
(a)
Interpretation:
Change in molar enthalpy of carbon dioxide has to be calculated for the temperature range
Concept introduction:
Enthalpy:
Enthalpy is a property of a thermodynamic system that is equal to the sum of the internal energy of the system and the product of pressure and volume. For a closed system where transfer of matter between system and surroundings is prohibited, for the processes that occur at constant pressure, the heat absorbed or released equals to the change in enthalpy.
It is denoted as
From
Where,
H is the enthalpy energy
P is the Pressure
V is the volume.
Specific heat capacity at constant pressure:
Specific heat capacity at constant pressure can be defined as the amount of energy requires increasing the temperature of a substance by
It is denoted as
(a)
Answer to Problem 2.4PR
The molar enthalpy change for carbon dioxide at the temperature range of
Explanation of Solution
According to the question the heat capacity of substance is often reported in the form,
Now the change of the molar enthalpy has to be determined.
From thermodynamics it can be stated that,
Now, combining the two equations,
Temperature range is given as
Now applying integration over the temperature range
Given that,
Hence the molar enthalpy change for carbon dioxide at the temperature range of
(b)
Interpretation:
The change of molar enthalpy of a substance over a limited temperature range using the expression of part (a) has to be plotted.
Concept introduction:
Enthalpy:
Enthalpy is a property of a thermodynamic system that is equal to the sum of the internal energy of the system and the product of pressure and volume. For a closed system where transfer of matter between system and surroundings is prohibited, for the processes that occur at constant pressure, the heat absorbed or released equals to the change in enthalpy.
It is denoted as
From thermodynamics,
Where,
H is the enthalpy energy of system
P is the Pressure of the system
V is the volume of the system.
Specific heat capacity at constant pressure:
Specific heat capacity at constant pressure can be defined as the amount of energy required to increase the temperature of a substance by
It is denoted as
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The expression for the change of enthalpy of a substance that has been determined is,
Now according to question molar enthalpy has to be plotted as function of temperature to see the change within a temperature limit.
Putting the values of the temperature, the values of enthalpy at
The graph is plotted below,
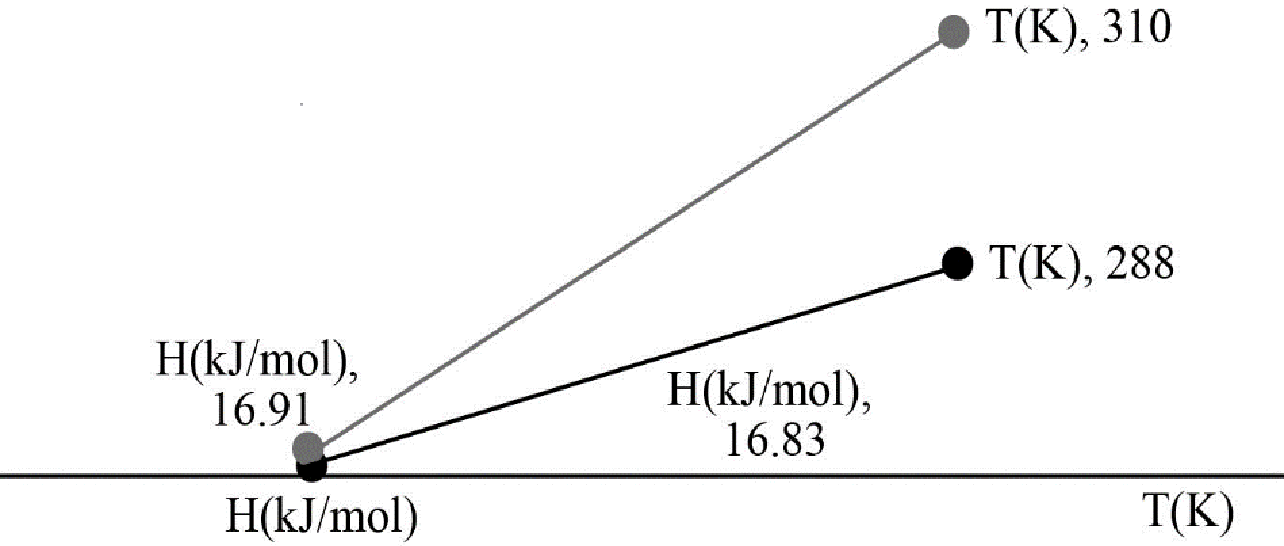
Figure-1
Hence from the plot it has been found that with increase in temperature the enthalpy value increases.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Elements Of Physical Chemistry
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





