
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
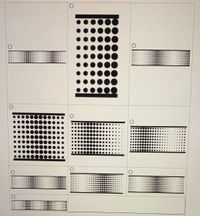
Consider standing waves in a pipe of length L = 7.5 m containing a column of air. The speed of sound in the columns is vs = 334 m/s. Each of the standing wave images provided may represent a case for which one or both ends are open.
Part (A) Select the image from the options provided showing the gas pressure for the third harmonic of a pipe with two open ends.
Part (B) Calculate the wavelength λ3 in m for the third harmonic in the pipe with two open ends.
Part (C) Calculate the frequency f1 in Hz for the fundamental harmonic in the pipe with two open ends.
Part (D) Select the image from the options provided showing the gas pressure for the third mode of a pipe with one open end and one closed end. (the third mode is the third possible excitation).
Part (E) Calculate the frequency f1 in Hz for the fundamental harmonic in the pipe with one open and one closed end.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The density of aluminum is 2700 kg/m3. If transverse waves propagate at 34 in a 7 mm diameter aluminum wire, what is the tension on the wire in Newtons? Give your numerical answer as a whole number please.arrow_forwardLoudness (L), in decibles (dB), of a sound of intensity I is defined to be L=10log( I/I0), where I0=10-12(W/M2) (watts per meter square) is the minimum intensity detectable by the human ear. A.) Find the loudness L, in decibles (dB), of a trombone given the intensity is 1010I0 B.) Find the intensity of a rock concert whose loudness is 115 decibles. C.) What is the NIOSH recommended Exposure Limit (REL) given in dB based on exposures at work 5 days per week?arrow_forwardThe linear mass density of a copper, 36.0cm long cable is 0.00750kg/m.The wire is fastened at each end. The speed of sound in air is 344m/s. The wavelength ofa standing wave that is set up in the wire is 14.4cm. The wire’s tension is 254.8N. a) Which harmonic is present in the standing wave? b) ) What is the velocity of the wave in the wire? c) ) What is the frequency of the wave? d) ) How far from the wire’s end is the first anti-node?arrow_forward
- A pipe has a length of 0.891 m and is open at both ends. Take the speed of sound to be v = 343 m/s. a) Calculate the two lowest harmonics of the pipe (in Hz). (Enter your answers from smallest to largest.) b) Calculate the two lowest harmonics (in Hz) after one end of the pipe is closed. (Enter your answers from smallest to largest.)arrow_forwardA sound wave enters the thin tube at P and exits at Q. Assume r = 0.41m and the wavelength is 1.86m. What is the smallest length d that results in destructive interference at Q?arrow_forwardThe density of aluminum is 2700 kg/m3. If transverse waves propagate at 34 in a 4 mm diameter aluminum wire, what is the tension on the wire in Newtons? Give your numerical answer as a whole number please.arrow_forward
- Question in attachmentsarrow_forwardAn interface is formed between a block of aluminium (with an acoustic impedance of 1.8 x 107 kg m2 s') and a block of copper (with an acoustic impedance of 4.6 x 107 kg m-2 s-1). Longitudinal sound waves travelling through the aluminium are normally incident on the boundary, and are partially reflected. a) What is the ratio of the amplitude of the reflected wave to that of the incident wave? Number b) What is the ratio of the amplitude of the transmitted wave to that of the incident wave? Number c) What percentage of the incident power is transmitted? Number d) What percentage of the incident power is reflected? Number % Ouit P Sove Questiarrow_forwardConsider standing waves in a pipe of length L = 3.5 m containing a column of air. The speed of sound in the columns is vs = 334 m/s. Each of the standing wave images provided may represent a case for which one or both ends are open. Select the image from the options provided showing the displacement of air particles for the third harmonic of a pipe with two open ends. Calculate the wavelength λ3 in m for the third harmonic in the pipe with two open ends. Calculate the frequency f1 in Hz for the fundamental harmonic in the pipe with two open ends.arrow_forward
- A row of seats is parallel to a stage at a distance of 8.4 m from it. At the center and front of the stage is a diffraction horn loudspeaker. This speaker sends out its sound through an opening that is like a small doorway with a width D of 0.074 m. The speaker is playing a tone that has a frequency of 2.00 104 Hz. The speed of sound is 343 m/s. What is the distance between two seats, located near the center of the row, at which the tone cannot be heard?arrow_forwardTwo loudspeakers emit sound waves of the same frequency along the x-axis. The amplitude of each wave is a. The sound intensity is minimum where speaker 2 is 10cm behind speaker 1. The intensity increases as speaker 2 is moved forward and first reaches minimum, with amplitude 2a, when it is 30cm in front of speaker 1. a. what is the wavelength of the soundarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON