
Corporate Finance (4th Edition) (Pearson Series in Finance) - Standalone book
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780134083278
Author: Jonathan Berk, Peter DeMarzo
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 36P
You are analyzing the leverage of two firms and you note the following (all values in millions of dollars):
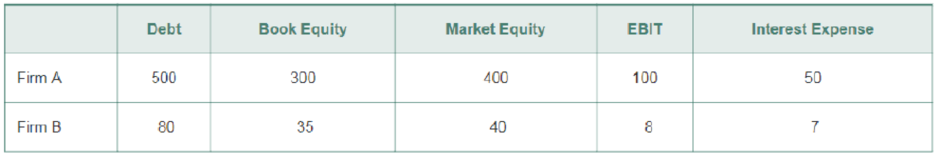
- a. What is the market debt-to-equity ratio of each firm?
- b. What is the book debt-to-equity ratio of each firm?
- c. What is the EBIT/interest coverage ratio of each firm?
- d. Which firm may have more difficulty meeting its debt obligations? Explain.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
7. What is a par value of a bond?*
The amount borrowed by the issuer of the bond and returned to the investors when the bond matures
The overall return earned by the bond investor when the bond matures
The difference between the amount borrowed by the issuer of bond and the amount returned to investors at maturity
The size of the coupon investors receive on an annual basis
What is an annuity?*
An investment that has no definite end and a stream of cash payments that continues forever
A stream of cash flows that start one year from today and continue while growing by a constant growth rate
A series of equal payments at equal time periods and guaranteed for a fixed number of years
A series of unequal payments at equal time periods which are guaranteed for a fixed number of years
If you were able to earn interest at 3% and you started with $100, how much would you have after 3 years?*
$91.51
$109.27
$291.26
$103.00
Chapter 2 Solutions
Corporate Finance (4th Edition) (Pearson Series in Finance) - Standalone book
Ch. 2.1 - Prob. 1CCCh. 2.1 - Prob. 2CCCh. 2.2 - Prob. 1CCCh. 2.2 - Prob. 2CCCh. 2.2 - Prob. 3CCCh. 2.3 - What it is the difference between a firms gross...Ch. 2.3 - What is the diluted earnings per share?Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 1CCCh. 2.4 - Prob. 2CCCh. 2.5 - Prob. 1CC
Ch. 2.5 - Prob. 2CCCh. 2.6 - Why is EBITDA used to assess a firms ability to...Ch. 2.6 - Prob. 2CCCh. 2.6 - Prob. 3CCCh. 2.6 - Prob. 4CCCh. 2.7 - Describe the transactions Enron used to increase...Ch. 2.7 - Prob. 2CCCh. 2 - Prob. 1PCh. 2 - Prob. 2PCh. 2 - Consider the following potential events that might...Ch. 2 - What was the change m Global Conglomerates book...Ch. 2 - Find online the annual 10-K report for Costco...Ch. 2 - In early 2012, General Electric (GE) had a book...Ch. 2 - In early-2015, Abercrombie Fitch (ANF) had a book...Ch. 2 - Prob. 10PCh. 2 - Suppose that in 2016, Global launches an...Ch. 2 - Find online the annual 10-K report for Costco...Ch. 2 - Prob. 13PCh. 2 - Prob. 14PCh. 2 - See Table 2.5 showing financial statement data and...Ch. 2 - See Table 2.5 showing financial statement data and...Ch. 2 - Suppose a firms tax rate is 35%. a. What effect...Ch. 2 - Prob. 18PCh. 2 - Prob. 19PCh. 2 - See Table 2.5 showing financial statement data and...Ch. 2 - See Table 2.5 showing financial statement data and...Ch. 2 - Prob. 22PCh. 2 - Can a firm with positive net income run out of...Ch. 2 - Suppose your firm receives a 5 million order on...Ch. 2 - Nokela Industries purchases a 40 million...Ch. 2 - See Table 2.5 showing financial statement data and...Ch. 2 - Find online the annual 10-K report for Costco...Ch. 2 - Prob. 28PCh. 2 - For fiscal year end 2015, Wal-Mart Stores, Inc....Ch. 2 - Prob. 30PCh. 2 - See Table 2.5 showing financial statement data and...Ch. 2 - See Table 2.5 showing financial statement data and...Ch. 2 - See Table 2.5 showing financial statement data and...Ch. 2 - See Table 2.5 showing financial statement data and...Ch. 2 - Use the data in Problem 8 to determine the change,...Ch. 2 - You are analyzing the leverage of two firms and...Ch. 2 - Prob. 37PCh. 2 - Prob. 38PCh. 2 - Prob. 39PCh. 2 - Prob. 40PCh. 2 - Prob. 41PCh. 2 - Prob. 42PCh. 2 - Consider a retailing firm with a net profit margin...Ch. 2 - Prob. 44PCh. 2 - Prob. 45P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, finance and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A proxy is an authorization that doesn’t allows one shareholder to vote on behalf of another shareholder. TRUE OR FALSEarrow_forwardNon-Investment-grade bonds are rated at least BBB by Standard and Poor’s. TRUE OR FALSEarrow_forwardNon-Investment-grade bonds are rated at least BBB by Standard and Poor’s. TRUE OR FALSEarrow_forward
- Moose Enterprises finds it is necessary to determine its marginal cost of capital. Moose’s current capital structure calls for 50 percent debt, 30 percent preferred stock, and 20 percent common equity. Initially, common equity will be in the form of retained earnings (Ke) and then new common stock (Kn). The costs of the various sources of financing are as follows: debt, 9.6 percent; preferred stock, 9 percent; retained earnings, 10 percent; and new common stock, 11.2 percent. a. What is the initial weighted average cost of capital? (Include debt, preferred stock, and common equity in the form of retained earnings, Ke.) b. If the firm has $18 million in retained earnings, at what size capital structure will the firm run out of retained earnings? c. What will the marginal cost of capital be immediately after that point? (Equity will remain at 20 percent of the capital structure, but will all be in the form of new common stock, Kn.) d. The 9.6 percent cost of debt referred to earlier…arrow_forward7. Berkeley Farms wants to determine the minimum cost of capital point for the firm. Assume it is considering the following financial plans: Cost (aftertax) Weights Plan A Debt .................................. 4.0% 30% Preferred stock .................. 8.0 15 Common equity ................. 12.0 55 Plan B Debt .................................. 4.5% 40% Preferred stock .................. 8.5 15 Common equity ................. 13.0 45 Plan C Debt .................................. 5.0% 45% Preferred stock .................. 18.7 15 Common equity ................. 12.8 40 Plan D Debt .................................. 12.0% 50% Preferred stock .................. 19.2 15 Common equity ................. 14.5 35 a. Which of the four plans has the lowest weighted average cost of capital? Use the Kd (cost of debt) = Y(1 - T), Kp (Cost of preferred stock) = Dp/Pp - F, Ke = D1/P0 + g formulas or I will not understand.arrow_forwardNeed use the Kd (cost of debt) = Y(1 - T), Kp (Cost of preferred stock) = Dp/Pp - F, Ke = D1/P0 + g formulas or I will not understand. Delta Corporation has the following capital structure: Cost Weighted (after-tax) Weights Cost Debt 8.1% 35% 2.84% Preferred stock (Kp) 9.6 5 .48 Common equity (Ke) (retained earnings) 10.1 60 6.06 Weighted average cost of capital (Ka) 9.38% a. If the firm has $18…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...
Finance
ISBN:9781285190907
Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark Bradshaw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Finance
ISBN:9781337514835
Author:MOYER
Publisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
Financial leverage explained; Author: The Finance story teller;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GESzfA9odgE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY