
Concept explainers
What reagent is needed to convert
a.
b.
(a)
Interpretation:
The reagent needed to convert
Concept introduction:
Acid chlorides, which contains good leaving group
Answer to Problem 20.44P
The reagent needed to convert
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is aldehyde. Acid chlorides on reaction with mild reducing agent like lithium tri-tert-butoxyaluminium hydride
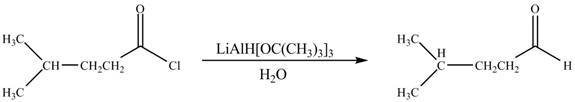
Figure 1
Therefore,
The reagent needed to convert
(b)
Interpretation:
The reagent needed to convert
Concept introduction:
Acid chlorides, which contains good leaving group
Answer to Problem 20.44P
The reagent needed to convert
Explanation of Solution
The structure of given ketone compound shows that one ethene molecule is attached to carbonyl carbon. Acid chlorides on reaction with one equivalent of organocuprate reagent convert into ketone. The organocuprate reagent removes the good leaving
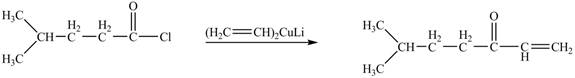
Figure 2
Therefore,
The reagent needed to convert
(c)
Interpretation:
The reagent needed to convert
Concept introduction:
Acid chlorides, which contains good leaving group
Answer to Problem 20.44P
The reagent needed to convert
Explanation of Solution
The structure of given ketone compound shows that the hydroxyl group is attached to tertiary carbon atom. Acid chlorides on reaction with two equivalents of Grignard reagent convert into tertiary alcohol. The first equivalent of Grignard reagent remove good leaving
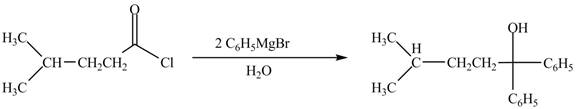
Figure 3
Therefore,
The reagent needed to convert
(d)
Interpretation:
The reagent needed to convert
Concept introduction:
Acid chlorides, which contains good leaving group
Answer to Problem 20.44P
The reagent needed to convert
Explanation of Solution
Acid chlorides on reaction with strong reducing agent like lithium aluminium hydride
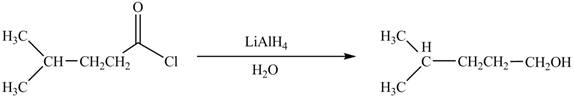
Figure 4
Therefore,
The reagent needed to convert
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
ALEKS 360 CHEMISTRY ACCESS
- Give the IUPAC name of the following:arrow_forwardGive the IUPAC name for each compound. CH3 CH2CH3 Br a. PHCH(CH3)2 b. С. d.arrow_forwardDraw the products formed when CH3CH2C ≡ C−Na+reacts with each compound. a. CH3CH2CH2Brb. (CH3)2CHCH2CH2Clc. (CH3CH2)3CCld. BrCH2CH2CH2CH2OHe. ethylene oxide followed by H2Of. propene oxide followed by H2Oarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





