
a)
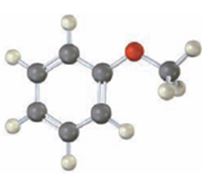
Interpretation:
Draw the products obtained when the compound shown (methoxybenzene) reacts with (i) Br2, FeBr3 and (2) CH3COCl, AlCl3.
Concept introduction:
Aromatic rings can be brominated using Br2 in the presence of FeBr3. The electrophile is Br+. Friedal-Crafts acylation reaction occurs when an
To draw:
The products obtained when the compound shown (methoxybenzene) reacts with (i) Br2, FeBr3 and (2) CH3COCl, AlCl3.
Answer to Problem 24VC
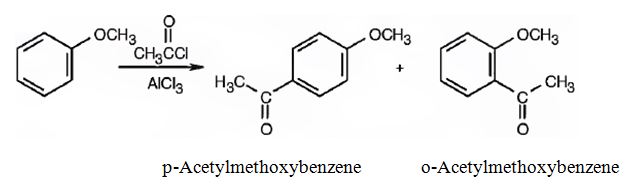
(i) The products obtained when the compound shown (methoxybenzene) reacts with Br2/FeBr3 are p-bromomethoxybenzene and o-bromomethoxybenzene.
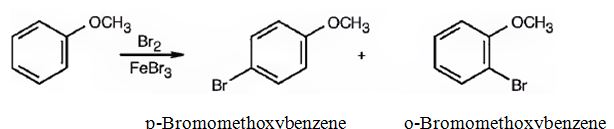
(ii) The products obtained when the compound shown (methoxybenzene) reacts with CH3COCl/AlCl3 are p-acetylmethoxybenzene and o-acetylmethoxybenzene.
Explanation of Solution
The methoxy group attached to the benzene ring is an ortho & para directing group. When methoxybenzene is brominated and alkylated it directs the incoming electrophiles, Br+ and CH3CO+ to ortho & para positions.
(i) The products obtained when the compound shown (methoxybenzene) reacts with Br2/FeBr3 are p-bromomethoxybenzene and o-bromomethoxybenzene.

(ii) The products obtained when the compound shown (methoxybenzene) reacts with CH3COCl/AlCl3 are p-acetylmethoxybenzene and o-acetylmethoxybenzene.

b)
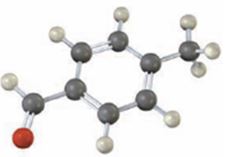
Interpretation:
Draw the structures of the products obtained when the compound shown, p-methylbenzaldehyde reacts with (i) Br2, FeBr3 and (2) CH3COCl, AlCl3.
Concept introduction:
Electrophilic substitution of disubstituted benzenes follows three simple rules. (i) If the directing influence of both the substituents reinforce each other, a single product results. (ii) If the directing influences of both the substituent groups oppose each other, the most powerful activating group among them has the dominant influence but usually a mixture of products results. (iii) In meta disubstituted compounds, further substitution in between the groups occurs only rarely, due to steric reasons.
To show:
The major product(s) produced when p-methylbenzaldehyde reacts with (i) Br2, FeBr3 and (2) CH3COCl, AlCl3.
Answer to Problem 24VC
(i) The major product produced when p-methylbenzaldehyde reacts with Br2/FeBr3 is 3-bromo-4-methylbenzaldehyde.
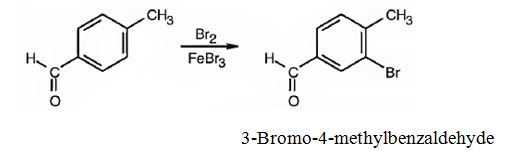
(ii) The major product produced when p-methylbenzaldehyde reacts with CH3COCl/AlCl3 is 3-acetyl-4-methylbenzaldehyde.
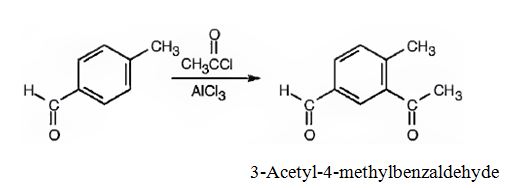
Explanation of Solution
The
(i) The major product produced when p-methylbenzaldehyde reacts with Br2/FeBr3 is 3-bromo-4-methylbenzaldehyde.

(ii)The major product produced when p-methylbenzaldehyde reacts with CH3COCl/AlCl3 is 3-acetyl-4-methylbenzaldehyde.

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- What reaction presented in this chapter is occurring in the following equation? Explain the resulting stereochemistry of the reaction.arrow_forwardGiven that an E2 reaction proceeds with anti periplanar stereochemistry, draw the products of each elimination. The alkyl halides in (a) and (b) are diastereomers of each other. How are the products of these two reactions related? Recall from Section 3.2A that C6H5 −is a phenyl group, a benzene ring bonded to another group.arrow_forwardaddition of hbr to a double bond with an ether (-or) substituent occurs regiospecifically to give a product in which the Br OR are bonded to the same carbon. Draw the two possible carbocation intermediates in this electrophilic addition reaction,and explain using resonance why the observed product is formed.arrow_forward
- Rank the reactivity of the following compounds according to the SN2 reaction? Please explain why a) Methyl chloride b) Methyl iodide c) isopropyl chloridearrow_forwardRank these alkyl halides in order of increasing reactivity in an SN2 reactionarrow_forwardIllsutrate the Energy diagram for carbocation formation in two different SN1 reactions ?arrow_forward
- Consider the following reaction. Draw the product (s) and if more than one product is formed determine which one is the major one. Discuss your reasons! DMSOarrow_forwardRank A, B, and C in order of increasing SN1 reactivity.arrow_forwardTaking into account anti periplanar geometry, predict the major E2 product formed from each starting material.arrow_forward
- Which of the products will react the fastest given an SN2 reaction ?arrow_forwardDraw the major products obtained from the reaction of one equivalent of HBr with the following compounds. For each reaction, indicate the kinetic product and the thermodynamic productarrow_forwardWhich compound would undergo carbocation rearrangement during an SN1 reaction? A B C Darrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

