
Concept explainers
DATA In your physics lab you release a small glider from rest at various points on a long, frictionless air track that is inclined at an angle θ above the horizontal. With an electronic photocell, you measure the time t it takes the glider to slide a distance x from the release point to the bottom of the track. Your measurements are given in Fig. P2.84, which shows a
Figure P2.84
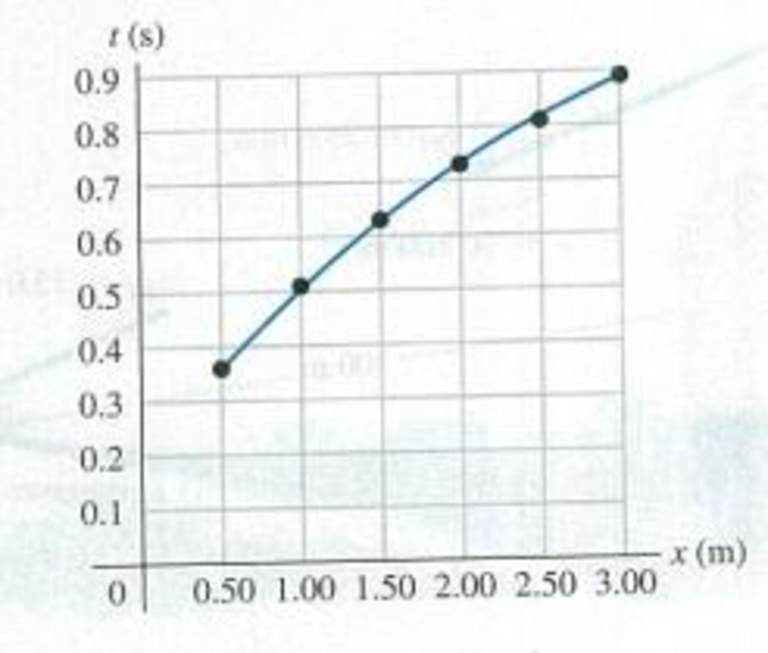
second-order polynomial (quadratic) fit to the plotted data. You are asked to find the glider’s acceleration, which is assumed to be constant. There is some error in each measurement, so instead of using a single set of x and t values, you can be more accurate if you use graphical methods and obtain your measured value of the acceleration from the graph, (a) How can you re-graph the data so that the data points fall close to a straight line? (Hint: You might want to plot x or t, or both, raised to some power.) (b) Construct the graph you described in part (a) and find the equation for the straight line that is the best fit to the data points, (c) Use the straight-line fit from part (b) to calculate the acceleration of the glider, (d) The glider is released at a distance x = 1.35 m from the bottom of the track. Use the acceleration value you obtained in part (c) to calculate the speed of the glider when it reaches the bottom of the track.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 2 Solutions
University Physics (14th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Introduction to Electrodynamics
College Physics
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Edition)
Essential University Physics: Volume 1 (3rd Edition)
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
- In the vertical jump, an Kobe Bryant starts from a crouch and jumps upward to reach as high as possible. Even the best athletes spend little more than 1.00 s in the air (their "hang time"). Treat Kobe as a particle and let ymax be his maximum height above the floor. Note: this isn't the entire story since Kobe can twist and curl up in the air, but then we can no longer treat him as a particle. Hint: Find v0 to reach y_max in terms of g and y_max and recall the velocity at y_max is zero. Then find v1 to reach y_max/2 with the same kinematic equation. The time to reach y_max is obtained from v0=g (t), and the time to reach y_max/2 is given by v1-v0= -g(t1). Now, t1 is the time to reach y_max/2, and the quantity t-t1 is the time to go from y_max/2 to y_max. You want the ratio of (t-t1)/t1 Note from Asker: I am generally confused on how to manipulate the formulas, so if you could show every step that would be great, Thank You. Part A Part complete To explain why…arrow_forwardAs you are driving to school one day, you pass a construction site of a new building and you stop to watch for a few minutes. A crane is lifting a batch of bricks on a pallet to an upper floor of the building. Suddenly a brick falls off the rising pallet. You measure the time it takes for the brick to hit the ground and you find it to be 2.5 seconds. The crane has height markings. You saw the brick fell off the pallet at a height of 30.7 meters above the ground. A falling brick can be dangerous, and you wonder how fast the brick was moving when it hit the ground. Since you are taking physics, you quickly calculate the answer.arrow_forwardAmel goes for a walk with a speed of 3kph. After 30 minutes of walk, his wife follows him. Walking 3.25 km for the first hour, 3.75 km for the second hour, 4 km for the third hour and so on maintaining a speed of .25 km per hour. How many hours does the wife take to catch up to her husband?arrow_forward
- The NEXT morning, you wake up in a strange room yet again, and this time you drop a ball from a height of 1.18 m above the floor. The ball hits the floor 0.147 s after your drop it. You guess that you must have been taken to an alien planet with gravity different from Earth s. What is this planet s g (that is, the magnitude of the acceleration due to gravity on this planet)?arrow_forwardThe velocity in ft/s of an object moving along a line is given byv = ƒ(t) on the interval 0 ≤ t ≤ 6 (see figure), where t ismeasured in seconds.a. Divide the interval [0, 6] into n = 3 subintervals, [0, 2], [2, 4],and [4, 6]. On each subinterval, assume the object moves at aconstant velocity equal to the value of v evaluated at the leftendpoint of the subinterval, and use these approximations toestimate the displacement of the object on [0, 6] b. Repeat part (a) for n = 6 subintervalsarrow_forwardA cat chases a mouse across a 1.7 m high table. The mouse steps out of the way, and the cat slides off the table and strikes the floor 1.5 m from the edge of the table. The acceleration of gravity is 9.81 m/s 2 . What was the cat’s speed when it slid off the table? Answer in units of m/s.arrow_forward
- A bridge that was 11.2 m long has been washed out by the rain several days ago. How fast must a car be going to successfully jump the stream? Although the road is level on both sides of the bridge, the road on the far side is 3.3 m lower than the road on this side. 喜 券arrow_forwardFrom a clifftop over the ocean 130 m above sea level, an object was shot straight up into the air with an initial vertical speed of 166.6 ms On its way down it missed the cliff and fell into the ocean. Its height (above sea level) as time passes can be modeled by the quadratic function f, where f(t)=−4.9t^2+166.6t+130 Here t represents the number of seconds since the object’s release, and f(t) represents the object’s height (above sea level) in meters. 1) After this, this object reached its maximum height. 2) This object flew before it landed in the ocean. 3) This object was above sea level 24s after its release. 4) This object was 1526.5 m above sea level twice: once after its release, and again later after its release.arrow_forwardA car moves along a straight road. It moves at a speed of 50 km/hr for 4 minutes, then during the next 4 minutes it gradually speeds up to 100 km/hr, continues at this speed for 4 minutes, then takes 4 minutes to gradually slow to a complete stop. Make a sketch like the figures in Section 1.2 of your textbook, marking dots for the position along the road every minute.arrow_forward
- For two decades, teams sought a connection between the Flint Ridge cave system and Mammoth cave in Kentucky. When the connection was finally discovered, the combined system was declared the world’s largest cave (more than 200 km long). The team that found the connection had to crawl, climb and squirm through countless passages, traveling a net 2.6 km westward, 3.9 km southward, and 25 km upward. What was their displacement from start to finish?arrow_forwardA particle starts at the point P = (7, −7, −3) and moves along a straight line toward Q = (8, −9, 0) at a speed of 5 cm/sec. Let x, y, z be measured in centimeters and t be measured in seconds. (a) Find the particle's velocity vector. v(t): = (b) Find parametric equations for the particle's motion. x(t) = y(t) = z(t) = =arrow_forwardThe next two questions are going to deal with Superman’s home planet of Krypton. Here on Earth, an athletic man can do a standing jump of about 1.5 m. On the moon, where gravity is 6 times weaker, an athletic man can do a standing jump of about 9.0 m. Originally, Superman was said to be able to “leap tall buildings with a single bound”. Based on this expression, let’s assume that Superman can jump 200 m here on Earth. Using this information, what is the gravitational acceleration, g, of Krypton?arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
