500 m.arrow_forwardA proton is fired from very far away directly at a fixed particle with charge q = 1.28 1018 C. If the initial speed of the proton is 2.4 105 m/s, what is its distance of closest approach to the fixed particle? The mass of a proton is 1.67 1027 kg.arrow_forward
- Four particles are positioned on the rim of a circle. The charges on the particles are +0.500 C, +1.50 C, 1.00 C, and 0.500 C. If the electric potential at the center of the circle due to the +0.500 C charge alone is 4.50 104 V, what is the total electric potential at the center due to the four charges? (a) 18.0 104 V (b) 4.50 104 V (c) 0 (d) 4.50 104 V (e) 9.00 104 Varrow_forwardA proton is released from rest at the origin in a uniform electric field in the positive x direction with magnitude 850 N/C. What is the change in the electric potential energy of the protonfield system when the proton travels to x = 2.50 m? (a) 3.40 1016 J (b) 3.40 1016 J (c) 2.50 1016 J (d) 2.50 1016 J (e) 1.60 1019 Jarrow_forwardTwo particles, with charges of 20.0 nC and 20.0 nC, are placed at the points with coordinates (0, 4.00 cm) and (0, 4.00 cm) as shown in Figure P20.19. A particle with charge 10.0 nC is located at the origin. (a) Find the electric potential energy of the configuration of the three fixed charges. (b) A fourth particle, with a mass of 2.00 1013 kg and a charge of 40.0 nC, is released from rest at the point (3.00 cm, 0). Find its speed after it has moved freely to a very large distance away.arrow_forward
- A proton is located at the origin, and a second proton is located on the x-axis at x = 6.00 fm (1 fm = 10-15 m). (a) Calculate the electric potential energy associated with this configuration. (b) An alpha particle (charge = 2e, mass = 6.64 1027 kg) is now placed at (x, y) = (3.00, 3.00) fm. Calculate the electric potential energy associated with this configuration. (c) Starting with the three-particle system, find the change in electric potential energy if the alpha particle is allowed to escape to infinity while the two protons remain fixed in place. (Throughout, neglect any radiation effects.) (d) Use conservation of energy to calculate the speed of the alpha particle at infinity. (e) If the two protons are released from rest and the alpha panicle remains fixed, calculate the speed of the protons at infinity.arrow_forwardTwo parallel plates 10 cm on a side are given equal and opposite charges of magnitude 5.0109 C. The plates are 1.5 mm apart. What is the potential difference between the plates?arrow_forwardA point charge of q=50108 C is placed at the center of an uncharged spherical conducting shell of inner radius 6.0 cm and outer radius 9.0 cm. Find the electric potential at (a) r = 4,0cm, (b) r = 8.0 cm, (c) r — 12.0 cm.arrow_forward
- An election enters a region between two large parallel plates made of aluminum separated by a distance of 2.0 cm and kept at a potential difference of 200 V. The electron enters through a small hole in the negative plate and moves toward the positive plate. At the time the electron is near the negative plate, its speed is 4.0103 m/s. Assume the electric field between the plates to be uniform, and find the speed of electron at (a) 0.10 cm, (b) 0.50 cm, (c) 1.0 cm, and (d) 1.5 cm from the negative plate, and (e) immediately before it hits the positive plate.arrow_forwardas soon as possiblearrow_forwardThe probability of fusion occurring is greatly enhanced when appropriate nuclei are brought close together, but mutual Coulomb repulsion must be overcome. This can be done using the kinetic energy of hightemperature gas ions or by accelerating the nuclei toward one another. (a) Calculate the potential energy of two singly charged nuclei separated by 1.00 × 10−12 m. (b) At what temperature will atoms of a gas have an average kinetic energy equal to this needed electrical potential energy?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning


Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics Capacitor & Capacitance part 7 (Parallel Plate capacitor) CBSE class 12; Author: LearnoHub - Class 11, 12;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JoW6UstbZ7Y;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY