
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9780321879721
Author: Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 17, Problem 13CQ
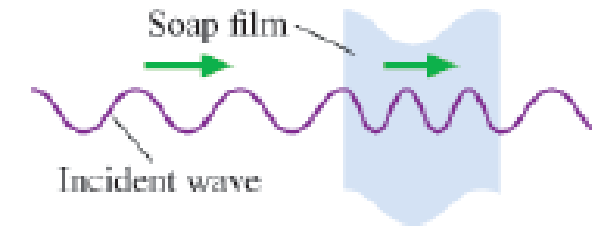
Figure Q17.13 shows a light wave incident on and passing through a thin soap film. Reflections from the front and back surfaces of the film create smaller waves (not shown in the figure) that travel to the left of the film, where they interfere. Is the interference constructive, destructive, or something in between? Explain.
Figure Q17.13
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
No chatgpt pls will upvote
a cubic foot of argon at 20 degrees celsius is isentropically compressed from 1 atm to 425 KPa. What is the new temperature and density?
Calculate the variance of the calculated accelerations. The free fall height was 1753 mm. The measured release and catch times were:
222.22 800.00
61.11 641.67
0.00 588.89
11.11 588.89
8.33 588.89
11.11 588.89
5.56 586.11
2.78 583.33
Give in the answer window the calculated repeated experiment variance in m/s2.
Chapter 17 Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Ch. 17 - The frequency of a light wave in air is 5.3 1014...Ch. 17 - Rank in order the following according to their...Ch. 17 - The wavelength of a light wave is 700 nm in air;...Ch. 17 - A double-slit interference experiment shows...Ch. 17 - Figure Q17.5 shows the fringes observed in a...Ch. 17 - In a double-slit interference experiment,...Ch. 17 - Figure Q17.7 shows the viewing screen in a...Ch. 17 - Figure Q17.7 is the interference pattern seen on a...Ch. 17 - Figure Q17.9 shows the light intensity on a...Ch. 17 - Figure Q17.10 shows the light intensity on a...
Ch. 17 - Light with a wavelength of 600 nm is incident on a...Ch. 17 - White light is incident on a diffraction grating....Ch. 17 - Figure Q17.13 shows a light wave incident on and...Ch. 17 - A soap bubble usually pops because some part of it...Ch. 17 - An oil film on top of water has one patch that is...Ch. 17 - Should the antireflection coating of a microscope...Ch. 17 - Example 17.5 showed that a thin film whose...Ch. 17 - Prob. 18CQCh. 17 - Prob. 19MCQCh. 17 - The frequency of a light wave in air is 4.6 1014...Ch. 17 - Light passes through a diffraction grating with a...Ch. 17 - Blue light of wavelength 450 nm passes through a...Ch. 17 - Yellow light of wavelength 590 nm passes through a...Ch. 17 - Light passes through a 10-m-wide slit and is...Ch. 17 - Prob. 25MCQCh. 17 - You want to estimate the diameter of a very small...Ch. 17 - Prob. 1PCh. 17 - a. How long (in ns) does it take light to travel...Ch. 17 - A 5.0-cm-thick layer of oil (n = 1.46) is...Ch. 17 - A light wave has a 670 nm wavelength in air. Its...Ch. 17 - How much time does it take a pulse of light to...Ch. 17 - A helium-neon laser beam has a wavelength in air...Ch. 17 - Two narrow slits 50 m apart are illuminated with...Ch. 17 - Light from a sodium lamp (= 589 nm) illuminates...Ch. 17 - Two narrow slits are illuminated by light of...Ch. 17 - A double-slit experiment is performed with light...Ch. 17 - Light from a helium-neon laser (= 633 nm) is used...Ch. 17 - Two narrow slits are 0.12 mm apart. Light of...Ch. 17 - In a double-slit experiment, the distance from one...Ch. 17 - A diffraction grating with 750 slits/mm is...Ch. 17 - A 1.0-cm-wide diffraction grating has 1000 slits....Ch. 17 - Light of wavelength 600 nm illuminates a...Ch. 17 - A lab technician uses laser light with a...Ch. 17 - The human eye can readily detect wavelengths from...Ch. 17 - A diffraction grating with 600 lines/mm is...Ch. 17 - A 500 line/mm diffraction grating is illuminated...Ch. 17 - What is the thinnest film of MgF2 (n = 1.38) on...Ch. 17 - A very thin oil film (n = 1.25) floats on water (n...Ch. 17 - A film with n = 1.60 is deposited on glass. What...Ch. 17 - Antireflection coatings can be used on the inner...Ch. 17 - Solar cells are given antireflection coatings to...Ch. 17 - A thin film of MgF2 (n = 1.38) coats a piece of...Ch. 17 - Looking straight downward into a rain puddle whose...Ch. 17 - A helium-neon laser (= 633 nm) illuminates a...Ch. 17 - For a demonstration, a professor uses a razor...Ch. 17 - A 0.50-mm-wide slit is illuminated by light of...Ch. 17 - The second minimum in the diffraction pattern of a...Ch. 17 - What is the width of a slit for which the first...Ch. 17 - A 0.50-mm-diameter hole is illuminated by light of...Ch. 17 - Light from a helium-neon laser (= 633 nm) passes...Ch. 17 - You want to photograph a circular diffraction...Ch. 17 - Infrared light of wavelength 2.5 m illuminates a...Ch. 17 - An advanced computer sends information to its...Ch. 17 - Figure P17.38 shows the light intensity on a...Ch. 17 - Figure P17.38 shows the light intensity on a...Ch. 17 - Your friend has been given a laser for her...Ch. 17 - A double slit is illuminated simultaneously with...Ch. 17 - Figure P17.42 shows the light intensity on a...Ch. 17 - A laser beam of wavelength 670 nm shines through a...Ch. 17 - The two most prominent wavelengths in the light...Ch. 17 - A diffraction grating produces a first-order...Ch. 17 - A diffraction grating is illuminated...Ch. 17 - White light (400-700 nm) is incident on a 600...Ch. 17 - A miniature spectrometer used for chemical...Ch. 17 - Figure P17.49 shows the interference pattern on a...Ch. 17 - Figure P17.4919 shows the interference pattern on...Ch. 17 - Because sound is a wave, it is possible to make a...Ch. 17 - The shiny surface of a CD is imprinted with...Ch. 17 - If sunlight shines straight onto a peacock...Ch. 17 - The wings of some beetles have closely spaced...Ch. 17 - A diffraction grating having 500 lines/mm...Ch. 17 - Light emitted by element X passes through a...Ch. 17 - Light of a single wavelength is incident on a...Ch. 17 - A sheet of glass is coated with a 500-nm-thick...Ch. 17 - A soap bubble is essentially a thin film of water...Ch. 17 - A laboratory dish, 20 cm in diameter, is half...Ch. 17 - You need to use your cell phone, which broadcasts...Ch. 17 - Light from a sodium lamp ( = 589 nm) illuminates a...Ch. 17 - The opening to a cave is a tall, 30-cm-wide crack....Ch. 17 - A diffraction grating has 500 slits/mm. What is...Ch. 17 - Figure P17.65 shows the light intensity on a...Ch. 17 - Figure P17.65 shows the light intensity on a...Ch. 17 - Figure P17.67 shows the light intensity on a...Ch. 17 - One day, after pulling down your window shade, you...Ch. 17 - Prob. 70GPCh. 17 - A helium-neon laser ( = 633 nm), shown in Figure...Ch. 17 - In the laser range-finding experiments of Example...Ch. 17 - Prob. 73MSPPCh. 17 - Prob. 74MSPPCh. 17 - Prob. 75MSPP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- How can i solve this if n1 (refractive index of gas) and n2 (refractive index of plastic) is not known. And the brewsters angle isn't knownarrow_forward2. Consider the situation described in problem 1 where light emerges horizontally from ground level. Take k = 0.0020 m' and no = 1.0001 and find at which horizontal distance, x, the ray reaches a height of y = 1.5 m.arrow_forward2-3. Consider the situation of the reflection of a pulse at the interface of two string described in the previous problem. In addition to the net disturbances being equal at the junction, the slope of the net disturbances must also be equal at the junction at all times. Given that p1 = 4.0 g/m, H2 = 9.0 g/m and Aj = 0.50 cm find 2. A, (Answer: -0.10 cm) and 3. Ay. (Answer: 0.40 cm)please I need to show all work step by step problems 2 and 3arrow_forward
- look at answer show all work step by steparrow_forwardLook at the answer and please show all work step by steparrow_forward3. As a woman, who's eyes are h = 1.5 m above the ground, looks down the road sees a tree with height H = 9.0 m. Below the tree is what appears to be a reflection of the tree. The observation of this apparent reflection gives the illusion of water on the roadway. This effect is commonly called a mirage. Use the results of questions 1 and 2 and the principle of ray reversibility to analyze the diagram below. Assume that light leaving the top of the tree bends toward the horizontal until it just grazes ground level. After that, the ray bends upward eventually reaching the woman's eyes. The woman interprets this incoming light as if it came from an image of the tree. Determine the size, H', of the image. (Answer 8.8 m) please show all work step by steparrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:9781938168185
Author:William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Laws of Refraction of Light | Don't Memorise; Author: Don't Memorise;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4l2thi5_84o;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY