
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The stereochemistry of the pyruvate reduction shown is to be stated. Whether NADH lose its pro-R or pro-S hydrogen is to be stated. Whether the addition of hydrogen occurs to the Si face or Re face of pyruvate is also to be stated.
Concept introduction:
When an achiral molecule such as
In addition a compound with a sp3 hybridized carbon also is said to be prochiral if by changing one of the attached groups it becomes a chiral centre. If the prochiral centre has two identical atoms, then that atom whose replacement leads to a R chirality centre is said to be pro R and that atom whose replacement leads to a S chirality centre is said to be pro S.
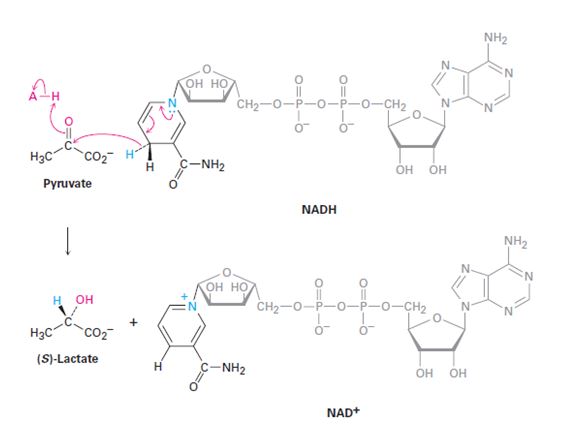
To show:
The stereochemistry of the pyruvate reduction to (s)-lactate shown and to state whether NADH lose its pro-R or pro-S hydrogen and whether the addition of hydrogen occurs to the Si face or Re face of pyruvate.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 19 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- 1. Problem Set 3b Chem 141 For each of the following compounds draw the BEST Lewis Structure then sketch the molecule (showing bond angles). Identify (i) electron group geometry (ii) shape around EACH central atom (iii) whether the molecule is polar or non-polar (iv) (a) SeF4 Best Lewis Structure e group arrangement:_ shape/molecular geometry: polarity: (b) AsOBr3 Best Lewis Structure e group arrangement:_ shape/molecular geometry: polarity: Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles):arrow_forward(c) SOCI Best Lewis Structure 2 e group arrangement: shape/molecular geometry:_ (d) PCls Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group geometry:_ shape/molecular geometry:_ (e) Ba(BrO2): Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group arrangement: shape/molecular geometry: polarity: Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles):arrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning


