
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
The acoustical system shown in Figure P14.38 is driven by a speaker emitting sound of frequency 756 Hz. (a) If constructive interference occurs at a particular instant, by what minimum amount should the path length in the upper U-shaped tube be increased so that destructive interference occurs instead? (b) What minimum increase in the original length of the upper tube will again result in constructive interference?
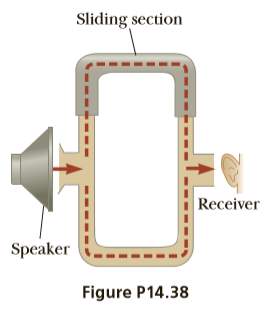
Transcribed Image Text:Sliding section
Receiver
Speaker
Figure P14.38
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- During ultrasound examination of a patient with spherocytosis, it was noted that 1 MHz signal after reflection from erythrocyte is determined by the detector as having a frequency 400 Hz higher. Find the rate of movement of erythrocyte. The speed of sound in blood is 1500 m/s.arrow_forwardAn enclosed chamber with sound-absorbing walls in Chamberlin Hall has a 2.0m x 1.0m opening for an outside window. A loudspeaker is located outdoors, 87 m away, and facing the window. The intensity level of the sound entering the window space from the loudspeaker is 79 db. Assume the acoustic output of the loudspeaker is uniform in all directions and that the acoustic energy incident upon the ground is completely absorbed and therefore is not reflected into the window. The threshold of hearing is 1.0 x 10 -12 W/m2. What is the acoustic power entering through the window spacearrow_forwardTwo speakers emit sound waves of different frequencies as shown in the figure: Speaker A has a power of 1.00 mW and Speaker B has a power of 1.50 mW. A 4.00 mi В 3.00 m 2.00 m (2.6 when speaker B is turned on at point c, how many dB ls the sound level at point C ,arrow_forward
- A sound wave enters the thin tube at P and exits at Q. Assume r = 0.41m and the wavelength is 1.86m. What is the smallest length d that results in destructive interference at Q?arrow_forwardcan i get help with this physics question, soundsarrow_forwardSound with a 29 cm wavelength travels rightward from a source and through a tube that consists of a straight portion and a half-circle. Part of the soundwave travels through the circle and rejoins the the rest of the wave which goes directly through the straight portion. This rejoining results in interference. What is the smallest radius r (in cm) that results in an intensity minimum at the detector. The maximum destructive interference will occur when the difference in the distance travelled by the two waves is 1/2 of a wavelength. To solve this problem express the difference in the distance travelled by the two waves as a function of r and set this amount equal to 1/2 of a wavelength.arrow_forward
- In the figure, two loudspeakers, separated by a distance of d1 = 2.87 m, are in phase. Assume the amplitudes of the sound from the speakers are approximately the same at the position of a listener, who is d2 = 4.20 m directly in front of one of the speakers. Consider the audible range for normal hearing, 20 Hz to 20 kHz. (a) What is the lowest frequency that gives the minimum signal (destructive interference) at the listener's ear? (b) What is the lowest frequency that gives the maximum signal (constructive interference) at the listener's ear? (Take the speed of sound to be 343 m/s.) di Speakers Listener dg- (a) Number i Units (b) Number i Units >arrow_forwardAn interface is formed between a block of aluminium (with an acoustic impedance of 1.8 x 107 kg m2 s') and a block of copper (with an acoustic impedance of 4.6 x 107 kg m-2 s-1). Longitudinal sound waves travelling through the aluminium are normally incident on the boundary, and are partially reflected. a) What is the ratio of the amplitude of the reflected wave to that of the incident wave? Number b) What is the ratio of the amplitude of the transmitted wave to that of the incident wave? Number c) What percentage of the incident power is transmitted? Number d) What percentage of the incident power is reflected? Number % Ouit P Sove Questiarrow_forwardTwo sinusoidal waves travel in the same direction with the same amplitude A = 1 m, same wavelength >=0.25m, and speed v = 2 m/s.If the phase difference between the two waves is =π/3, then the resultant interference wave function is expressed as: y_res (x,t)=1.73sin (0.5mx-16nt+n/6) y_res (x,t)=0.86sin(8nx-16nt+n/6) Oy_re's (x,t)=0.86sin(0.5mx-16nt+n/6) Oy_res (x,t)=1.73sin(8nx-16nt+n/6)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON