
Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780133915389
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 16.5, Problem 9FP
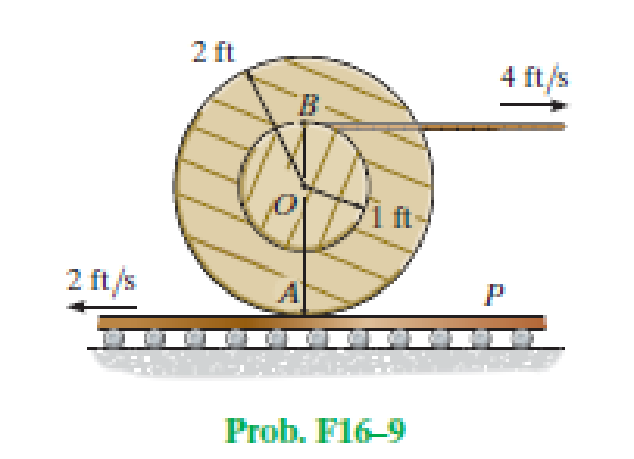
The cable wraps around the inner core, and the spool does not slip on the platform P.
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule03:31
Students have asked these similar questions
Hi! Can you help me in getting the expression for the torque t required to maintain equilibrium in the first gear? Thank you!
3. Find the Foroe required to lift the 15 slug cylinder.
Draw 3 Free Body Diagrams.
15 slug
F
The hand brake for a bicycle is shown. Portions DE and FG are free to rotate on bolt A which is screwed into the frame BC of the bicycle. The brake is actuated by a shielded cable where T1 is applied to point E and T2 is applied to point G. A spring having 40 N compressive force is placed between points E and G so that the brake stays open when it is not being used. Assume the change in the spring's force is negligible when the brake is actuated to produce the F = 100 N forces at points D and F. Determine the necessary cable forces T1 in N.
Chapter 16 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics (14th Edition)
Ch. 16.3 - Determine its constant angular acceleration and...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the angular acceleration when it has...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the time it takes to achieve an angular...Ch. 16.3 - If the angular displacement of the wheel is =...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the magnitude of the velocity and...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the velocity of the cylinder and the...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the magnitudes of the velocity and...Ch. 16.3 - If the disk is originally rotating at 0 = 12...Ch. 16.3 - It it is subjected to a constant angular...Ch. 16.3 - If it is subjected to a constant angular...
Ch. 16.3 - Determine the number of revolutions, the angular...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the number of revolutions it must...Ch. 16.3 - Also, find the number of revolutions of gear D to...Ch. 16.3 - Gears A, B, C, and D have radii of 15 mm, 50 mm,...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the magnitude of acceleration of point B...Ch. 16.3 - pulley A is given a constant angular acceleration...Ch. 16.3 - Starting from rest, determine the angular...Ch. 16.3 - If the engine turns pulley A at A = (20t + 40)...Ch. 16.3 - If the engine turns pulley A at A = 60 rad/s,...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the angular velocity of the disk and its...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the magnitudes of the normal and...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the magnitudes of the normal and...Ch. 16.3 - If this gear is initially turning at A = 15 rad/s,...Ch. 16.3 - If this gear is initially turning at A = 15 rad/s,...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the brushs angular velocity when t = 4...Ch. 16.3 - If this gear is initially turning at (A)0 = 20...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the magnitudes of the velocity and the n...Ch. 16.3 - If the motor turns gear A with an angular...Ch. 16.3 - If the motor turns gear A with an angular...Ch. 16.3 - and the meshed pinion gear B on the propeller...Ch. 16.3 - determine the magnitude of the velocity and...Ch. 16.3 - If the gears A and have the dimensions shown,...Ch. 16.3 - and the meshed pinion gear B on the propeller...Ch. 16.3 - and the meshed pinion gear B on the propeller...Ch. 16.3 - If the canisters are centered 200 mm apart on the...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the largest angular velocity of gear B...Ch. 16.3 - The shaft of the motor M turns with an angular...Ch. 16.3 - If A has a constant angular acceleration of A = 30...Ch. 16.3 - If the angular displacement of A it A = (5t3 +...Ch. 16.3 - This gear is connected to gear B, which is fixed...Ch. 16.3 - Express the result in Cartesian vector form.Ch. 16.3 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of point D...Ch. 16.3 - At the instant shown it is rotating about the y...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the magnitudes of the velocity and...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the angular velocity and angular...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the angular acceleration and angular...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the angular acceleration and angular...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the angular velocity and angular...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the angular velocity of the connecting...Ch. 16.4 - The cam rotates with a constant counterclockwise...Ch. 16.4 - The pin connection at O does not cause an...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the velocity of the follower rod AB as...Ch. 16.4 - The pin connection at O does not cause an...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of the peg...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of block...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the angular velocity and angular...Ch. 16.4 - If the slotted arm is causing A to move downward...Ch. 16.4 - If the wedge moves to the left with a constant...Ch. 16.4 - If the rollers do not slip, determine their...Ch. 16.4 - If no slipping occurs between the disk D and the...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of...Ch. 16.5 - If roller A moves to the right with a constant...Ch. 16.5 - Determine the magnitude of the velocity of point B...Ch. 16.5 - The cable wraps around the inner core, and the...Ch. 16.5 - If crank OA rotates with an angular velocity of =...Ch. 16.5 - If rod AB slides along the horizontal slot with a...Ch. 16.5 - Determine the velocity of the peg at B at this...Ch. 16.5 - Determine the velocity of point B at this instant.Ch. 16.5 - If the block at C is moving downward at 4 ft/s,...Ch. 16.5 - Determine the velocity of block C and the angular...Ch. 16.5 - Determine the angular velocities of links A B and...Ch. 16.5 - Also, sketch the position of link BC when = 55,...Ch. 16.5 - Link BC rotates clockwise with an angular velocity...Ch. 16.5 - If the angular velocity of link AB is AB = 3...Ch. 16.5 - Determine the velocity of the gear rack C.Ch. 16.5 - If B is moving to the right at 8 ft/s and C is...Ch. 16.5 - Determine the angular velocity of the gear and the...Ch. 16.5 - Determine the velocity of point A on the rim of...Ch. 16.5 - Link CB is horizontal at this instant.Ch. 16.5 - Determine the velocity of the slider C at the...Ch. 16.5 - Determine the velocity of block C and the angular...Ch. 16.5 - If AB has an angular velocity AB = 8 rad/s,...Ch. 16.5 - If the slider block A is moving downward at vA = 4...Ch. 16.5 - If the slider block A is moving downward at A = 4...Ch. 16.5 - This gear has an inner hub C which is fixed to B...Ch. 16.5 - If link AB is rotating at AB =3 rad/s, determine...Ch. 16.5 - If link CD is rotating at CD = 5 rad/s, determine...Ch. 16.5 - By locking or releasing certain gears, it has the...Ch. 16.5 - If the ring gear A rotates clockwise with an...Ch. 16.5 - It consists of a driving piston A, three links,...Ch. 16.5 - Because of the rotational motion of lint AB and...Ch. 16.6 - Establish the location of the instantaneous center...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the angular velocity of the rod and the...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the angular velocity of link BC and...Ch. 16.6 - The gear rack B is fixed.Ch. 16.6 - If cable AB is unwound with a speed of 3 m/s, and...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the angular velocity of link BC and the...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the angular velocity of links BC and CD...Ch. 16.6 - Assume the geometry is known.Ch. 16.6 - Determine the angular velocity of link AB at the...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the angular velocity of the link CB at...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the velocities of the cylinders center C...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the velocities of points A and B on the...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the velocities of points A and B.Ch. 16.6 - If rod CD is rotating with an angular velocity CD...Ch. 16.6 - If bar AB has an angular velocity AB = 6 rad/s,...Ch. 16.6 - Under these conditions, what is the speed at A if...Ch. 16.6 - Due to slipping, points A and B on the rim of the...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the velocities of the center point C and...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the velocity of point D and the angular...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the velocity of point P, and the angular...Ch. 16.6 - If connected bar CD is rotating with an angular...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the speeds of points A, B, and C caused...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the velocity of the gear rack C.Ch. 16.6 - If the hub gear H and ring gear R have angular...Ch. 16.6 - What is the angular velocity of the spur gear?Ch. 16.6 - Determine the angular velocity of rod CD at the...Ch. 16.6 - If bar CD is rotating with an angular velocity of...Ch. 16.6 - If the link rotates about the fixed point B at 4...Ch. 16.7 - if the sun gear D is rotating clockwise at D = 5...Ch. 16.7 - The angular velocity is given.Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular acceleration of the rod and...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the acceleration of point A.Ch. 16.7 - At the instant shown, the center O of the gear...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular acceleration of the gear at...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular acceleration of link BC at...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular acceleration of link BC and...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the velocity sod acceleration of the...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the acceleration of the top of the...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the acceleration of the bottom A of the...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of the...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of the...Ch. 16.7 - At the instant shown, point A has the motion...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular velocity and angular...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular velocity and angular...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular acceleration of link AB and...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular acceleration of link CD if...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of point A...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of point B...Ch. 16.7 - If it is pulled with a constant velocity v,...Ch. 16.7 - If it does not slip at A, determine the...Ch. 16.7 - If it does not slip at A, determine the...Ch. 16.7 - As cord CF unwinds from the inner rim of the...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of point B...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular velocity and angular...Ch. 16.7 - If link DE has the angular motion shown, determine...Ch. 16.7 - If member AB has the angular motion shown,...Ch. 16.7 - If member AB has the angular motion shown,...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the acceleration of points A and B on...Ch. 16.7 - At a given instant, A has a velocity of vA = 4...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular acceleration of rod AB at...Ch. 16.8 - Determine the acceleration of A at the instant...Ch. 16.8 - If at the same instant the disk has the angular...Ch. 16.8 - At the same instant, the boom is extending with a...Ch. 16.8 - Prob. 131PCh. 16.8 - Prob. 132PCh. 16.8 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of a water...Ch. 16.8 - At the instant shown, the cord is pulled down...Ch. 16.8 - Prob. 135PCh. 16.8 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of point C...Ch. 16.8 - Prob. 137PCh. 16.8 - Determine the magnitudes of the velocity and...Ch. 16.8 - If link AD is rotating at a constant rate of AD =...Ch. 16.8 - Determine the angular velocity and angular...Ch. 16.8 - If rod AB has an angular velocity of 2 rad/s and...Ch. 16.8 - Prob. 142PCh. 16.8 - If the gears center O moves with the velocity and...Ch. 16.8 - Prob. 144PCh. 16.8 - Prob. 145PCh. 16.8 - Also at this instant the car mounted at the end of...Ch. 16.8 - If the slider block C is fixed to the disk that...Ch. 16.8 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of car A...Ch. 16.8 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of car B...Ch. 16.8 - Link AB has a pin at B which is confined to move...Ch. 16.8 - Prob. 151PCh. 16.8 - The star wheel A makes one sixth of a revolution...Ch. 16.8 - If the tires do not slip on the pavement,...Ch. 16.8 - Determine the velocity and deceleration of the...Ch. 16.8 - Determine the speed of block B when it has risen s...Ch. 16.8 - At the instant shown, it has an acceleration of...Ch. 16.8 - If bar AB has an angular velocity AB = 6 rad/s,...Ch. 16.8 - If the cable does not slip on the pulley's...Ch. 16.8 - Determine the acceleration of the pin at C and the...Ch. 16.8 - If it does not slip at A, determine the...Ch. 16.8 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of the...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
What parts are included in the vehicle chassis?
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, and Service (5th Edition)
Use Mohrs circle to determine the normal stress and shear stress acting on the inclined plane AB.
Statics and Mechanics of Materials (5th Edition)
Replace the loading system by an equivalent resultant force and specify where the resultants line of action int...
Engineering Mechanics: Statics
2.15 Compute the rectangular components parallel and perpendicular to the inclined planes shown.
Applied Statics and Strength of Materials (6th Edition)
Then establish the triangle rule, where FR = F1 + F2. Label all known and unknown sides and internal angles. Pr...
INTERNATIONAL EDITION---Engineering Mechanics: Statics, 14th edition (SI unit)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The homogeneous 240-lb bar is supported by a rough horizontal surface at A, a smooth vertical surface at B, and the cable BC. Draw the FBD of the bar and count the unknowns.arrow_forwardIf the angle a = 30°, what is the magnitude of the force P required for tipping to impend, assuming that there is no slipping?arrow_forwardThe 250-N block rests upon a level plane for which fk = 0.2. It is pulled by force P = 100N inclined at 20o with the horizontal. If the 100-N pull is then removed, find the distance the block will travel.arrow_forward
- pls answer fast thank you A system of blocks is shown in the figure. Assume the pulley is frictionless *show FBD 1. Which of the following most nearly gives the least value of P required to prevent the system of blocks from sliding to the left? 2. Which of the following most nearly gives the least value of P required to cause the system of blocks to have impending motion to the right? 3. Which of the following most nearly gives the reaction at the pulley if the system of blocks is to have an impending motion to the right?arrow_forwardA spring with squared and ground ends has 16 active coils diameter of 6 mm and pitch of 10 mm . If spring rate is 85 KN/m , determine the solid force?arrow_forwardQ3. Determine the equilibrium values of 0 and the stability of equilibrium at each position for the unbalanced wheel on the 10° incline. Static friction is sufficient to prevent slipping. The mass center is at G. O C G 10⁰ r = 100 mm F = 60 mm Aarrow_forward
- The woman is trying to move the crate of weight W by pulling on the rope at the angle to the horizontal. Find the smallest possible tension that would cause the crate to slide and the corresponding angle .arrow_forwardThe 320-lb homogeneous spool is placed on the inclined surface. Determine the vertical force P that is required to keep the spool in the position shown. Assume that there is enough friction to prevent slipping at A.arrow_forwardThe force P applied to the brake handle enables the band brake to reduce the angular speed of a rotating drum. If the tensile strength of the band is 3800 lb, find the maximum safe value of P and the corresponding braking torque acting on the drum. Assume that the drum is rotating clockwise.arrow_forward
- Draw the FBD for the bar described in Prob. 5.1 if the bar is homogeneous of mass 50 kg. Count the unknowns.arrow_forwardFind the largest value of b/h at which the folding table is in equilibrium. The coefficients of static friction are 0.5 at A and 0.3 at C. Neglect the weight of the table.arrow_forwardThe weightless bars AB and CE, together with the 5-lb weight BE, form a parallelogram linkage. The ideal spring attached to D has a free length of 2 in. and a stiffness of 7.5 lb/in. Find the two equilibrium positions that are in the range 0/2, and determine their stability. Neglect the weight of slider F.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
EVERYTHING on Axial Loading Normal Stress in 10 MINUTES - Mechanics of Materials; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jQ-fNqZWrNg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY