
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
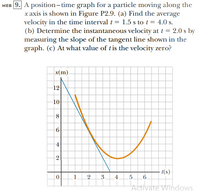
Transcribed Image Text:WEB 9. A position-time graph for a particle moving along the
x axis is shown in Figure P2.9. (a) Find the average
velocity in the time interval i = 1.5 s to t = 4.0 s.
(b) Determine the instantaneous velocity at i = 2.0 s by
measuring the slope of the tangent line shown in the
graph. (c) At what value of tis the velocity zero?
x(m).
12
10-
8
6
4
2
- t(s)
6.
1
2.
3.
.5
"Activate Windows
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Position, Velocity, and Acceleration 1. A position-time graph for a particle moving along the x axis is shown in the figure. (a) Find the average velocity in the time interval t = 1.50 s to t = 4s (b) Find the average velocity in the time interval t = 1.00 s to t = 6.00s (c) Determine the instantaneous velocity at t = 2.00 s by measuring the slope of the tangent line shown in the graph. (d) At what value of t is the velocity zero x (m) -t (s) 5 -12 -10 -8 -6 4 2- 0. 9 3 6arrow_forwardTraumatic brain injury such as concussion results when the head undergoes a very large acceleration. Generally, an acceleration less than 800 m/s2 lasting for any length of time will not cause injury, whereas an acceleration greater than 1000 m/s2 lasting for at least 1 ms will cause injury. Suppose a small child rolls off a bed that is 0.36 m above the floor. If the floor is hardwood, the child's head is brought to rest in approximately 2.2 mm. If the floor is carpeted, this stopping distance is increased to about 1.2 cm. Calculate the magnitude and duration of the deceleration in both cases, to determine the risk of injury. Assume that the child remains horizontal during the fall to the floor. Note that a more complicated fall could result in a head velocity greater or less than the speed you calculate. Hardwood floor magnitude m/s2 duration ms Carpeted floor magnitude m/s2 duration msarrow_forwardA particle moves in one dimension, and its position as a function of time is given by x (2.0 m/s)t + (-3.6 m/s²)e². (a) What is the particle's average velocity from t 0.45 s to t = 0.55 s? (Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.) m/s (b) What is the particle's average velocity from t = 0.49 s to t = 0.51 s? (Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.) m/s MacBook Air 888 F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 @ #3 $4 3 4 Q W E R T Garrow_forward
- The acceleration function (in m/s2) and the initial velocity are given for a particle moving along a line.Constants b and c are positive. a(t) = bt + c, and initial velocity v(0)> 0 ; where 0 ≤ t ≤ x (a) Find the velocity at time t.v(t) = m/s(b) Find the distance traveled during the given time interval.distance (t) = marrow_forwardAt t=0 an object has a velocity of 35 m/s and a steady acceleration of -10 m/s2. Make a sketch of velocity vs. time for this motion from t=0 to t=5 s. Make a sketch of acceleration vs. time for this motion from t=0 to t=5 s. Does the object change directions between 0 and 6 s?arrow_forwardan object has a velocity of (5.4 m/s)i - (5.8 m/s)j. over a period of 1.3 s, its velocity changes to (1.7 m/s)i + (5.9 m/s)j. What is the displacementarrow_forward
- The velocity of a particle moving along the x-axis varies in time according to the expression v(t) = α - βt2 where α = 52.9m/s , β = 3.72m/s3, and t is in seconds. a) Find the acceleration in the time interval from t = 0 to 2.97s in units of m/s2 b) Determine the acceleration of the particle tf = 2.97s in m/s2arrow_forwardThe acceleration of an object as a function of time is given by a(t) = 6.0 t² where t and a are in Sl units. If the object has a velocity 2.0 m/s at time t=0.0 s. What is the velocity of this object as a function of time?arrow_forwardThe figure shows the acceleration-versus-time graph of a particle moving along the x-axis. Its initial velocity is vox = 6.00 m/s at to = 0 s. What is the particle's velocity at t = 2.00 s? (Figure 1) 1 of 1 Figure a (m/s²) 4 2- 0 2 4 t(s) Part A Express your answer with the appropriate units. μA ? m 14 S Submit Previous Answers Request Answer X Incorrect; Try Again; 2 attempts remaining Provide Feedbackarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON