
Concept explainers
The largest value of β in the ensuing motion.
Answer to Problem 18.141P
The largest value of βmax in the ensuing motion is 27.5°_.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The position of the sphere β is zero.
The rate of precession ˙ϕ0=√17g/11a.
Calculation:
Conservation of angular momentum about the Z and z axes:
The only external forces are acting in homogenous sphere is weight of the sphere and reaction at A. Hence, the angular momentum is conserved about the Z and z axes.
Choose the principal axes Axyz with taking y horizontal and pointing into the paper.
Write the expression for the angular velocity ω.
ω=−˙ϕcosβi+˙βj+(˙ψ−˙ϕsinβ)k
The principal moment of inertia are Ix=Iy=m(25a2+(2a)2) and Iz=25ma2.
Draw the Free body diagram of homogeneous sphere and the forces acting on it as in Figure (1).
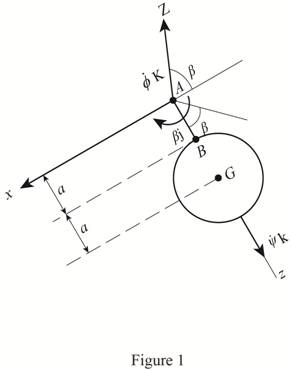
Write the expression for the angular momentum about point A.
HA=Ixωxi+Iyωyj+Izωzk
Substitute m(25a2+(2a)2) for Ix, −˙ϕcosβ for ωx, m(25a2+(2a)2) for Iy, ˙β for ωy, , 25ma2 for Iz, and (˙ψ−˙ϕsinβ) for ωz.
HA=m(25a2+(2a)2)(−˙ϕcosβ)i+m(25a2+(2a)2)˙βj+25ma2(˙ψ−˙ϕsinβ)k=−225ma2˙ϕcosβi+225ma2˙βj+25ma2(˙ψ−˙ϕsinβ)k
Consider Hz=constant or HA⋅K=constant.
The scalar value of i⋅K=−cosβ, j⋅K=0, and k⋅K=−sinβ.
Determine the conservation of angular momentum about fixed Z axis HA⋅K.
HA⋅K=constant
Substitute −225ma2˙ϕcosβi+225ma2βj+25ma2(˙ψ−˙ϕsinβ)k for HA, −cosβ for (i⋅K), 0 for (j⋅K), and −cosβ for (k⋅K).
{−225ma2˙ϕcosβ(i⋅K)+225ma2˙β(j⋅K)+25ma2(˙ψ−˙ϕsinβ)(k⋅K)}=constant{−225ma2˙ϕcosβ(−cosβ)+225ma2˙β(0)+25ma2(˙ψ−˙ϕsinβ)(−sinβ)}=constant{−225ma2˙ϕcosβ(−cosβ)+25ma2(˙ψ−˙ϕsinβ)(−sinβ)}=constant (1)
Substitute ˙ϕ0 for ˙ϕ, 0 for ˙ψ, and 0 for β in Equation (1).
{−225ma2˙ϕ0cos0(−cos0)+25ma2(0−˙ϕ0sin0)(−sin0)}=constantconstant=225ma2˙ϕ0
Substitute 225ma2˙ϕ0 for constant in Equation (1).
−225ma2˙ϕcosβ(−cosβ)+25ma2(˙ψ−˙ϕsinβ)(−sinβ)=225ma2˙ϕ025ma2[11˙ϕcos2β−(˙ψ−˙ϕsinβ)sinβ]=25×11˙ϕ011˙ϕcos2β−(˙ψ−˙ϕsinβ)sinβ=11˙ϕ0 (2)
Determine the constant value using the angular momentum along z–axis.
Hz=constantIzωz=constant
Substitute 25ma2 for Iz and (˙ψ−˙ϕsinβ) for ωz.
25ma2(˙ψ−˙ϕsinβ)=constant (3).
Substitute ˙ϕ0 for ˙ϕ, 0 for ˙ψ, and 0 for β in Equation (3).
25ma2(0−˙ϕ0sin(0))=constantconstant=0
Substitute 0 for constant in Equation (3).
25ma2(˙ψ−˙ϕsinβ)=0˙ψ−˙ϕsinβ=0
Substitute 0 for (˙ψ−˙ϕsinβ) in Equation (2).
11˙ϕcos2β−(˙ψ−˙ϕsinβ)sinβ=11˙ϕ011˙ϕcos2β−0(sinβ)=11˙ϕ0˙ϕ=11˙ϕ011cos2β˙ϕ=˙ϕ0sec2β
Conservation of energy:
Determine the value of kinetic energy T.
T=12(Ixω2x+Iyω2y+Izω2z)
Substitute m(25a2+(2a)2) for Ix, −˙ϕcosβ for ωx, m(25a2+(2a)2) for Iy, ˙β for ωy, , 25ma2 for Iz, and (˙ψ−˙ϕsinβ) for ωz.
T={12(m(25a2+(2a)2)(−˙ϕcosβ)2+m(25a2+(2a)2)(˙β)2+25ma2(˙ψ−˙ϕsinβ)2)}=12(225ma2˙ϕ2cos2β+225ma2(˙β)2+25ma2(˙ψ−˙ϕsinβ)2)
Select the datum at β=0.
Determine the value of conservation of energy using the relation.
T+V=constant
Here, E is the constant and V is the potential energy.
Substitute 12(225ma2˙ϕ2cos2β+225ma2(β)2+25ma2(˙ψ−˙ϕsinβ)2) for T and −2mgasinβ for V.
{12(225ma2˙ϕ2cos2β+225ma2(˙β)2+25ma2(˙ψ−˙ϕsinβ)2)−2mgasinβ}=constant (4)
Substitute ˙ϕ0 for ˙ϕ, 0 for β, 0 for ˙β, and 0 for ˙ψ in Equation (4).
{12(225ma2˙ϕ20cos20+225ma2(0)2+25ma2(0−˙ϕ0sin0)2)−2mgasin0}=constantconstant=115ma2˙ϕ20
Substitute 115ma2˙ϕ20 for constant in Equation (4).
{12(225ma2˙ϕ2cos2β+225ma2(˙β)2+25ma2(˙ψ−˙ϕsinβ)2)−2mgasinβ}=115ma2˙ϕ2012×25ma2((11˙ϕ2cos2β+11(˙β)2+(˙ψ−˙ϕsinβ)2)−10gasinβ)=115ma2˙ϕ20((11˙ϕ2cos2β+11(˙β)2+(˙ψ−˙ϕsinβ)2)−10gasinβ)=11˙ϕ20 (5)
Consider ˙β=0 for the maximum value of β.
Substitute ˙ϕ0sec2β for ˙ϕ, 0 for (˙ψ−˙ϕsinβ), and 0 for ˙β in Equation (5).
11(˙ϕ0sec2β)2cos2β+11(0)2−10gasinβ=11˙ϕ2011˙ϕ20sec4β×1sec2β−10gasinβ=11˙ϕ2011˙ϕ20sec2β−11˙ϕ20=10gasinβ11˙ϕ20(1−cos2βcos2β)=10gasinβ
˙ϕ20(sin2βcos2β)=1011gasinβ˙ϕ20=1011gasinβ×cos2βsin2β˙ϕ20=1011gacos2βsinβ (6)
Substitute √17g/11a for ˙ϕ0 in Equation (6).
(√17g/11a)2=1011gacos2βsinβ17g11a=1011ga(1−sin2β)sinβ17sinβ=10−10sin2β10sin2β+17sinβ−10=0 (7)
Solve the Equation (7).
The value of sinβ is 0.462 and –2.162.
Determine the largest value of βmax using the relation.
sinβmax=0.462βmax=sin−1(0.462)βmax=27.5°
Therefore, the largest value of βmax in the ensuing motion is 27.5°_.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
- A 40-cm-diameter, 127-cm-high cylindrical hot water tank is located in the bathroom of a house maintained at 20°C. The surface temperature of the tank is measured to be 44°C and its emissivity is 0.4. Taking the surrounding surface temperature to be also 20°C, determine the rate of heat loss from all surfaces of the tank by natural convection and radiation. The properties of air at 32°C are k=0.02603 W/m-K, v=1.627 x 10-5 m²/s, Pr = 0.7276, and ẞ = 0.003279 K-1 The rate of heat loss from all surfaces of the tank by natural convection is The rate of heat loss from all surfaces of the tank by radiation is W. W.arrow_forwardA 2.5-m-long thin vertical plate is subjected to uniform heat flux on one side, while the other side is exposed to cool air at 5°C. The plate surface has an emissivity of 0.73, and its midpoint temperature is 55°C. Determine the heat flux subjected on the plate surface. Uniform heat flux -Plate, € = 0.73 Cool air 5°C 7 TSUIT Given: The properties of water at Tf,c= 30°C. k=0.02588 W/m.K, v=1.608 x 10-5 m²/s Pr = 0.7282 The heat flux subjected on the plate surface is W/m²arrow_forwardHot water is flowing at an average velocity of 5.82 ft/s through a cast iron pipe (k=30 Btu/h-ft-°F) whose inner and outer diameters are 1.0 in and 1.2 in, respectively. The pipe passes through a 50-ft-long section of a basement whose temperature is 60°F. The emissivity of the outer surface of the pipe is 0.5, and the walls of the basement are also at about 60°F. If the inlet temperature of the water is 150°F and the heat transfer coefficient on the inner surface of the pipe is 30 Btu/h-ft².°F, determine the temperature drop of water as it passes through the basement. Evaluate air properties at a film temperature of 105°C and 1 atm pressure. The properties of air at 1 atm and the film temperature of (Ts+ T∞)/2 = (150+60)/2 = 105°F are k=0.01541 Btu/h-ft-°F. v=0.1838 × 10-3 ft2/s, Pr = 0.7253, and ẞ = 0.00177R-1arrow_forward
- hand-written solutions only, please. correct answers upvoted!arrow_forwardhand-written solutions only, please. correct answers upvoted!arrow_forward! Required information Consider a flat-plate solar collector placed horizontally on the flat roof of a house. The collector is 1.3 m wide and 2.8 m long, and the average temperature of the exposed surface of the collector is 42°C. The properties of air at 1 atm and the film temperature are k=0.02551 W/m-°C, v = 1.562 × 10-5 m²/s, Pr = 0.7286, and ẞ= 0.003356 K-1 Determine the rate of heat loss from the collector by natural convection during a calm day when the ambient air temperature is 8°C. The rate of heat loss from the collector by natural convection is W.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





