
PRIN.OF CORPORATE FINANCE
13th Edition
ISBN: 9781260013900
Author: BREALEY
Publisher: RENT MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 20, Problem 28PS
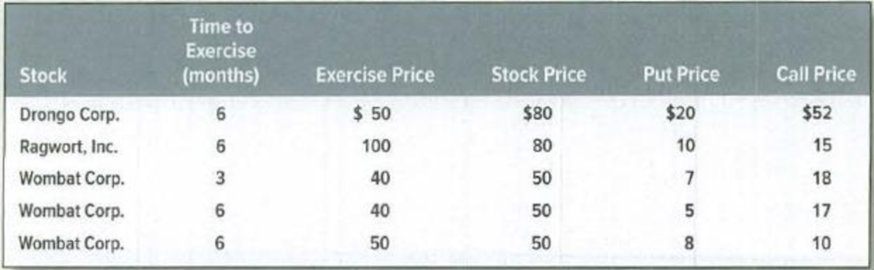
Option values* Table 20.4 lists some prices of options on common stocks (prices are quoted to the nearest dollar). The interest rate is 10% a year. Can you spot any mispricing? What would you do to take advantage of it?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
You are given the following information concerning options on a particular stock:
Stock price=
Exercise price=
Risk-free rate=
Maturity=
Standard deviation=
$83
Intrinsic value=$
$80
6% per year, compounded continuously
6 months
47% per year
(a)What is the intrinsic value of the call option? (Please keep two digits after the decimal point.)
(b)What is the time premium of the call option? (Please keep two digits after the decimal point.)
Time premium of the call option=$
Consider a two period economy. You can buy stocks in period 0, and then sell them in period 1. You can also enter into futures contracts in period 0, which expire in period 1.
Suppose a stock has a β of 0.5. The stock pays no dividends, and is trading at $100. The market has an expected return of 10%. The interest rate is 2%. Suppose the CAPM holds. What is the stock’s expected return? What is the expected price of the stock in period 1?
Consider a futures contract on the stock, expiring at t = 1. What is the fair price of the futures contract, in t = 1 dollars?
Suppose you take a long position in the futures contract in period 0 (so, you promise to pay money, in exchange for getting the stock in period 1). When the futures contract expires in period 1, you receive the stock and immediately sell it. What is the expected amount you will pay in money for the stock? What is the expected amount you get from selling the stock?
Since buying single-stock futures appears to be a fairly…
Consider a put option on a stock that currently sells for £100, but may rise to £120 or
fall to £80 after 1 year. The risk free rate of return is 10%, and the exercise price is £90.
(a) Calculate the value of the put option using the risk-neutral valuation relationship
(RNVR). Explain the reasoning behind your calculations.
Chapter 20 Solutions
PRIN.OF CORPORATE FINANCE
Ch. 20 - Vocabulary Complete the following passage: A _____...Ch. 20 - Option payoffs Note Figure 20.12 below. Match each...Ch. 20 - Option payoffs Look again at Figure 20.12. It...Ch. 20 - Option payoffs What is a call option worth at...Ch. 20 - Option payoffs The buyer of the call and the...Ch. 20 - Option combinations Suppose that you hold a share...Ch. 20 - Option combinations Dr. Livingstone 1. Presume...Ch. 20 - Option combinations Suppose you buy a one-year...Ch. 20 - Option combinations Suppose that Mr. Colleoni...Ch. 20 - Option combinations Option traders often refer to...
Ch. 20 - Prob. 11PSCh. 20 - Option combinations Discuss briefly the risks and...Ch. 20 - Put-call parity A European call and put option...Ch. 20 - Putcall parity a. If you cant sell a share short,...Ch. 20 - Putcall parity The common stock of Triangular File...Ch. 20 - Put-call parity What is put-call parity and why...Ch. 20 - Putcall parity There is another strategy involving...Ch. 20 - Putcall parity It is possible to buy three-month...Ch. 20 - Putcall parity In April 2017, Facebooks stock...Ch. 20 - Option bounds Pintails stock price is currently...Ch. 20 - Option values How does the price of a call option...Ch. 20 - Option values Respond to the following statements....Ch. 20 - Option values FX Bank has succeeded in hiring ace...Ch. 20 - Option values Is it more valuable to own an option...Ch. 20 - Option values Youve just completed a month-long...Ch. 20 - Option values Table 20.4 lists some prices of...Ch. 20 - Option bounds Problem 21 considered an arbitrage...Ch. 20 - Prob. 30PSCh. 20 - Prob. 31PSCh. 20 - Prob. 32PS
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, finance and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the following information on a particular stock: Stock price = $89 Exercise price = $85 Risk-free rate = 3% per year, compounded continuously Maturity = 8 months Standard deviation = 59% per year 1. What is the delta of a call option? 2. What is the delta of a put option?arrow_forward4) A stock is currently trading at $45. A call option has strike price $44, 0=23%, and maturity of 6 months. Interest rates are 3% per year. 4a) What is the probability that the option will end up "in-the-money"? 4b) What is the delta of the option? 4c) What is the price of the option?arrow_forwardSuppose the European call and put options with strike price $20 and maturity date in 1 month cost $2.0 and $1.0, respectively. The underlying stock price is $18 and the risk-free continuously compounded interest rate is 8%. (a) Is there an arbitrage opportunity? (b)If yes, how would you implement arbitrage opportunity?arrow_forward
- Consider a put option on a stock that currently sells for £100, but may rise to £120 or fall to £80 after 1 year. The risk free rate of return is 10%, and the exercise price is £90. (c) What is the price of a call option on the same stock with the same exercise price and the same expiration date? Explain the reasoning behind your your calculations.arrow_forwardConsider a European call option and a European put option that have the same underlying stock, the same strike price K = 40, and the same expiration date 6 months from now. The current stock price is $45. a) Suppose the annualized risk-free rate r = 2%, what is the difference between the call premium and the put premium implied by no-arbitrage? b) Suppose the annualized risk-free borrowing rate = 4%, and the annualized risk-free lending rate = 2%. Find the maximum and minimum difference between the call premium and the put premium, i.e., C − P such that there is no arbitrage opportunities.arrow_forward4. A stock is selling today for $100. The stock has an annual volatility of 45 percent and the annual risk-free interest rate is 12 percent. A 1 year European put option with an exercise price of $90 is available to an investor .a.Use Excel’s data table feature to construct a Two-Way Data Table to demonstrate the impact of the risk free rate of interest and the volatility on the price of this put option: i. Risk Free Rates of 5%, 7%, 9%, 12%, 15% and 18%. ii. Volatility of 35%, 45%, 55%, and 65%. b. How is the put option price impacted by varying the risk free rate of interest? c.How is the put option price impacted by varying the volatility?arrow_forward
- Consider shorting a call option c on a stock S where S = 24 is the value of the stock, K = 30 is the strike price, T = ½ is the expiration date, r = 0.04 is the continuously compounded interest rate per year, and = 0.3 is the volatility of the price of the stock. Determine the delta ratio Δ .arrow_forwardYou are interested to value a put option with an exercise price of $100 and one year to expiration. The underlying stock pays no dividends, its current price is $100, and you believe it either increases to $120 or decreases to $80. The risk-free rate of interest is 10%. Calculate the put option's value using the binomial pricing model, presenting your calculations and explanations as follows: a. Draw tree-diagrams to show the possible paths of the share price and put payoffs over one year period. (Note: Show the numbers that are known and use letter(s) for what is unknown in your diagrams.) b. Compute the hedge ratio. c. Find the put option price. Explain your calculations clearly. d. Use put-call parity, find the price of a call option with the same exercise price and the same expiration date.arrow_forwardCalculate the value of a European put option on Apple stock. You are given the following parameter values: • The stock pays no dividends. • The exercise price is $115. • The interest rate is 4%. • The current stock price is $115. • The time to maturity of the option on Apple is 3 months. • The value of a European call option with the same maturity and strike is equal to $12.15.arrow_forward
- Consider a put option on a stock that currently sells for £100, but may rise to £120 or fall to £80 after 1 year. The risk free rate of return is 10%, and the exercise price is £90. (b) Calculate the value of the put option by using first principles (No Arbitrage prin- ciples). Explain the reasoning behind your calculations.arrow_forwardSuppose the following for European options: Stock price = $94 3-month call options with strike price $97 3-month put option with strike price $98 1-year risk-free rate is 3%. The put option is trading at $5 and there is a similar put option with an exercise price of $101 is trading at $8.5. The arbitrage gain that can be made is equal toarrow_forwardYou are pricing options with the following characteristics: •Current stock price (St): $35.60 •Exercise price (X): $50 •Time to expiration (T-t): 9 months •Risk-free rate (rf): 3.25% •Volatility (0): 45% (a): What is the Black-Scholes value of call option? In your hand-written solution, provide the calculations of d1,d2, and the final call price. Use Excel or another spreadsheet program to compute the values of N(d1) and N(d2). See the notes for details. (b): Using put-call parity, what is the value of a put option? For this case, assume continuous compounding, which implies that PVt(X)=e-r(T-t).X.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

Accounting for Derivatives Comprehensive Guide; Author: WallStreetMojo;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9D-0LoM4dy4;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Option Trading Basics-Simplest Explanation; Author: Sky View Trading;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=joJ8mbwuYW8;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY