
Concept explainers
Determine the kinetic energy of the 100-kg object.
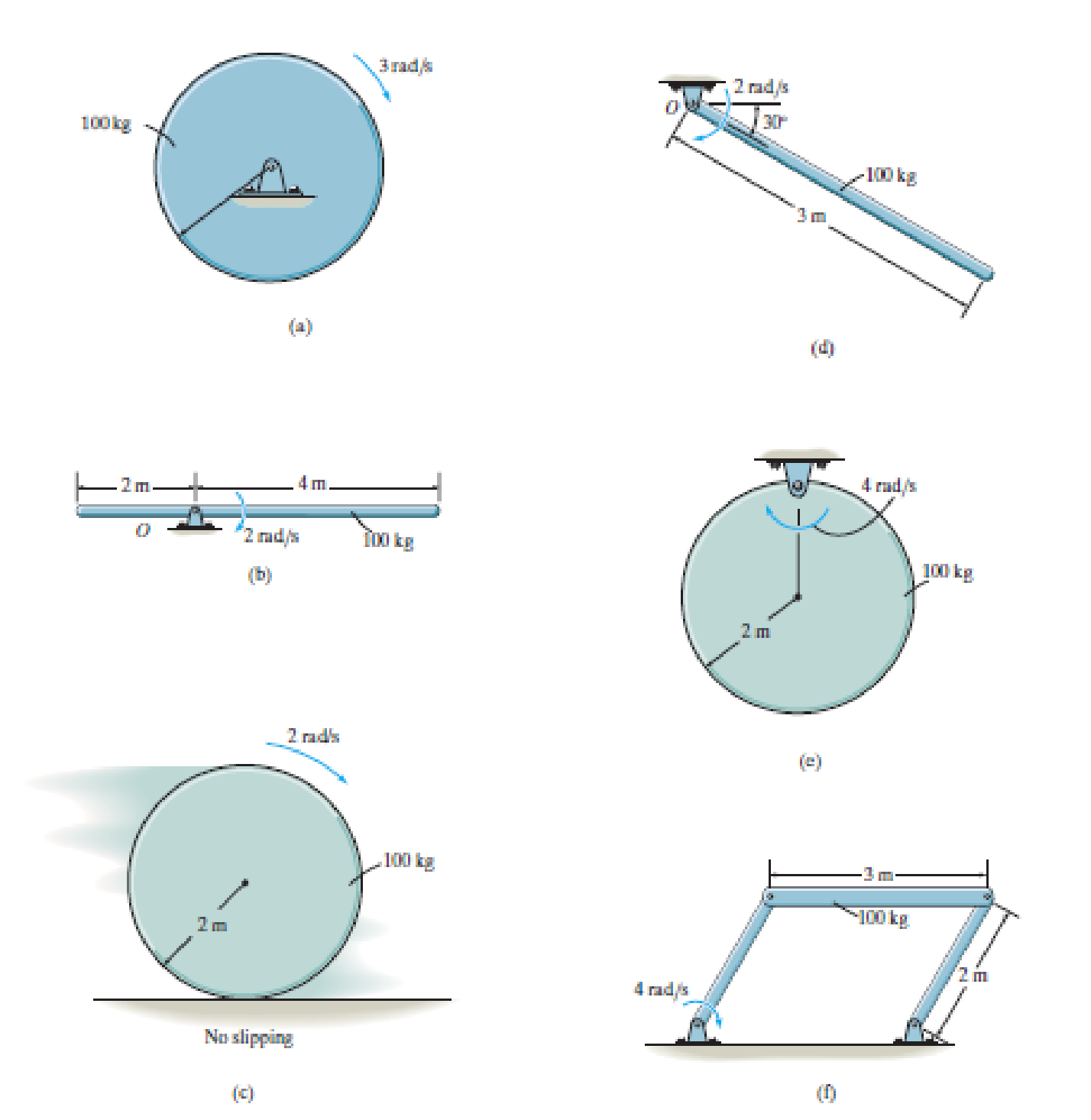
a)
The kinetic energy of the object:
Answer to Problem 1PP
The kinetic energy of the disk is 900 J.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The mass of disk is 100 kg.
The angular velocity of the disk is ω=3 rad/s.
The radius of the disk is 2 m.
Draw the free body diagram of the rod as shown in Figure (1a).
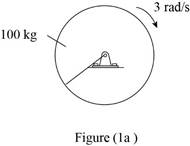
Refer Figure (1a).
Write the formula for mass moment of inertia (I) of the disk about it is center.
I=12mr2
Here, m is the mass and r is the radius of the disk.
Write the formula for kinetic energy (T)
(Rotation about fixed axis).
T=12Iω2
Substitute 12mr2 for I.
T=12(12mr2)ω (I)
Here, ω is the angular velocity.
Conclusion:
Calculate the kinetic energy of the disk.
Substitute 100 kg for m, 2 m for r and 3 rad/s for ω in Equation (I).
T=12[12(100 kg)(2 m)2](3 rad/s)2=12(200)(9)=900 J
Thus, the kinetic energy of the disk is 900 J.
b)
The kinetic energy of the object:
Answer to Problem 1PP
The kinetic energy of the disk is 800 J.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The mass of rod is 100 kg.
The angular velocity of the rod is ω=2 rad/s.
The length of the rod is 6 m.
Draw the free body diagram of the rod as shown in Figure (1b).
Refer Figure (1b).
Write the formula for mass moment of inertia (IO) of the rod about the point O.
IO=IG+mlOG2 (I)
Here, IG is the moment of inertial about the centroid G and IG=112ml2.
Substitute 112ml2 for IG in Equation (I).
IO=112ml2+mlOG2
Here, IO is the mass moment of inertia about point O, m is the mass, l is the total length of the rod and lOG, distance between the point O and G.
Write the formula for kinetic energy (T).
T=12IOω2
Substitute 112ml2+mlOG2 for IO.
T=12(112ml2+mlOG2)ω2 (I)
Here, ω is the angular velocity.
Conclusion:
Refer Figure (1b).
Calculate the kinetic energy of the rod.
Substitute 100 kg for m, 6 m for l, 1 m for lOG and 2 rad/s for ω in Equation (I).
T=12[112(100 kg)(6 m)2+(100 kg)(1 m)2](2 rad/s)2=12(400)(4)=800 J
Thus, the kinetic energy of the rod is 800 J.
c)
The kinetic energy of the object:
Answer to Problem 1PP
The kinetic energy of the disk is 1200 J.
Explanation of Solution
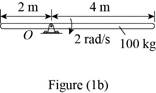
Given:
The mass of disk is 100 kg.
The angular velocity of the disk is ω=3 rad/s.
The radius of the disk is 2 m.
Draw the free body diagram of the disk as shown in Figure (1c).
Refer Figure (1c).
Write the formula for mass moment of inertia (I) of the disk about it is center.
I=12mr2
Here, m is the mass and r is the radius of the disk.
Write the formula for kinetic energy (T).
T=12mv2+12Iω2
Here, v=rω.
Substitute rω for v and 12mr2 for I.
T=12m(rω)2+12(12mr2)ω2 (I)
Here, m is the mass, r is radius, I is the mass moment of inertia and ω is the angular velocity.
Conclusion:
Refer Figure (1c).
Calculate the kinetic energy of the disk.
Substitute 100 kg for m, 2 m for r and 3 rad/s for ω in Equation (I).
T=[12(100 kg)(2 m×2 rad/s)2]+12[12(100 kg)(2 m)2](2 rad/s)2=800+400=1200 J
Thus, the kinetic energy of the disk is 1200 J.
d)
The kinetic energy of the object:
Answer to Problem 1PP
The kinetic energy of the rod is 600 J.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The mass of rod is 100 kg.
The angular velocity of the rod is ω=2 rad/s.
The length of the rod is 3 m.
Draw the free body diagram of the rod as shown in Figure (1d).
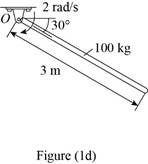
Refer Figure (1d).
Write the formula for mass moment of inertia (IO) of the rod having the rotation axis at one end.
IO=13ml2
Here, m is the mass and l is the length of the rod about mass center O.
Write the formula for kinetic energy (T)
(Rotation about fixed axis).
T=12IOω2
Substitute 13ml2 for IO.
T=12(13ml2)ω2 (I)
Here, IO is the mass moment of inertia and ω is the angular velocity.
Conclusion:
Refer Figure (1d).
Calculate the kinetic energy of the rod.
Substitute 100 kg for m, 3 m for l and 2 rad/s for ω in Equation (I).
T=12[13(100 kg)(3 m)2](2 rad/s)2=12(300)(4)=600 J
Thus, the kinetic energy of the rod is 600 J.
e)
The kinetic energy of the object:
Answer to Problem 1PP
The kinetic energy of the disk is 4800 J.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The mass of disk is 100 kg.
The angular velocity of the disk is ω=4 rad/s.
The radius of the disk is 2 m.
Draw the free body diagram of the disk as shown in Figure (1e).
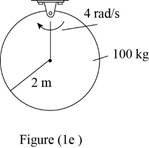
Refer Figure (1e).
Write the formula for mass moment of inertia (I) of the disk about it is center.
I=12mr2
Here, m is the mass and r is the radius of the disk.
Write the formula for kinetic energy (T).
T=12mv2+12Iω2
Here, v=rω.
Substitute rω for v and 12mr2 for I.
T=12m(rω)2+12(12mr2)ω2 (I)
Here, m is the mass, r is radius, I is the mass moment of inertia and ω is the angular velocity.
Conclusion:
Refer Figure (1e).
Calculate the kinetic energy of the disk.
Substitute 100 kg for m, 2 m for r and 4 rad/s for ω in Equation (I).
T=[12(100 kg)(2 m×4 rad/s)2]+12[12(100 kg)(2 m)2](4 rad/s)2=3200+1600=4800 J
Thus, the kinetic energy of the disk is 4800 J.
f)
The kinetic energy of the object:
Answer to Problem 1PP
The kinetic energy of the disk is 3200 J.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The mass of rod is 100 kg.
The angular velocity is ω=4 rad/s.
Draw the free body diagram of the object as shown in Figure (1f).
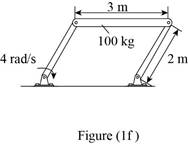
Refer Figure (1f).
Here, the ends of the rod are connected to two rods of same length. Hence the rod travels in circular motion.
Consider as the mass travels in a radius of r=2 m.
Write the formula for kinetic energy (T)
(Rotation about fixed axis).
T=12mv2
Here, v=rω.
Substitute rω for v.
T=12m(rω)2 (I)
Here, m is the mass, r is radius and ω is the angular velocity.
Conclusion:
Refer Figure (1f).
Here r=2 m.
Calculate the kinetic energy of the disk.
Substitute 100 kg for m, 2 m for r and 4 rad/s for ω in Equation (I).
T=12(100 kg)[(4 rad/s)(2 m)]2=50(64)=3200 J
Thus, the kinetic energy of the disk is 3200 J.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
ENGINEERING MECH DYNAMICS W/MASTREV
- Assis+ 2019-2018 Assi A. SALE تمارين السيطرة النوعية 1- سحبت عينة عشوائية يومياً تتكون من 50 دائرة كهربائية تستخدم لـ صناعة إحدى الأجهزة الأليكترونية ولمدة 20 يوماً ، وبعد فحصها كانت عدد الدوائر المعابة لكل يوم كالآتي : 43.2.6.3.1.3.2.9.3.5.3.2.5.2.2.1.3.2.1 أوجد حدي السيطرة النوعية لنسبة الوحدات المعابة (ans.0, 0.1533) 2- سحبت 10 عينات عشوائية من مصنع لتعبئة الأسماك البحرية وكل عينة تحتوي على كانت أوزانها ( باوند ( كالآتي : ب ، 1 71 X₁ X₂ 1.04 1.01 measurements X3 X4 X5 0.98 1.02 1.00 2 1.02 0.97 0.96 1.01 1.02 3 1.01 1.07 4 0.98 0.97 1.02 0.99 1.03 1.00 0.98 0,98 5 6 0.99 1.03 1.02 0.95 0.98 1.02 1.01 1.04 1.02 0.95 7 1.00 0.99 0.99 1.02 1.03 1.04 0.99 1.02 0.94 8 9 10 1.02 0.98 1.00 0.99 1.02 1.01 1.02 1.01 1.00 1.04 1.09 أوجد حدي السيطرة النوعية : أ) للوسط الحسابي و ب) للمدى (ans. a) 0.9679, 1.0429, b) 0, 0.137) 18 محاضرة السيطرة النوعية / الهندسة الصناعية - 4 ميكانيك / هندسة ج تكريت 3- كون مخطط سيطرة نوعية مناسب للعملية الإنتاجية المتمثلة بالبيانات التالية التي جمعت خلال شهر معين…arrow_forward42 VOLTE 4G+ EV Suggested Que... Problem: You and your team are tasked with designing an around-coil system for an air- conditioning unit that will be installed in a hospital. The system must provide a controlled environment for the hospital's air-conditioning needs, ensuring that fresh air is brought in while exhaust air is expelled, without allowing contamination between the two airflow directions. The air-conditioning system will include two coils and two pumps (one duty pump and one standby pump) in a configuration that accommodates both exhaust and supply airflows. The system needs to comply with ASHRAE Standards, and ASME BPVC Section VIII, with attention to safety, reliability, and efficiency. The system will be used in a climate with moderate temperature variations, and its design will need to consider a range of operating and design specifications. Given data Desired Pressure in the Pipe: According to the (ASHRAE) standard for pressure drop limits. Pipe Diameter: Must comply…arrow_forwardcompute the work done by a fuel-water interaction assuming that the 40,000 kg of mixed oxide fuel and 4000 kg of water expand independently and isentropically to 1 atmosphere. Assume that the initial fuel and water conditions are such that equilibrium mixture temperature achieved is 1945 K. Other water conditions are as follows: Tinitial = 400K, ro initial = 945 kg/m^3, cv = 4184 J/kg-K. Caution: Equation 6.9 is inappropriate for these conditions since the cooland at state e is supercritial.arrow_forward
- If the W12x50 beam below is made of steel having an allowable bending stress of 36 ksi and an allowable shear stress of 15 ksi, determine the maximum cable force, P, that can safely be supported by the beam.arrow_forwardThis is a tilt and rotation question. Here are notes attached for reference. I prefer handwritten solutions. ONLY UPLOAD A SOLUTION IF YOU ARE SURE ABOUT THE ANSWER PLEASE. I prefer handwritten solutions.(If you had once answered this question don't answer it as I am looking for a different solution)arrow_forward3- Find the optimum of y = 9x - 0.1x ^ 2 in the interval 0 <= x <= 100 and alpha = 0.05 Use two and three experiments sequential search methods?arrow_forward
- 1- A manufacturing company is optimizing the cooling time of a newly developed plastic molding process. The goal is to minimize the total production cost, which depends on the cooling time (t) in minutes. The production cost (C, in dollars) is given by: C=50+10(t)-0.5(t)^2 where: 5 st≤ 20 (cooling time in minutes) Using the Two-Experiments Sequential Method (up to five cycles) find the optimal cooling time (t) that minimizes the production cost. 3:29 مarrow_forward2- Find the optimum minimum point of y = x²-6x + 2 in the interval 0 ≤ x ≤ 10 using sequential search method with three experiments. the accuracy a = 0.06. 3- Find the optimum of y = 9x -0.1 x² in the interval 0 ≤ x ≤ 100, and α = 0.05 Use two and three experiments sequential search methods?arrow_forwardhand-written solutions only pleasearrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





