
(a)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism of a given reaction under strongly acidic condition is to be drawn and major organic product is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
When an
Answer to Problem 18.58P
The complete, detailed mechanism of a given reaction in the acidic medium is shown below and ketone is a major product.
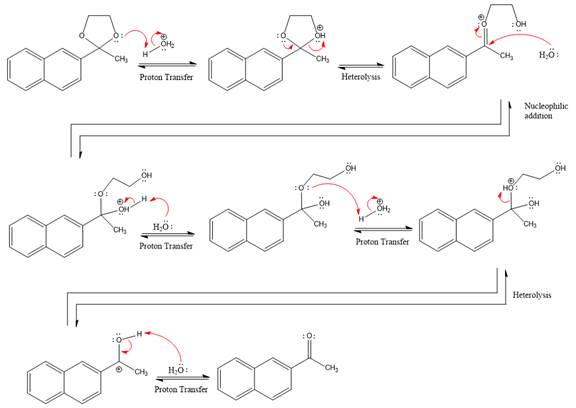
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
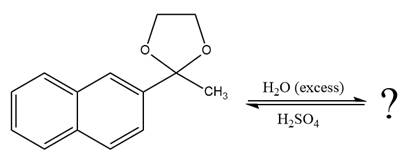
This is an acetal hydrolysis reaction under strongly acidic conditions to produce ketone as a major product. The leaving group is an uncharged alcohol and water acts as the nucleophile.
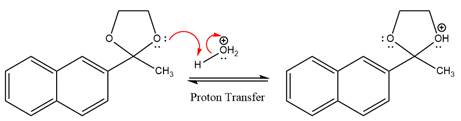
In the first step, the lone pairs on the O atom abstract the proton from water, which makes positively charged O ion.
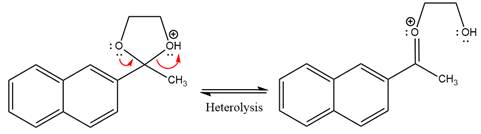
In the next step, the bond between positively charged O and C breaks and forms a new double bond in another
Next, nucleophile water attacks on the electropositive carbon atom in the nucleophilic addition reaction.
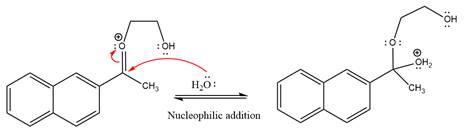
In the deprotonation step, water abstracts the H atom and produces a hemiacetal group.
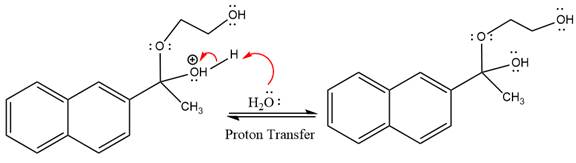
The lone pairs on
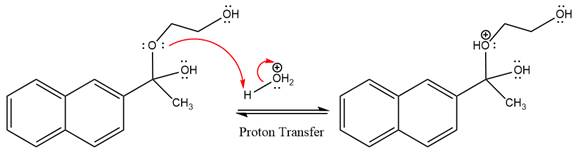
The diol leaving group departs and forms resonance stabilized carbocation.
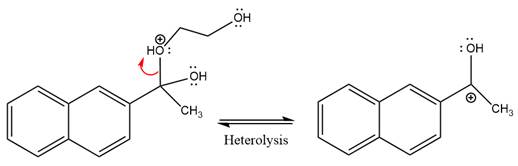
Water nucleophile abstracts the proton from the
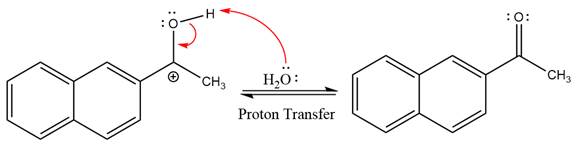
The complete, detailed mechanism of a given reaction in the acidic medium is shown below and ketone is a major product.
The complete, detailed mechanism of the given reaction under acidic medium and excess water is drawn.
(b)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism of a given reaction under stongly acidic condition is to be drawn and major organic product is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
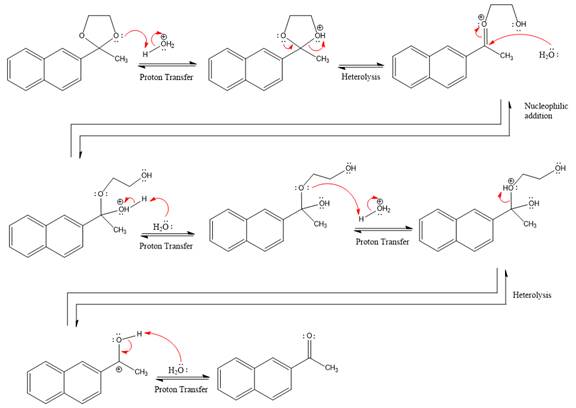
When an aldehyde or ketone is treated with an alcohol under acidic conditions, the hemiacetal product is formed. By using an excess amount of alcohol under acidic conditions, after that nucleophilic addition produces hemiacetal, which further forms an acetal. The acetal has two alkoxy groups are bonded to the same carbon. The formation of the acetal product is favored by using excess alcohol. In the hydrolysis of acetal reaction, because of the addition of water results in the breaking of
The hydrolysis reaction of acetal produces ketone as a major product.
Answer to Problem 18.58P
The complete, detailed mechanism of a given reaction in the acidic medium is shown below and ketone is a major product.
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
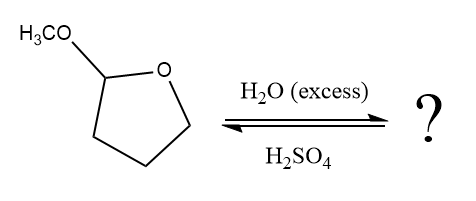
This is an acetal hydrolysis reaction under strongly acidic condition, not strong bases should appear to produce ketone as a major product. The leaving group is an uncharged alcohol, and water acts as the nucleophile.
In the first step, the lone pairs on the O atom abstract the proton from water, which makes positively charged O ion.
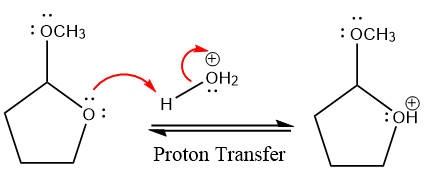
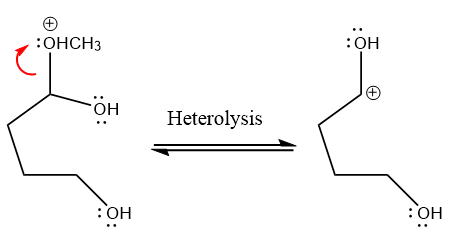
In the next step, the bond between positively charged O and C breaks and forms a new double bond in another
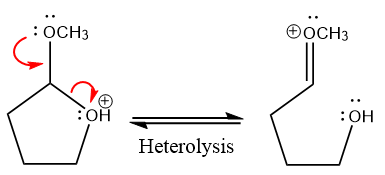
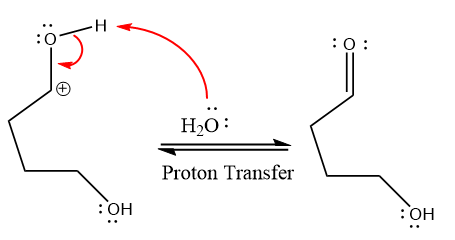
Next, nucleophile water attacks the electropositive carbon atom in the nucleophilic addition reaction.
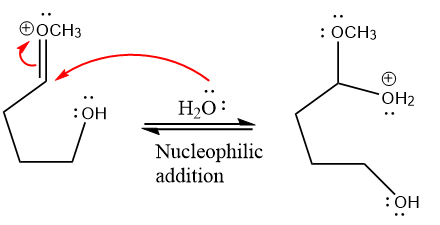
In the deprotonation step, water abstracts the H atom and produces a hemiacetal group.
