
Essential Organic Chemistry (3rd Edition)
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9780321937711
Author: Paula Yurkanis Bruice
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 18.3, Problem 3P
Which of the following amino acid side chains can aid the departure of a leaving group?
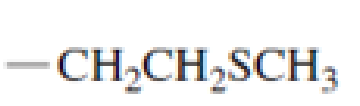
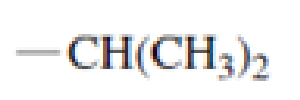
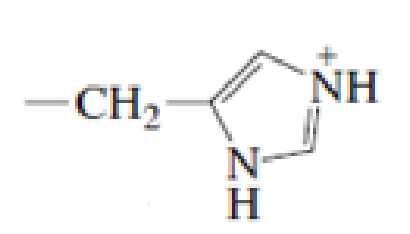
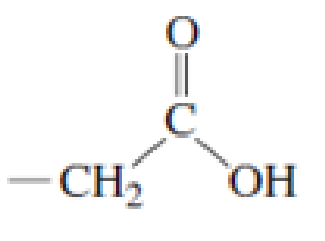
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
The hydrolysis of an ester can be sped up by both acidic and basic conditions. Aminolysis of an ester can be sped up by acidic conditions, but not by basic conditions. Explain why.
Chorismate mutase is an enzyme that promotes a pericyclic reaction by forcing the substrate to assume the conformation needed for the reaction. The product of the pericyclic reaction is prephenate that is subsequently converted into the amino acids phenylalanine and tyrosine. What kind of a pericyclic reaction does chorismate mutase catalyze?
Complete the given reaction
Chapter 18 Solutions
Essential Organic Chemistry (3rd Edition)
Ch. 18.1 - Prob. 1PCh. 18.2 - If H218O were used to hydrolyze lysozyme, which...Ch. 18.3 - Which of the following amino acid side chains can...Ch. 18.3 - Arginine and lysine side chains fit into trypsins...Ch. 18.4 - Which of the following amino acid side chains can...Ch. 18.4 - Prob. 6PCh. 18.5 - Prob. 7PCh. 18.5 - Draw the mechanism for the hydroxide-ion-catalyzed...Ch. 18.5 - What advantage does the enzyme gain by forming an...Ch. 18.7 - Prob. 10P
Ch. 18.7 - Prob. 11PCh. 18.8 - How many conjugated double bonds are there in a....Ch. 18.8 - Instead of adding to the 4a-position and...Ch. 18.8 - In succinate dehydrogenase, FAD is covalently...Ch. 18.8 - Prob. 15PCh. 18.9 - Acetolactate synthase is another TPP-requiring...Ch. 18.9 - Acetolactate synthase can also transfer the acyl...Ch. 18.9 - Prob. 18PCh. 18.9 - Prob. 19PCh. 18.10 - Prob. 21PCh. 18.11 - Prob. 23PCh. 18.11 - Which compound is more easily decarboxylated?Ch. 18.11 - Explain why the ability of PLP to catalyze an...Ch. 18.11 - Explain why the ability of PLP to catalyze an...Ch. 18.12 - What groups are interchanged in the following...Ch. 18.13 - Why is the coenzyme called tetrahydrofolate?Ch. 18.13 - What amino acid is formed by the following...Ch. 18.13 - How do the structures of tetrahydrofolate and...Ch. 18.13 - What is the source of the methyl group in...Ch. 18 - Prob. 32PCh. 18 - Prob. 33PCh. 18 - From what vitamins are the following coenzymes...Ch. 18 - Prob. 35PCh. 18 - For each of the following reaction, name both the...Ch. 18 - Explain why serine proteases do not catalyze...Ch. 18 - Prob. 38PCh. 18 - For each of the following enzyme catalyzed...Ch. 18 - Trisephosphate isomerase (TIM) catalyzes the...Ch. 18 - Prob. 41PCh. 18 - What acyl groups have we seen transferred by...Ch. 18 - When UMP is dissolved in T2O, exchange of T for H...Ch. 18 - Prob. 44PCh. 18 - When transaminated, the three branched-chain amino...Ch. 18 - Aldolase shows no activity if it is incubated with...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Separate the list P,F,V,,T,a,m,L,t, and V into intensive properties, extensive properties, and nonproperties.
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
To test your knowledge, discuss the following topics with a study partner or in writing ideally from memory. Th...
HUMAN ANATOMY
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. If Earth were twice as far as it actua...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Label each statement about the polynucleotide ATGGCG as true or false. The polynucleotide has six nucleotides. ...
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
Single penny tossed 20 times and counting heads and tails: Probability (prediction): _______/20 heads ________/...
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Give the IUPAC name for each compound.
Organic Chemistry
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Draw the electron pushing reaction mechanism for the hydrolysis of the artificial sweetener aspartame, a potential substrate of chymotrypsin, under acid, base and enzymatic conditions.arrow_forwardIdentify the organic functional group and reaction type for the following reaction. The reactant is a(n) - carboxylic acid hexose - Aldohexose - aldotetrose -deoxyhexose -carboxylic acid tetrose - ketohexose The product is a(n) - carboxylic acid tetrose - aldotetrose -alcohol hexose -aldohexose -carboxylic acid hexose - alcohol tetrose The reaction type is - hemiacetal formation -hydrolysis -oxidation( Benedict’s) -acetal formation -reduction( hydrogenation) - mutarotationarrow_forwardExplain why the rate of aminolysis of an ester cannot be increased by H+, HO-, or RO-.arrow_forward
- Triosephosphate isomerase (TIM) catalyzes the conversion of dihydroxyacetone phosphate to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. The enzyme’s catalytic groups are Glu 165 and His 95. In the first step of the reaction, these catalytic groups function as a general-base and a general-acid catalyst, respectively. Propose a mechanism for the reaction.arrow_forwardChorismate mutase is an enzyme that promotes a pericyclic reaction by forcing the substrate to assume the conformation needed for the reaction. The product of the pericyclic reaction is prephenate that is subsequently converted into the amino acids phenylalanine and tyrosine. What kind of a pericyclic reaction does chorismate mutase catalyze?arrow_forwardProvide an electron pushing mechanism for the conversion shown below. Abbreviate the enzyme catalyst active site groups (BH* and B:) as needed. Which purine base is used? NH₂ Enz H₂O 'N NHarrow_forward
- Several compounds have been found to inhibit -lactamase, and drugs based on these compounds can be taken in combination with penicillins and cephalosporins to restore their effectiveness when resistance is known to be a problem. The commonly prescribed formulation called Augmentin is a combination of the -lactamase inhibitor shown below with amoxicillin (shown above). It is used to treat childhood ear infections when resistance is suspected, and many kids know it as the white liquid that tastes like bananas. Which of the statements below are true statements? 1. The stereochemistry of the fusion between the four-and five-membered rings in the inhibitor and amoxicillin are different. 2. The inhibitor possesses enol ether and allylic alcohol functional groups while the antibiotic possesses a phenol and a secondary amide functional group. 3. Neither the inhibitor nor the antibiotic contains strained rings. 4. Both 1 and 2 are true.arrow_forwardEsterase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of esters. It hydrolyzes esters of L-amino acids more rapidly than esters of d-amino acids. How can this enzyme be used to separate a racemic mixture of amino acids?arrow_forwardThe reaction of an ester with an amine is not as slow as the reaction of an ester with water or an alcohol. Explain with reason. Explain why the rate of aminolysis of an ester cannot be increased by H+, OH- or OR-. How can you activate the carboxylic acid? Is acid catalyzed hydrolysis of acetamide a reversible or an irreversible reaction. Explain.arrow_forward
- Serine esterase contains a catalytic triad at its active site. Which amino acid in serine esterase is responsible for mediating general acid catalysis for the breakdown of tetrahedral intermediate to the carboxyl product? Explain.arrow_forwardImidazoleglycerol‑phosphate dehydratase is an enzyme in the histine biosynthesis pathway. It catalyzes the E1 dehydration of D‑erthyro‑imidazole‑glycerol phosphate to imidazole acetol‑phosphate. This is a rare example of a biological E1 reaction, as most biological elimination reactions occur through E1cB instead. In this reaction, D‑erthyro‑imidazole‑glycerol phosphate is first protonated to form a good leaving group. Then, the leaving group is ejected to form the resonance‑stabilized carbocation shown. Draw curved arrows forming the most stable resonance structure to explain why this reaction goes through an E1 mechanism. Draw curved arrows to form the most stable resonance structure.arrow_forwardWhat is the structure of (2S,3S)-2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid and (2R,3S)-2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285869759
Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Biomolecules - Protein - Amino acids; Author: Tutorials Point (India) Ltd.;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ySNVPDHJ0ek;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY