
(a)
Interpretation:
6-phosphoglucono-⏹-lactone should be identified.
Concept introduction:
6-phosphoglucono-⏹-lactone is formed during the pentose phosphate pathway. In the first step of pentose phosphate pathway, dehydrogenation of glucose-6-phosphate at C-1 takes produce 6-phosphoglucono-⏹-lactone.
Answer to Problem 28P
The compound C in the reaction is 6-phosphoglucono-⏹-lactone.
Explanation of Solution
6-phosphoglucono-⏹-lactone is an intramolecular ester formed by the reaction of C-1 carboxyl group and C-5 hydroxyl group. It is formed by dehydrogenation of C-1 carbon of Glucose-6-phosphate. Hydroxyl group at C-1 of glucose-6-phosphate is converted to carbonyl group. Therefore, the structure of 6-phosphoglucono-⏹-lactone is (C).
(b)
Interpretation:
The reactions producing NADPH should be determined.
Concept introduction:
Two molecules of NADPH are produced duringthe oxidative phase of pentose phosphate pathway.
Answer to Problem 28P
The reactions B and F produce NADPH.
Explanation of Solution
First NADPH is produced when the C-1 in glucose-6-phosphate is dehydrogenated into 6-phosphoglucono-⏹-lactone by glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. This 6-phosphoglucono-⏹-lactone is hydrolyzed by a lactonase resulting 6-phosphogluconate. This 6C sugar acid is then decarboxylated by 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase into ribulose-5-phosphate. In this step also NADP+ acts as the electron acceptor and produce NADPH.
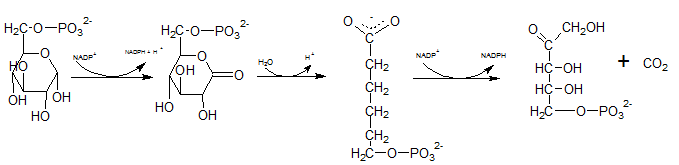
Therefore,reactions B and F produces NADPH.
(c)
Interpretation:
Ribulose-5-phosphate should be identified.
Concept introduction:
Ribulose-5-phosphate is the productof pentose phosphate pathway.
Answer to Problem 28P
The compound G in the reaction is Ribulose-5-phosphate.
Explanation of Solution
As the first step of oxidative phase of pentose phosphate pathway, C-1 of glucose-6-phosphate is dehydrogenated into 6-phosphoglucono-⏹-lactone by glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Then this 6-phosphoglucono-⏹-lactone is hydrolyzed by a lactonase resulting 6-phosphogluconate. This 6 C sugar acid is then decarboxylated by 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase into ribulose-5-phosphate.
Therefore, Gis Ribulose-5-phosphate.
(d)
Interpretation:
The CO2generating reaction should be determined.
Concept introduction:
The decarboxylation reactions generate CO2 as a by-product.
Answer to Problem 28P
The reactions F produce CO2.
Explanation of Solution
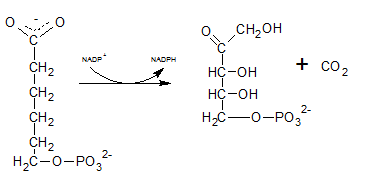
The six C sugar acid, 6-phosphogluconate formed during pentose phosphate pathway is oxidatively decarboxylated by 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase into ribulose-5-phosphate. The final product is a five-carbon sugar, and release CO2.
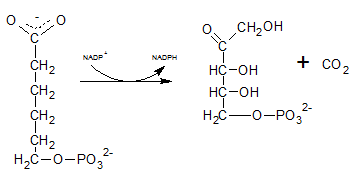
So. the reaction F produce CO2.
(e)
Interpretation:
6-phosphogluconate should be identified.
Concept introduction:
6-phosphogluconate is a 6C sugar acid which forms during pentose phosphate pathway.
Answer to Problem 28P
The compound E in the reaction is 6-phosphogluconate.
Explanation of Solution
In the first step of the oxidative phase of pentose phosphate pathway, C-1 of glucose-6-phosphate is dehydrogenated into 6-phosphoglucono-⏹-lactone by glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase which is hydrolyzed by a lactonase resulting 6-phosphogluconate.
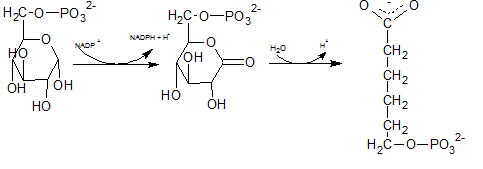
The end product of above reaction is 6-phosphogluconate. Thus the compound E in the reaction is 6-phosphogluconate.
(f)
Interpretation:
The reaction that is catalyzed by phosphopentose isomerase should be determined.
Concept introduction:
Phosphopentose isomerase is an enzyme which involves in isomerization reaction.
Answer to Problem 28P
The reactions H uses Phosphopentose isomerase enzyme.
Explanation of Solution
Ribulose-5-phosphate is isomerized to ribose-5-phosphate by phosphopentose isomerase. The enzyme, phosphopentose isomerase catalyze the conversion of a ketose sugar (Ribulose-5-phosphate ) to an aldose sugar (ribose-5-phosphate).
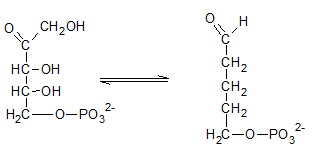
Therefore, the reaction H needs the enzyme phosphopentose isomerase.
(g)
Interpretation:
Ribose-5-phosphate should be identified.
Concept introduction:
Ribose-5-phosphate is the end product of the oxidative phase of pentose phosphate pathway.
Answer to Problem 28P
The compound I in the reaction is Ribose-5-phosphate.
Explanation of Solution
The ribulose-5-phosphate is obtained in pentose phosphate pathway when the ribose-5-phosphate is isomerized by phosphopentose isomerase.
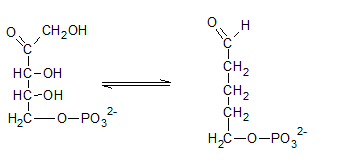
Therefore, the compound I in the reaction is Ribose-5-phosphate.
(h)
Interpretation:
Reaction catalyzed by lactonase should be determined.
Concept introduction:
Lactonases catalyzes the hydrolysis of ester bonds.
Answer to Problem 28P
The reactions D uses the enzymeLactonases.
Explanation of Solution
The degydrogenated product of glucose-6-phospahte is 6-phosphoglucono-⏹-lactone. This is a 6 membered ring structure and have an ester bond between C-1 carbonyl carbon and C-5 hydroxyl Oxygen. This bond is hydrolyzed by lactonase and to produce 6-phosphogluconate. The reaction is indicated by letter D.
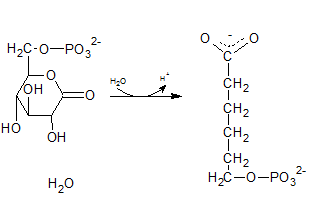
(i)
Interpretation:
Glucose-6-phosphate should be identified.
Concept introduction:
The pentose phosphate pathway is initiated by the oxidation of glucose-6-phosphate.
Answer to Problem 28P
The compound A in the reaction is glucose-6-phosphate.
Explanation of Solution
Glucose-6-phosphate is a 6-carbon sugar and have a ring structure where the hydroxyl group at C-6 is phosphorylated.
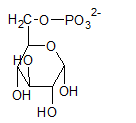
The compound A in the reaction is glucose-6-phosphate.
(j)
Interpretation:
The reaction catalyzed by 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase should be determined.
Concept introduction:
Dehydrogenases are the enzymes which catalyzes the removal of hydrogen molecules with the help of coenzymes NAD and FAD.
Answer to Problem 28P
The reactions F uses the enzymedehydrogenases.
Explanation of Solution
6-phosphogluconate is oxidatively decarboxylated by 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase into ribulose-5-phosphate which is indicated by reaction F.
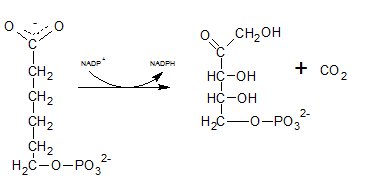
(k)
Interpretation:
Reaction that is catalyzed by glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase should be determined.
Concept introduction:
In the first reaction of pentose phosphate pathway glucose-6-phosphate is dehydrogenated to produce phosphoglucono-⏹-lactone.
Answer to Problem 28P
The reactions B uses the enzymeglucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenases.
Explanation of Solution
In the first step of pentose phosphate pathway, Glucose-6-phosphate is dehydrogenated at C-1 by glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase enzyme into 6-phosphoglucono-⏹-lactone.
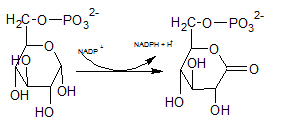
So, the reactions B uses the enzymeglucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenases.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
BIOCHEM-ACHIEVE(FIRST DAY DISCOUNTED)
- Instructions. Given each set of information which may include common name(s) and the reaction catalyzed, you are required to identify the main class of the specific enzyme described. _____________________ Name: alkaline phosphatase Reaction: a phosphate monoester + H2O = an alcohol + phosphate _____________________ Reaction: L-threonine = D-threonine. Other information: Inverts both chiral centers, a racemase. _____________________ Name: glycine-N-acylase Reaction: acyl-COA + glycine = CoA + N-acylglycine _____________________ Name: lysine decarboxylase Reaction: L-lysine = cadaverine + CO2 _____________________ Name: methanol dehydrogenase Reaction: methanol + NAD+ = formaldehyde + NADH + H+ _____________________ Name: citryl-CoA synthetase Reaction: ATP + citrate + CoA = ADP + phosphate + (3S)-citryl-CoA _____________________ Name: D-xylulose reductase Reaction: xylitol + NAD+ = D-xylulose + NADH + H+ _____________________ Name: cellobiose phosphorylase Reaction:…arrow_forwardPlease answer clearly and directly.Give 3 types of specificity of enzyme and an example for each. Example: Relative Specificty - α-amylase enzyme can hydrolyze α-1-4 glycosidic linkage in starch and glycogenarrow_forwardENZYMES. Match the name of the enzyme with the biochemical reaction. Enzymes may be used more than once a. amylase 1. casein hydrolysis b. cysteine desulfurase 2.gelatin liquefaction c. lipase 3. hydrogen sulfide production d. protease 4. indole e. tryptophanase 5.starch hydrolysis f.urease 6.triglyceride hydrolysis urea hydrolysisarrow_forward
- Help please. This question is specifically asking for the identification of the biomolecules that are attached to the sphingosine core, then we need to answer what bond causes those biomolecules to be connected to the sphingosine, what reaction created that bond (maybe addition or oxidation etc.), what were the starting materials and lastly what reagents or conditions are needed for the reaction to occur. Thank you!arrow_forward. Explain what is meant by the term, “high energy compound”. Name a thioester molecule that is commonly found in biochemical reactions. Explain why thioesters are “high energy” compounds. Describe the molecular structure of cellulose. How does this structure explain why cellulose forms strong fibers? Explain why digestion of cellulose takes a long time even when catalyzed by an enzyme. The enzyme phosphofructokinase transfers a phosphate from ATP to the hydroxyl group a C1 of fructose. Similar to fructose, water also has a hydroxyl group and the concentration of water is much higher than that of fructose. Explain why the phosphate is transferred to fructose and not to water.arrow_forwardIdentification. Write in CAPITAL LETTERS. Wrong spelling, wrong. Two types of nucleic acids are: ____________________________ and __________________________________. Two forms of glucose isomers based on the anomeric carbon: __________________ and ___________________.arrow_forward
- Fill-out the table. Primary metabolic pathway Building blocks of seconday metabolite Primary metabolite Secondary metabolite Give an example for each secondary metabolite. Show its structure and encircle the building block it is made of.arrow_forwardENZYMES. Match the name of the enzyme with the biochemical reaction. Enzymes may be used more than once. a. amylase b. cysteine desulfurase c. lipase d. protease e. tryptophanase f. urease casein hydrolysis gelatin liquefaction hydrogen sulfide production indole starch hydrolysis triglyceride hydrolysis urea hydrolysisarrow_forwardFill in the Blanks. Supply the missing enzyme (E), pathway (P) or intermediate (I) by typing the 3-LETTER LABEL ONLY (e.g., ABA only and not ABA. Glycolysis) on the blanks provided ( glucose $12. E 11.E glucose-1-P glucose-6-P 1.1 6-phosphogluconate 10. E ribose-5-phosphate 1 2. P POOL OF CHOICES: ABA. glycolysis ACA. gluconeogenesis AGA. glycogenolysis ADA. glycogen synthesis AJA. TCA cycle AEA. beta-oxidation AFA. fatty acid synthesis AHA. TAG synthesis AZA. nucleotide synthesis AXA. fermentation AKA. pentose phosphate pathway ALA. pyruvate AMA. H₂O ANA. acetyl CoA AQA. mevalonate ASA. CO₂ ATA. beta-hydroxybutyrate AWA. oxaloacetate BAB. GTP SAB. 6-phosphogluconolactone axaloacetate lactate 6.1 1/20₂ 9. P oxaloacetate Mitochondria NADH, FADH₂ NAD+, FAD ADP, P ATP phosphoenolpyruvate 8.1 acety CoA 7. P NAD+, FAD succinate citrate alpha-ketoglutarate steroids 5.1 palmitoyl CoA 4.1 3. P malonyl CoA citrate Dracticar Acety CoA HMG-CoA ↓ acetoacetate CAB. pyruvate dehydrogenase complex…arrow_forward
- Remember for T/F questions, either answer TRUE or FALSE, but if the answer is FALSE make sure to explain WHY the answer is false. A metabolic pathway can have unfavorable reactions within the pathway as long as the total sum of all reactions are favorable. $$ S OiLearn Video Warrow_forwardFill in the blank. The molecule necessary for carbon to enter the Krebs cycle is _____________.arrow_forwardInstructions. Given each set of information which may include common name(s) and the reaction catalyzed, you are required to identify the main class of the specific enzyme described. Name: citryl-CoA synthetase Reaction: ATP + citrate + CoA = ADP + phosphate + (3S)-citryl-CoA Name: D-xylulose reductase Reaction: xylitol + NAD+ = D-xylulose + NADH + H+ Name: cellobiose phosphorylase Reaction: cellobiose phosphate = α-D-glucose 1-phosphate + D-glucose Name: carbonic anhydrase Reaction: H2CO3 = CO2 + H2O Other info: The enzyme catalyzes the reversible hydration of gaseous CO2 to carbonic acid, which dissociates to give hydrogencarbonate above neutral pH. Name: pantoate activating enzyme Reaction: ATP + (R)-pantoate = AMP + diphosphate + (R)-pantothenate.arrow_forward
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON