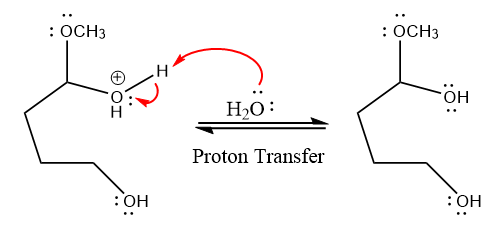
The lone pairs on
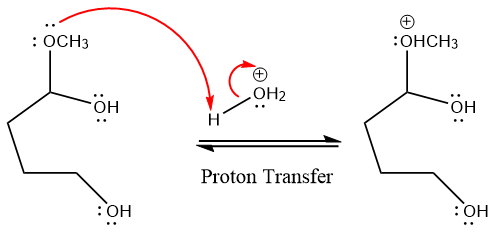
The methanol leaving group departs and form resonance stabilized carbocation.
water nucleophile abstracts the proton from the amino group and makes ketone as a product.
The complete, detailed mechanism of a given reaction under acidic medium is shown below and a ketone is a major product.

The complete, detailed mechanism of given reaction under acidic medium and excess water is drawn.
(c)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism of a given reaction under strongly acidic condition is to be drawn and major organic product is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
In the hydrolysis of nitriles reaction, addition of water results in the breaking of
Answer to Problem 18.58P
The complete, detailed mechanism of a given reaction in the acidic medium is shown below and amide is a major product.
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
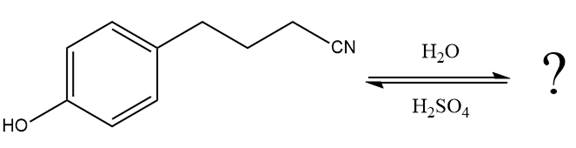
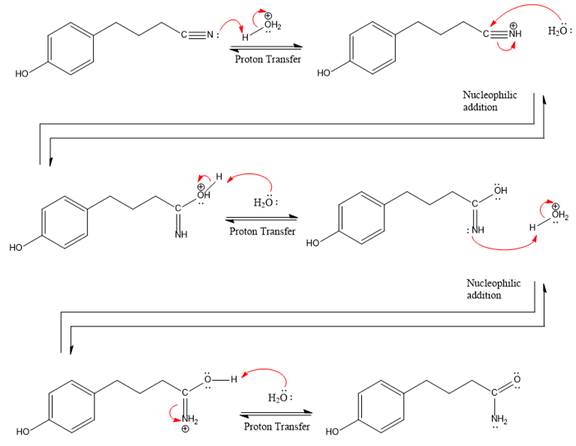
This is a nitrile hydrolysis reaction under the strongly acidic condition to produce an amide as a major product. The nitrile group is protonated first and water act as the nucleophile.
In the first step, the lone pairs on the N atom abstract the proton from water, which makes positively charged N ion.
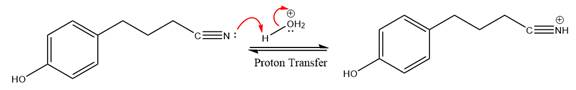
Next, nucleophile water attacks on the electropositive carbon atom in the nucleophilic addition reaction.
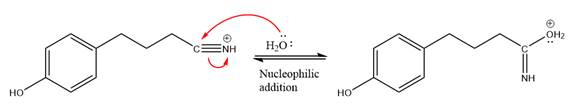
In the deprotonation step, water abstracts the H atom in the protonation step.
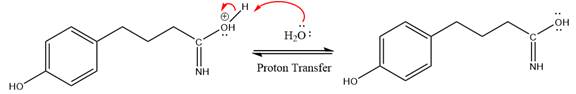
The lone pairs on N atom accept the proton in the protonation step by generating an amino group.
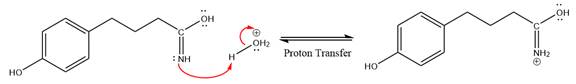
The nucleophile water abstracts the proton in the resonance stabilized carbocation and produces amide as a major product.
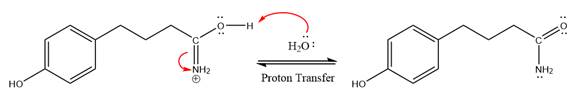
The complete, detailed mechanism of a given reaction under the strongly acidic medium is shown below and an amide is a major product.
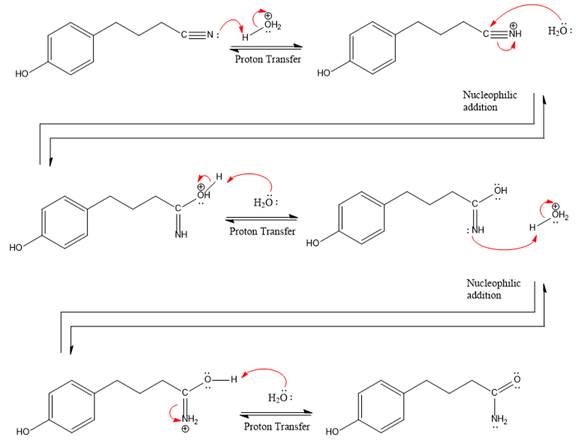
The complete, detailed mechanism of given reaction under acidic medium and excess water is drawn.
(d)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism of a given reaction under stongly acidic condition is to be drawn and major organic product is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
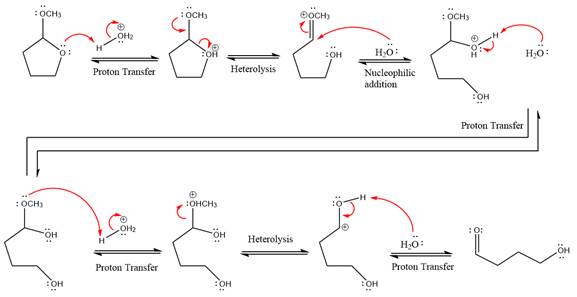
When an aldehyde or ketone is treated with an alcohol under acidic conditions, the hemiacetal product is formed. By using an excess amount of alcohol under acidic conditions the hemiacetals, nucleophilic addition produces hemiacetal, which further form an acetal. The acetal has two alkoxy groups are bonded to the same carbon. The formation of the acetal product is favored by using excess alcohol. In the hydrolysis of acetal reaction, addition of water results in the breaking of
Answer to Problem 18.58P
The complete, detailed mechanism of a given reaction in the acidic medium is shown below and ketone is a major product.
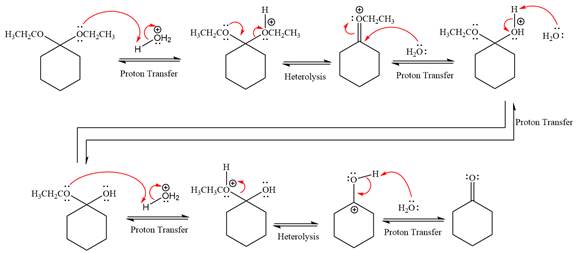
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
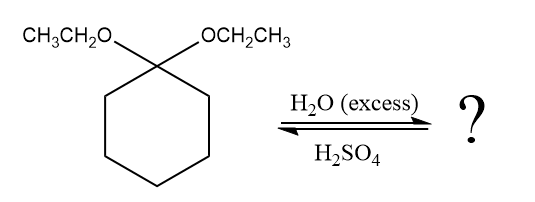
This is an acetal hydrolysis reaction under strongly acidic condition, not strong bases should appear to produce ketone as a major product. The leaving group is an uncharged alcohol and water acts as the nucleophile.
In the first step, the lone pairs on the O atom abstract the proton from water, which makes positively charged O ion as a good leaving group.
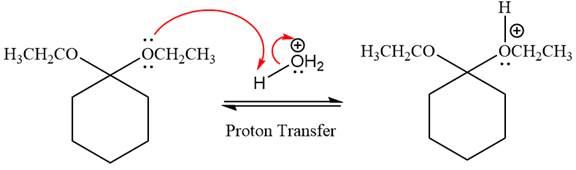
In the next step, the ethanol good leaving group departs and forms a new double bond in another
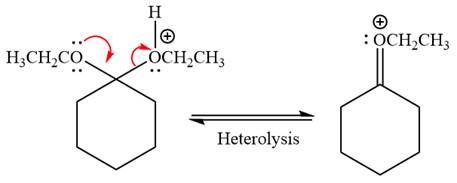
Next, nucleophile water attacks on the electropositive carbon atom in the nucleophilic addition reaction.
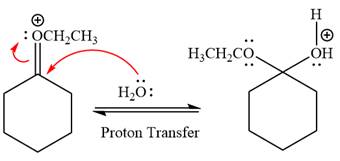
In the deprotonation step, water abstracts the H atom and produces a hemiacetal group.
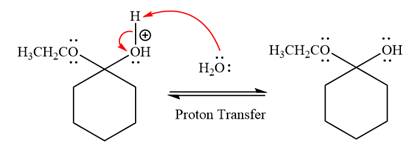
The lone pairs on
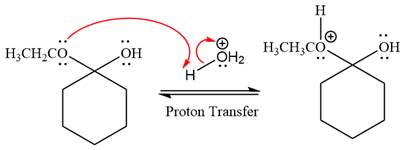
In the next step, the ethanol good leaving group departs and forms resonance stabilized carbocation.
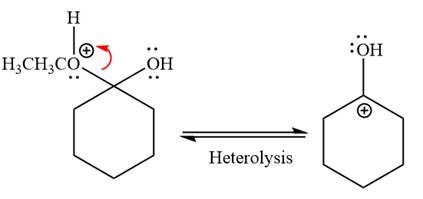
Water nucleophile abstracts the proton from the carbon ring and forms ketone as a product.
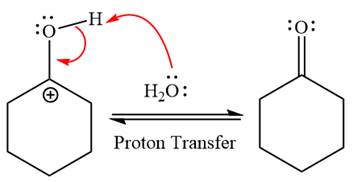
The complete, detailed mechanism of a given reaction in the acidic medium is shown below and ketone is a major product.
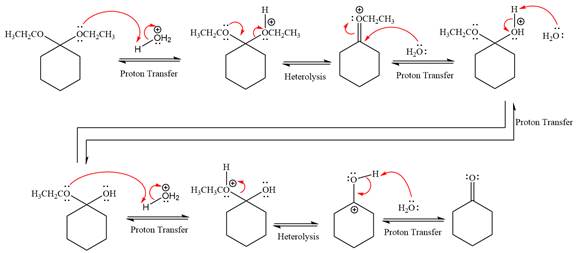
The complete, detailed mechanism of given reaction under acidic medium and excess water is drawn.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles And Mechanisms
- Indicate the correct option.a) Graphite conducts electricity, being an isotropic materialb) Graphite is not a conductor of electricityc) Both are falsearrow_forward(f) SO: Best Lewis Structure 3 e group geometry:_ shape/molecular geometry:, (g) CF2CF2 Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group arrangement:_ shape/molecular geometry: (h) (NH4)2SO4 Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group arrangement: shape/molecular geometry: polarity: Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles):arrow_forward1. Problem Set 3b Chem 141 For each of the following compounds draw the BEST Lewis Structure then sketch the molecule (showing bond angles). Identify (i) electron group geometry (ii) shape around EACH central atom (iii) whether the molecule is polar or non-polar (iv) (a) SeF4 Best Lewis Structure e group arrangement:_ shape/molecular geometry: polarity: (b) AsOBr3 Best Lewis Structure e group arrangement:_ shape/molecular geometry: polarity: Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles):arrow_forward
- (c) SOCI Best Lewis Structure 2 e group arrangement: shape/molecular geometry:_ (d) PCls Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group geometry:_ shape/molecular geometry:_ (e) Ba(BrO2): Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group arrangement: shape/molecular geometry: polarity: Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles):arrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- reaction scheme for C39H4202 Hydrogenation of Alkyne (Alkyne to Alkene) show reaction (drawing) pleasearrow_forwardGive detailed mechanism Solution with explanation needed. Don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forwardShow work with explanation needed....don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





