
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781259977268
Author: Ferdinand P. Beer, E. Russell Johnston Jr., David Mazurek
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 2.138RP
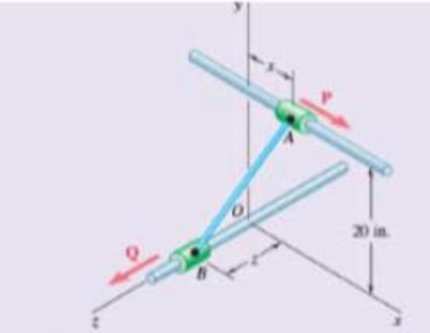
Fig. P2.137 and P2.138
2.138 Collars A and B are connected by a 25-in.-long wire and can slide freely on frictionless rods. Determine the distances x and z for which the equilibrium of the system is maintained when P = 120 lb and Q = 60 lb.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
3.
9.
10.
The centrifugal tension in belts
(a) increases power transmitted
(b) decreases power transmitted
(c) have no effect on the power transmitted
(d) increases power transmitted upto a certain speed and then decreases
When the belt is stationary, it is subjected to some tension, known as initial tension. The value of this
tension is equal to the
(a) tension in the tight side of the belt
(b) tension in the slack side of the belt
(c) sum of the tensions in the tight side and slack side of the belt
(d) average tension of the tight side and slack side of the belt
The relation between the pitch of the chain (p) and pitch circle diameter of the sprocket (d) is given by
60°
(a) p=d sin
(c) p=d sin
(120°
T
where T Number of teeth on the sprocket.
90°
(b) p=d sin
T
180°
(d) p=d sin
T
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS
1.
The maximum fluctuation of energy is the
2.
(a) sum of maximum and minimum energies
(b) difference between the maximum and minimum energies
(c) ratio of the maximum energy and minimum energy
(d) ratio of the mean resisting torque to the work done per cycle
In a turning moment diagram, the variations of energy above and below the mean resisting torque line
is called
(a) fluctuation of energy
(b) maximum fluctuation of energy
(c) coefficient of fluctuation of energy
(d) none of the above
Chapter 16: Turning Moment Diagrams and Flywheel 611
The ratio of the maximum fluctuation of speed to the mean speed is called
3.
(a) fluctuation of speed
(c) coefficient of fluctuation of speed
4.
(b) maximum fluctuation of speed
(a) none of these
The ratio of the maximum fluctuation of energy to the.......... is called coefficient of fluctuation of
energy.
(a) minimum fluctuation of energy
(b) work done per cycle
The maximum fluctuation of energy in a flywheel is equal to
5.…
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS
1.
The velocity ratio of two pulleys connected by an open belt or crossed belt is
2.
(a) directly proportional to their diameters
(b) inversely proportional to their diameters
(c) directly proportional to the square of their diameters
(d) inversely proportional to the square of their diameters
Two pulleys of diameters d, and d, and at distance x apart are connected by means of an open belt
drive. The length of the belt is
(a)(d+d₁)+2x+
(d₁+d₂)²
4x
(b)(d₁-d₂)+2x+
(d₁-d₂)²
4x
(c)(d₁+d₂)+ +2x+
(d₁-d₂)²
4x
(d)(d-d₂)+2x+
(d₁ +d₂)²
4x
3.
In a cone pulley, if the sum of radii of the pulleys on the driving and driven shafts is constant, then
(a) open belt drive is recommended
(b) cross belt drive is recommended
(c) both open belt drive and cross belt drive are recommended
(d) the drive is recommended depending upon the torque transmitted
Due to slip of the belt, the velocity ratio of the belt drive
4.
(a) decreases
5.
(b) increases
(c) does not change
When two pulleys…
Chapter 2 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics
Ch. 2.1 - Two forces are applied as shown to a hook....Ch. 2.1 - Two forces are applied as shown to a bracket...Ch. 2.1 - Two forces P and Q are applied as shown at point A...Ch. 2.1 - Two forces P and Q are applied as shown at point A...Ch. 2.1 - A stake is being pulled out of the ground by means...Ch. 2.1 - A telephone cable is clamped at A to the pole AB....Ch. 2.1 - A telephone cable is clamped at A to the pole AB....Ch. 2.1 - A disabled automobile is pulled by means of two...Ch. 2.1 - A disabled automobile is pulled by means of two...Ch. 2.1 - Two forces are applied as shown to a hook support....
Ch. 2.1 - A steel tank is to be positioned in an excavation....Ch. 2.1 - A steel tank is to be positioned in an excavation....Ch. 2.1 - A steel tank is to be positioned in an excavation....Ch. 2.1 - For the hook support of Prob. 2.10, determine by...Ch. 2.1 - The barge B is pulled by two tugboats A and C. At...Ch. 2.1 - Solve Prob. 2.1 by trigonometry.Ch. 2.1 - Solve Prob. 2.4 by trigonometry.Ch. 2.1 - For the stake of Prob. 2.5, knowing that the...Ch. 2.1 - Two structural members A and B are bolted to a...Ch. 2.1 - Two structural members A and B are bolted to a...Ch. 2.2 - Determine the x and y components of each of the...Ch. 2.2 - Determine the x and y components of each of die...Ch. 2.2 - Determine the x and y components of each of the...Ch. 2.2 - Determine the x and y components of each of the...Ch. 2.2 - Member BC exerts on member AC a force P directed...Ch. 2.2 - Member BD exerts on member ABC a force P directed...Ch. 2.2 - The hydraulic cylinder BC exerts cm member AB a...Ch. 2.2 - Cable AC exerts on beam AD a force P directed...Ch. 2.2 - The hydraulic cylinder BD exerts on member ABC a...Ch. 2.2 - The guy wire BD exerts on the telephone pole AC a...Ch. 2.2 - Determine the resultant of the three forces of...Ch. 2.2 - Determine the resultant of the three forces of...Ch. 2.2 - Determine the resultant of the three forces of...Ch. 2.2 - Determine the resultant of the three forces of...Ch. 2.2 - Knowing that = 35, determine the resultant of the...Ch. 2.2 - Knowing that the tension in cable BC is 725 N,...Ch. 2.2 - Knowing that = 40, determine the resultant of the...Ch. 2.2 - Knowing that = 75, determine the resultant of the...Ch. 2.2 - PROBLEM 2.39 A collar that can slide on a vertical...Ch. 2.2 - Prob. 2.40PCh. 2.2 - PROBLEM 2.41 Determine (a) the required tension in...Ch. 2.2 - PROBLEM 2.42 For the block of Problems 2.37 and...Ch. 2.3 - Two cables are tied together at C and loaded as...Ch. 2.3 - Two forces of magnitude TA = 8 kips and TB = 15...Ch. 2.3 - The 60-lb collar A can slide on a frictionless...Ch. 2.3 - A chairlift has been stopped in the position...Ch. 2.3 - Two cables are tied together at C and are loaded...Ch. 2.3 - Two cables are tied together at C and are loaded...Ch. 2.3 - Two cables are tied together at C and loaded as...Ch. 2.3 - Two cables are tied together at C and are loaded...Ch. 2.3 - Two cables are tied together at C and are loaded...Ch. 2.3 - Knowing that = 20, determine the tension (a) in...Ch. 2.3 - Two cables are tied together at C and are loaded...Ch. 2.3 - Two cables are tied together at C and are loaded...Ch. 2.3 - Two forces P and Q are applied as shown to an...Ch. 2.3 - Prob. 2.52PCh. 2.3 - A welded connection is in equilibrium under the...Ch. 2.3 - A welded connection is in equilibrium under the...Ch. 2.3 - A sailor is being rescued using a boatswains chair...Ch. 2.3 - A sailor is being rescued using a boatswains chair...Ch. 2.3 - For the cables of Prob. 2.44, find the value of ...Ch. 2.3 - For the cables of Prob. 2.46, it is known that the...Ch. 2.3 - For the situation described in Fig. P2.48,...Ch. 2.3 - Two cables tied together at C are loaded as shown....Ch. 2.3 - A movable bin and its contents have a combined...Ch. 2.3 - Free-Body Diagram...Ch. 2.3 - Collar A is connected as shown to a 50-lb load and...Ch. 2.3 - Collar A is connected as shown to a 50-lb load and...Ch. 2.3 - A cable loop of length 1.5 m is placed around a...Ch. 2.3 - A 200-kg crate is to be supported by the...Ch. 2.3 - A 600-lb crate is supported by several...Ch. 2.3 - Solve parts b and d of Prob. 2.67, assuming that...Ch. 2.3 - A load Q is applied to the pulley C, which can...Ch. 2.3 - An 1800-N load Q is applied to pulley C, which can...Ch. 2.4 - Determine (a) the x, y, and z components of the...Ch. 2.4 - Determine (a) the x, y, and z components of the...Ch. 2.4 - A gun is aimed at a point A located 35 east of...Ch. 2.4 - Solve Prob. 2.73 assuming that point A is located...Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 2.75PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 2.76PCh. 2.4 - Cable AB is 65 ft long, and the tension in that...Ch. 2.4 - PROBLEM 2.78 Cable AC is 70 ft long, and the...Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 2.79PCh. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude and direction of the force...Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 2.81PCh. 2.4 - A force acts at the origin of a coordinate system...Ch. 2.4 - A force F of magnitude 210 N acts at the origin of...Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 2.84PCh. 2.4 - Two cables BG and BH are attached to frame ACD as...Ch. 2.4 - Two cables BG and BH are attached to frame ACD as...Ch. 2.4 - In order to move a wrecked truck, two cables are...Ch. 2.4 - In order to move a wrecked truck, two cables are...Ch. 2.4 - A rectangular plate is supported by three cables...Ch. 2.4 - A rectangular plate is supported by three cables...Ch. 2.4 - Find the magnitude and direction of the resultant...Ch. 2.4 - Find the magnitude and direction of the resultant...Ch. 2.4 - Knowing that the tension is 425 lb in cable AB and...Ch. 2.4 - Knowing that the tension is 510 lb in cable AB and...Ch. 2.4 - For the frame of Prob. 2.85, determine the...Ch. 2.4 - For the plate of Prob. 2.89; determine the...Ch. 2.4 - The boom OA carries a load P and is supported by...Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 2.98PCh. 2.5 - Three cables are used to tether a balloon as...Ch. 2.5 - A container of mass m = 120 kg is supported by...Ch. 2.5 - A 150-lb cylinder is supported by two cables AC...Ch. 2.5 - A transmission tower is held by three guy wires...Ch. 2.5 - A container is supported by three cables that are...Ch. 2.5 - A container is supported by three cables that are...Ch. 2.5 - Three cables are used to tether a balloon as...Ch. 2.5 - Three cables are used to tether a balloon as...Ch. 2.5 - A crate is supported by three cables as shown....Ch. 2.5 - A crate is supported by three cables as shown....Ch. 2.5 - A 12-lb circular plate of 7-in. radius is...Ch. 2.5 - Prob. 2.106PCh. 2.5 - Three cables are connected at A, where the forces...Ch. 2.5 - Fig. P2.107 and P2.108 2.108 Three cables are...Ch. 2.5 - A rectangular plate is supported by three cables...Ch. 2.5 - A rectangular plate is supported by three cables...Ch. 2.5 - A transmission tower is held by three guy wires...Ch. 2.5 - A transmission tower is held by three guy wires...Ch. 2.5 - In trying to move across a slippery icy surface, a...Ch. 2.5 - Fig. P2.113 2.114 Solve Prob. 2.113 assuming that...Ch. 2.5 - For the rectangular plate of Probs. 2.109 and...Ch. 2.5 - PROBLEM 2.116 For the cable system of Problems...Ch. 2.5 - PROBLEM 2.117 For the cable system of Problems...Ch. 2.5 - Three cables are connected at D, where an upward...Ch. 2.5 - Prob. 2.119PCh. 2.5 - Three wires are connected at point D, which is...Ch. 2.5 - A container of weight W is suspended from ring A,...Ch. 2.5 - Knowing that the tension in cable AC of the system...Ch. 2.5 - A container of weight W is suspended from ring A....Ch. 2.5 - For the system of Prob. 2.123, determine W and P...Ch. 2.5 - Fig. P2.113 2.114 Solve Prob. 2.113 assuming that...Ch. 2.5 - Prob. 2.126PCh. 2 - Two forces P and Q are applied to the lid of a...Ch. 2 - Determine the x and y components of each of the...Ch. 2 - A hoist trolley is subjected to the three forces...Ch. 2 - Knowing that = 55 and that boom AC exerts on pin...Ch. 2 - Two cables are tied together at C and loaded as...Ch. 2 - Two cables tied together at C are loaded as shown....Ch. 2 - The end of the coaxial cable AE is attached to the...Ch. 2 - Knowing that the tension in cable AC is 2130 N,...Ch. 2 - Find the magnitude and direction of the resultant...Ch. 2 - Cable BAC passes through a frictionless ring A and...Ch. 2 - Collars A and B are connected by a 25-in.-lang...Ch. 2 - Fig. P2.137 and P2.138 2.138 Collars A and B are...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
The ____________ is always transparent.
Web Development and Design Foundations with HTML5 (8th Edition)
The solid steel shaft AC has a diameter of 25 mm and is supported by smooth bearings at D and E. It is coupled ...
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Write a summary list of the problem-solving steps identified in the chapter, using your own words.
BASIC BIOMECHANICS
Why is the study of database technology important?
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Assume a telephone signal travels through a cable at two-thirds the speed of light. How long does it take the s...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
17–1C A high-speed aircraft is cruising in still air. How does the temperature of air at the nose of the aircra...
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Q3: (10 MARKS) A piston with a weight of 29.4 N is supported by a spring and dashpot. A dashpot of damping coefficient c = 275 N.s/m acts in parallel with the spring of stiffness k = 2400 N/m. A fluctuating pressure p = 960 sin 30t N/m² acts on the piston, whose top surface area is 0.05 m². Determine the steady-state displacement as a function of time and the maximum force transmitted to the base. P=Po sin cot Warrow_forward9. Design a spur gear drive required to transmit 45 kW at a pinion speed of 800 r.p.m. The velocity ratio is 3.5 : 1. The teeth are 20° full-depth involute with 18 teeth on the pinion. Both the pinion and gear are made of steel with a maximum safe static stress of 180 MPa. Assume a safe stress of 40 MPa for the material of the shaft and key. 10. Design a pair of spur gears with stub teeth to transmit 55 kW from a 175 mm pinion running at 2500 r.p.m. to a gear running at 1500 r.p.m. Both the gears are made of steel having B.H.N. 260. Approximate the pitch by means of Lewis equation and then adjust the dimensions to keep within the limits set by the dynamic load and wear equation.arrow_forward7. A motor shaft rotating at 1440 r.p.m. has to transmit 15 kW to a low speed shaft rotating at 500 r.p.m. The teeth are 20° involute with 25 teeth on the pinion. Both the pinion and gear are made of cast iron with a maximum safe stress of 56 MPa. A safe stress of 35 MPa may be taken for the shaft on which the gear is mounted. Design and sketch the spur gear drive to suit the above conditions. The starting torque may be assumed as 1,25 times the running torque. Ruins 20 LW at 100 nm to another shaft running approxiarrow_forward
- 6. A two stage reduction drive is to be designed to transmit 2 kW; the input speed being 960 r.p.m. and overall reduction ratio being 9. The drive consists of straight tooth spur gears only, the shafts being spaced 200 mm apart, the input and output shafts being co-axial.arrow_forward2 A metal block of mass m = 10 kg is sliding along a frictionless surface with an initial speed Vo, as indicated below. The block then slides above an electromagnetic brake that applies a force FEB to the block, opposing its motion. The magnitude of the electromagnetic force varies quadratically with the distance moved along the brake (x): 10 FEB = kx², with k = 5 N m² V₁ = 8 m/s m = 10 kg FEB Frictionless surface Electromagnetic brake ⇒x Determine how far the block slides along the electromagnetic brake before stopping, in m.arrow_forwardQ1: Determine the length, angle of contact, and width of a 9.75 mm thick leather belt required to transmit 15 kW from a motor running at 900 r.p.m. The diameter of the driving pulley of the motor is 300 mm. The driven pulley runs at 300 r.p.m. and the distance between the centers of two pulleys is 3 meters. The density of the leather is 1000 kg/m³. The maximum allowable stress in the leather is 2.5 MPa. The coefficient of friction between the leather and pulley is 0.3. Assume open belt drive.arrow_forward
- 5. A 15 kW and 1200 r.p.m. motor drives a compressor at 300 r.p.m. through a pair of spur gears having 20° stub teeth. The centre to centre distance between the shafts is 400 mm. The motor pinion is made of forged steel having an allowable static stress as 210 MPa, while the gear is made of cast steel having allowable static stress as 140 MPa. Assuming that the drive operates 8 to 10 hours per day under light shock conditions, find from the standpoint of strength, 1. Module; 2. Face width and 3. Number of teeth and pitch circle diameter of each gear. Check the gears thus designed from the consideration of wear. The surface endurance limit may be taken as 700 MPa. [Ans. m = 6 mm; b= 60 mm; Tp=24; T=96; Dp = 144mm; DG = 576 mm]arrow_forward4. G A micarta pinion rotating at 1200 r.p.m. is to transmit 1 kW to a cast iron gear at a speed of 192 r.p.m. Assuming a starting overload of 20% and using 20° full depth involute teeth, determine the module, number of teeth on the pinion and gear and face width. Take allowable static strength for micarta as 40 MPa and for cast iron as 53 MPa. Check the pair in wear.arrow_forwardI want to solve these choicesarrow_forward
- 2. A spur gear made of bronze drives a mid steel pinion with angular velocity ratio of 32: 1. The pressure angle is 14½. It transmits 5 kW at 1800 r.p.m. of pinion. Considering only strength, design the smallest diameter gears and find also necessary face width. The number of teeth should not be less than 15 teeth on either gear. The elastic strength of bronze may be taken as 84 MPa and of steel as 105 MPa. Lewis factor for 14½½ pressure angle may be taken 0.684 0.124 y = No. of teeth as [Ans. m 3 mm; b= 35 mm; Dp = 48 mm; D= 168 mm]arrow_forwardQ2. Determine the safety factors for the bracket rod shown in Figure 2 based on both the distortion-energy theory and the maximum shear theory and compare them. Given: The material is 2024-T4 aluminum with a yield strength of 47 000 psi. The rod length /= 6 in. and arm a = 8 in. The rod outside diameter od 1.5 in., id = 1 in, h=2 in., t=0.5 in., Load F= 1000 lb. Assumptions: The load is static and the assembly is at room temperature. Consider shear due to transverse loading as well as other stresses. (Note: solve in SI units) wall tube Figure 2 armarrow_forwardThe question has been set up with all the cuts needed to accurately derive expressions for V(x) and M(x). Using the cuts free body diagrams set up below, derive expressions for V(x) and M(x). If you use the method of cuts then validate your answers using calculus or vice versa.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Differences between Temporary Joining and Permanent Joining.; Author: Academic Gain Tutorials;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PTr8QZhgXyg;License: Standard Youtube License