
Foundations of Financial Management
16th Edition
ISBN: 9781259277160
Author: Stanley B. Block, Geoffrey A. Hirt, Bartley Danielsen
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 16, Problem 8P
Assume the par
The yield to maturity for 10-year bonds is as follows for four different bond rating categories:
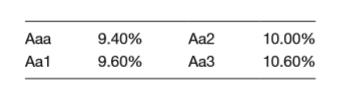
The bonds of Falter Corporation were rated as Aaa and issued at par a few weeks ago. The bonds have just been downgraded to Aa2. Determine the new price of the bonds, assuming a 10-year maturity and semiannual interest payments. (Refer to “Semiannual Interest and Bond Prices� in Chapter 10 for a review if necessary.)
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Eccles Inc., a zero-growth firm, has an expected EBIT of $100.000 and a corporate tax rate of 30%. Eccles uses $500,000 of 12.0% debt, and the cost of equity to an unlevered firm in the same risk class is 16.0%.
If the effective personal tax rates on debt income and stock income are Td = 25% and TS = 20% respectively, what is the value of the firm according to the Miller model (Based on the same unlevered firm value in the earlier question)?
a. $475,875
b. $536,921
c. $587,750
d. $623,050
e. $564,167
Refer to the data for Eccles Inc. earlier. If the effective personal tax rates on debt income and stock income are Td = 25% and TS = 20% respectively, what is the value of the firm according to the Miller model (Based on the same unlevered firm value in the earlier question)?
a. $475,875
b. $536,921
c. $587,750
d. $623,050
O $564,167
Warren Supply Inc. wants to use debt and common equity for its capital budget of $800,000 in the coming year, but it will not issue any new common stock. It is forecasting an EPS of $3.00 on its 500,000 outstanding shares of stock and is committed to maintaining a $2.00 dividend per share. Given these constraints, what percentage of the capital budget must be financed with debt?
a. 33.84%
b. 37.50%
c. 32.15%
d. 30.54%
e. 35.63%
Chapter 16 Solutions
Foundations of Financial Management
Ch. 16 - Prob. 1DQCh. 16 - What are some specific features of bond...Ch. 16 - What is the difference between a bond agreement...Ch. 16 - Discuss the relationship between the coupon rate...Ch. 16 - Prob. 5DQCh. 16 - What method of “bond repayment� reduces debt...Ch. 16 - What is the purpose of serial repayments and...Ch. 16 - Under what circumstances would a call on a bond be...Ch. 16 - Discuss the relationship between bond prices and...Ch. 16 - Prob. 10DQ
Ch. 16 - Prob. 11DQCh. 16 - Bonds of different risk classes will have a spread...Ch. 16 - Prob. 13DQCh. 16 - Prob. 14DQCh. 16 - Explain how the zero-coupon rate bond provides...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16DQCh. 16 - Prob. 17DQCh. 16 - Prob. 18DQCh. 16 - Prob. 19DQCh. 16 - Prob. 20DQCh. 16 - Prob. 1PCh. 16 - Prob. 2PCh. 16 - Assume the par value of the bonds in the following...Ch. 16 - Assume the par value of the bonds in the following...Ch. 16 - Assume the par value of the bonds in the following...Ch. 16 - Assume the par value of the bonds in the following...Ch. 16 - Prob. 7PCh. 16 - Assume the par value of the bonds in the following...Ch. 16 - Assume the par value of the bonds in the following...Ch. 16 - Prob. 10PCh. 16 - Prob. 11PCh. 16 - Prob. 12PCh. 16 - Prob. 13PCh. 16 - Prob. 14PCh. 16 - Prob. 15PCh. 16 - Prob. 16PCh. 16 - Prob. 17PCh. 16 - Prob. 18PCh. 16 - Prob. 19PCh. 16 - Prob. 20PCh. 16 - Prob. 21PCh. 16 - Prob. 22PCh. 16 - Prob. 2WECh. 16 - Go back to the summary page and follow the same...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, finance and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Eccles Inc., a zero-growth firm, has an expected EBIT of $100.000 and a corporate tax rate of 30%. Eccles uses $500,000 of 12.0% debt, and the cost of equity to an unlevered firm in the same risk class is 16.0%. What is the firm's cost of equity according to MM with corporate taxes? Ο 32.0% Ο 25.9% Ο 21.0% Ο 28.8% Ο 23.3%arrow_forwardP&L Corporation wants to sell some 20-year, annual interest, $1,000 par value bonds. Its stock sells for $42 per share, and each bond would have 75 warrants attached to it each exercisable into one share of stock at an exercise price of $47. The firm's straight bonds yield 10%. Each warrant is expected to have a market value of $2.00 given that the stock sells for $42. What coupon interest rate must the company set on the bonds in order to sell the bonds with-warrants at par? a. 9.54% b. 8.65% c. 9.08% d. 8.24% e. 83%arrow_forwardPotter & Lopez Inc. just sold a bond with 50 warrants attached. The bonds have a 20-year maturity and an annual coupon of 12%, and they were issued at their $1,000 par value. The current yield on similar straight bonds is 15%. What is the implied value of each warrant? Ο $4.35 O $3.76 O $4.56 O $4.14 O $3.94arrow_forward
- If a firm adheres strictly to the residual dividend policy, the issuance of new common stock would suggest that The dividend payout ratio is decreasing. The dividend payout ratio has remained constant. The dollar amount of investments has decreased. No dividends were paid during the year. the dividend payout ratio is increasing.arrow_forwardq6) Which of the following statements is CORRECT? If Congress increases taxes on capital gains but leaves tax rates on dividends unchanged, this will motivate companies to increase stock repurchases. The clientele effect explains why firms change their dividend policies so often.. One advantage of the residual dividend policy is that it helps corporations to develop a specific and well-identified dividend clientele. If a firm splits its stock 2-for-1, then its stock price will be doubled. If a firm follows the residual dividend policy, then a sudden increase in the number of profitable projects is likely to reduce the firm's dividend payout.arrow_forwardAmold Rossiter is a 40-year-old employee of the Barrington Company who will retire at age 60 and expects to live to age 75. The firm has promised a retirement income of $20.000 at the end of each year following retirement until death. The firm's pension fund is expected to earn 7 percent annually on its assets and the firm uses 7% to discount pension benefits. What is Barrington's annual pension contribution to the nearest dollar for Mr. Rossiter? (Assume certainty and end-of-year cash flows. a. $3,642 b.$4,443 c. $4,967 d.$5,491 e.$2,756arrow_forward
- Morales Publishing's tax rate is 40%, its beta is 1.10, and it uses no debt. However, the CFO is considering moving to a capital structure with 30% debt and 70% equity. If the risk free rate is 5.0% and the market risk premium is 6.0%, by how much would the capital structure shift change the firm's cost of equity? Ο 1.53% Ο 2.05% Ο 1.70% Ο 1.87% O 2.26%arrow_forwardThe common stock of Southern Airlines currently sells for $33, and its 8% convertible debentures (issued at par, or $1,000) sell for $850. Each debenture can be converted into 25 shares of common stock at any time before 2025. What is the conversion value of the bond? a. $825.00 b.$866.25 c. $744.56 d. $783.75 e. $707.33arrow_forwardBailey and Sons has a levered beta of 1.10, its capital structure consists of 40% debt and 60% equity, and its tax rate is 40%. What would Bailey's beta be if it used no debt, i.e., what is its unlevered beta? a. 0.79 b. 0.71 c. 0.67 d. 0.64 e. 0.75arrow_forward
- Eccles Inc., a zero-growth firm, has an expected EBIT of $100.000 and a corporate tax rate of 30%. Eccles uses $500,000 of 12.0% debt, and the cost of equity to an unlevered firm in the same risk class is 16.0%. What is the value of the firm according to MM with corporate taxes? a. $710,875 b. $587,500 c. $646,250 d. $475,875 e. $528,750arrow_forwardMikkleson Mining stock is selling for $40 per share and has an expected dividend in the coming year of $2.00 and has an expected constant growth rate of 5%. The company is considering issuing a 10-year convertible bond that would be priced at $1,000 par value. The bonds would have an 8% annual coupon, and each bond could be converted into 20 shares of common stock. The required rate of return on an otherwise similar nonconvertible bond is 10.00%. What is the estimated floor price of the convertible at the end of Year 3? a. $926.10 b. $794.01 c. $835.81 d. $879.80 $972.41arrow_forwardMs. Lloyd, who is 25 and expects to retire at age 60, has just been hired by the Chambers Corporation. Ms. Lloyd's current salary is $30,000 per year, but her wages are expected to increase by 5 percent annually over the next 35 years. The firm has a defined benefit pension plan in which workers receive 2 percent of their final year's wages for each year of employment. Assume a world of certainty. Further, assume that all payments occur at year-end. What is Ms. Lloyd's expected annual retirement benefit, rounded to the nearest thousands of dollars? a. $116,000 b. $35,000 c. $89,000 d. $57,000 e. $132,000arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College

Principles of Accounting Volume 1
Accounting
ISBN:9781947172685
Author:OpenStax
Publisher:OpenStax College
Bonds 101 (DETAILED EXPLANATION FOR BEGINNERS); Author: It's Your Girl Rose;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Gskqx8dy9To;License: Standard Youtube License