
Concept explainers
Draw the products of each reaction.
a. 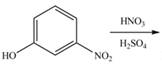 d.
d. 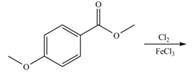
b.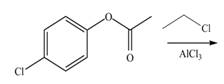 e.
e. 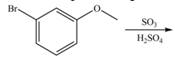
c. 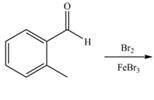 f.
f. 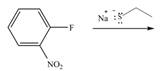
(a)
Interpretation: The products of given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron deficient chemical species that contains positive charge are known as electrophile. In electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, electrophile takes the position of hydrogen atom by attacking the electron rich carbon atom of benzene.
Answer to Problem 18.38P
The products of given reaction are shown below:
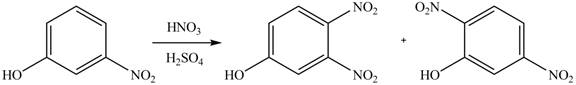
Explanation of Solution
An aromatic compound undergoes nitration on reaction with
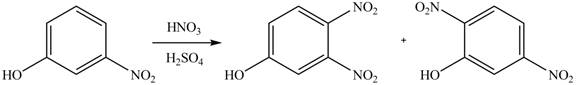
Figure 1
The products of given reaction are shown in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation: The products of given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron deficient chemical species that contains positive charge are known as electrophile. In electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, electrophile takes the position of hydrogen atom by attacking the electron rich carbon atom of benzene.
Answer to Problem 18.38P
The products of given reaction are shown below:
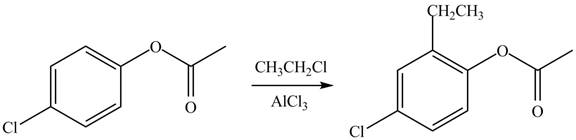
Explanation of Solution
An aromatic compound undergoes Friedel-Craft alkylation on reaction with
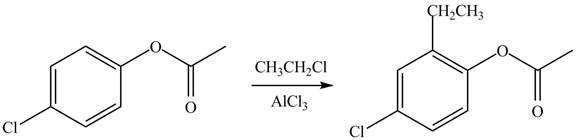
Figure 2
The products of given reaction are shown in Figure 2.
(c)
Interpretation: The products of given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron deficient chemical species that contains positive charge are known as electrophile. In electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, electrophile takes the position of hydrogen atom by attacking the electron rich carbon atom of benzene.
Answer to Problem 18.38P
The products of given reaction are shown below:
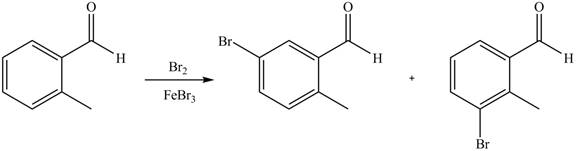
Explanation of Solution
An aromatic compound undergoes bromination on reaction with
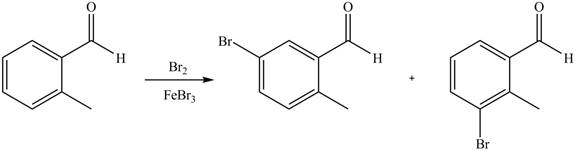
Figure 3
The products of given reaction are shown in Figure 3.
(d)
Interpretation: The products of given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron deficient chemical species that contains positive charge are known as electrophile. In electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, electrophile takes the position of hydrogen atom by attacking the electron rich carbon atom of benzene.
Answer to Problem 18.38P
The products of given reaction are shown below:
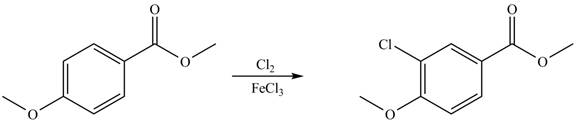
Explanation of Solution
An aromatic compound undergoes chlorination on reaction with
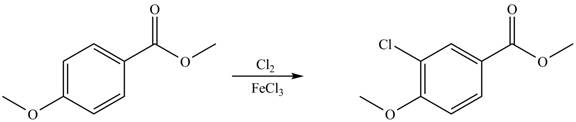
Figure 4
The products of given reaction are shown in Figure 4.
(e)
Interpretation: The products of given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron deficient chemical species that contains positive charge are known as electrophile. In electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, electrophile takes the position of hydrogen atom by attacking the electron rich carbon atom of benzene.
Answer to Problem 18.38P
The products of given reaction are shown below:
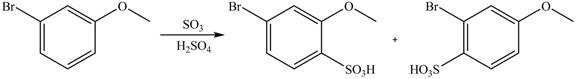
Explanation of Solution
An aromatic compound undergoes sulfonation on reaction with
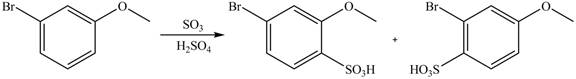
Figure 5
The products of given reaction are shown in Figure 5.
(f)
Interpretation: The products of given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron deficient chemical species that contains positive charge are known as electrophile. In electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, electrophile takes the position of hydrogen atom by attacking the electron rich carbon atom of benzene.
Answer to Problem 18.38P
The products of given reaction are shown below:
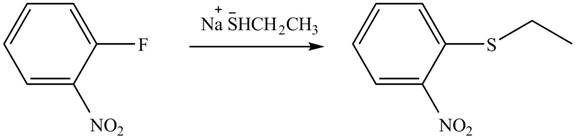
Explanation of Solution
In the given reaction,
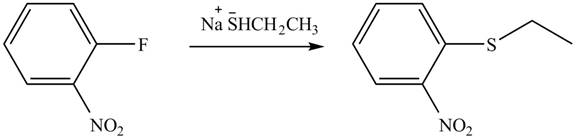
Figure 6
The products of given reaction are shown in Figure 6.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Synthesize each compound from acetylene. You may use any other organic or inorganic reagents.arrow_forwardDraw the structure of a dihalide that could be used to prepare each alkyne. There may be more than one possible dihalide.arrow_forwardLabel the electrophilic and nucleophilic sites in each molecule.arrow_forward
- Draw the organic products formed when each alkyne is treated with two equivalents of HBr.arrow_forwardWhat alkyne yields each ketone as the only product both with acid-catalyzed hydration and after hydroboration–oxidation?arrow_forwardUsing ethynylcyclohexane as a starting material and any other needed reagents, how can the following compounds be synthesized?arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning


