
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The stronger acid has to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Base and its conjugate Acid: A Base is a species that can gain a proton. When a base gains a proton
Electron delocalization stabilizes base: If a base has delocalized electrons, then the negative charge that results when the base’s conjugate acid loses a proton will belong to one atom. If a base has delocalized electrons, then the negative charge that results when the base’s conjugate acid loses a proton will be shared by two or more atoms. A base with delocalized electron is more stable than a similar base with localized electrons.
Relative Acid strength: Replacing hydrogen with an electronegative substituent that pulls bonding electrons toward itself increases the strength of the acid.
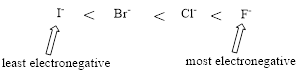
The more electronegative the substituent that replaces hydrogen, the stronger the acid becomes.
Example:
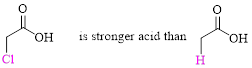
(b)
Interpretation:
The stronger acid has to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Base and its conjugate Acid: A Base is a species that can gain a proton. When a base gains a proton
Electron delocalization stabilizes base: If a base has delocalized electrons, then the negative charge that results when the base’s conjugate acid loses a proton will belong to one atom. If a base has delocalized electrons, then the negative charge that results when the base’s conjugate acid loses a proton will be shared by two or more atoms. A base with delocalized electron is more stable than a similar base with localized electrons.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 2 Solutions
Essential Organic Chemistry (3rd Edition)
- this is an organic chemistry question please answer accordindly!! please post the solution draw the figures on a paper please hand drawn and post, please answer EACH part till the end and dont just provide wordy explanations, please draw them on a paper and post clearly!! answer the full question with all details EACH PART CLEARLY please thanks!! im reposting this please solve all parts and draw it not just word explanations!!arrow_forwardA mixture of 0.412 M C12, 0.544 M F2, and 0.843 M CIF is enclosed in a vessel and heated to 2500 K. C12(g) + F2(g )2CIF(g) Kc = 20.0 at 2500 K Calculate the equilibrium concentration of each gas at 2500 K. [C12] = M [F2] = M [ CIF] =arrow_forwardShow reaction mechanism with explanation. don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forward
- Don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardthis is an organic chemistry question please answer accordindly!! please post the solution draw the figures and post, answer the question in a very simple and straight forward manner thanks!!!!! please answer EACH part till the end and dont just provide wordy explanations wherever asked for structures or diagrams, please draw them on a paper and post clearly!! answer the full question with all details EACH PART CLEARLY please thanks!! im reposting this kindly solve all parts and draw it not just word explanations!!arrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
