
(a)
To draw the vector diagram of motion of a boat across stream and the velocity of the boat relative to water.
(a)
Answer to Problem 1SP
The vector diagram is shown in the figure 1 and the velocity of the boat relative to water is labelled as
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The velocity of the boat in still water is
Following figure gives the diagram of the vector form of the motion of boat across the figure.
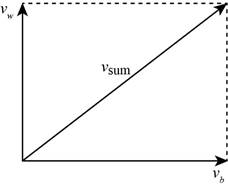
Figure 1
The figure 1 shows the velocity of water as
Conclusion:
Therefore, the vector diagram is shown in the figure 1 and the velocity of the boat relative to water is labelled as
(b)
To determine the magnitude of the velocity of boat relative to the Earth.
(b)
Answer to Problem 1SP
The magnitude of the velocity of boat relative to the Earth is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression to find the magnitude of the resultant of two vectors
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnitude of the velocity of boat relative to the Earth is
(c)
To determine the time taken for the boat to cross the stream.
(c)
Answer to Problem 1SP
The time taken for the boat to cross the stream is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the time taken for boat to cross the stream.
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the time taken for the boat to cross the stream is
(d)
To determine the distance from starting point till the ending point along the downward flow of the stream.
(d)
Answer to Problem 1SP
The distance from starting point till the ending point along the downward flow of the stream is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression to find the distance of the between the starting and ending point of the boat along the flow of the stream.
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the distance from starting point till the ending point along the downward flow of the stream is
(e)
To determine the distance travelled by the boat before reaching the opposite bank.
(e)
Answer to Problem 1SP
The distance travelled by the boat before reaching the opposite bank is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression to find the magnitude of the resultant of two vectors
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the distance travelled by the boat before reaching the opposite bank is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
Physics of Everyday Phenomena
- (a) Using the information in the previous problem, what velocity do you need to escape the Milky Way galaxy from our present position? (b) Would you need to accelerate a spaceship to this speed relative to Earth?arrow_forwardTwo birds begin next to each other and then fly through the air at the same elevation above level ground at 22.5 m/s. One flies northeast, and the other flies northwest. After flying for 10.5 s, what is the distance between them? Ignore the curvature of the Earth.arrow_forwardA map suggests that Atlanta is 730 miles in a direction 5.00c north of east from Dallas. The same map shows that Chicago is 560 miles in a direction 21.0 west of north from Atlanta. Figure P3.18 shows the location of these three cities. Modeling the Earth as flat, use this information to find the displacement from Dallas to Chicago. Figure P3.18arrow_forward
- A map suggests that Atlanta is 730 miles in a direction of 5.00 north of cast from Dallas. The same map slum's that Chicago is 560 miles in a direction of 21.0 west of north from Atlanta. Figure P3.24 shows the locations of these three cities. Modeling the Earth as flat, use this information to find the displacement from Dallas 10 Chicago.arrow_forward(a) If AF=BF , can we conclude A=B ? (b) If AF=BF , can we conclude A=B ? (c) If FA=BF , can we conclude A=B ? Why or why not?arrow_forwarda snake crawls from a hole to find food. it starts at 8m southwest; then goes 10m 40 degrees north of west; then sensed something moving 9m south from where it is and moves to it. a. how far and in what direction was the moving object from the hole? b. if after realizing that the moving object was not good for food, the snake moved from it because it saw another moving thing, moved to its direction by covering a fourth displacement and is now 20m and 30 degrees east of south from the hole. what is the magnitude and direction of the fourth displacement?arrow_forward
- A plane is flying at 324km/h with respect to the air. The wind is blowing at 67km/h [North30.° East]. The plane wants to fly directly West with respect to the ground.a. What is the plane's speed with respect to the ground? b. If the plane has to travel 2.24x10^3m, how long will it take to complete this trip?arrow_forwardA stone is thrown outward, at an angle of 30° with the horizontal into the river from a cliff, that is 75 meters above the water level at a velocity of 54 km/hr. How long it will take the stone to hit the surface of the river? a. 0.06159 minb. 0.059157minc. 0.01596 mind. 0.07915 minarrow_forwardShips A and B leave port together. For the next two hours, ship A travels at 20 mph in a direction 30° west of north while ship B travels 20° east of north at 25 mph. a. What is the distance between the two ships two hours after they depart? b. What is the speed of ship A as seen by ship B?arrow_forward
- 1. The final push to the summit of Mt. Everest starts at Camp 3. Your displacement from Camp 3 to Camp 4 is 400 meter west, 600 meter south, and 100 meter up. From Camp 4 to the peak is 900 meter east, 200 meter south, and 200 meter up. a. What is the displacement from Camp 3 to the peak of Mt. Everest? Give distances east/west, north/south and up/down from Camp 3 to the peak. b. What is the straight-line distance from Camp 3 to the peak of Mt. Everest? The straight-line distance is the distance if you drew a straight line from Camp 3 to Mt. Everest.arrow_forwardA large wheel with a radius of 7 m completes a revolution every 16 seconds. The bottom of the wheel is 1.5 m above the ground. a) Draw a graph showing the change in height of a person above the ground as a function of time for three revolutions, starting from the lowest point on the wheel. b) Formulate the equation corresponding to the graph. c) Predict the change in the graph and the equation if the Ferris wheel spins more slowly. d) Verify the prediction you made in c) by plotting the graph for three revolutions and revolutions and formulating the corresponding equation, if the wheel completes one revolution every 20 s. The average height of water in a harbour is 5 m. At low tide, the height of the water .arrow_forwardDuring this pandemic, Timothy's father asked an engineer to survey the field behind their house. He wanted to plant some orange and tangerine trees there. According to the survey, the field is thirty-two feet long and six yards wide. What is the perimeter of the field in feet? a. 100 b. 50 c. 576 d. 192arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University





