
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
1st Edition
ISBN: 9781133939146
Author: Katz, Debora M.
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 16, Problem 1PQ
Case Study For each velocity listed, state the position and acceleration of the rubber disk in Crall and Whipple’s experiment (Figs. 16.3–16.5). There may be more than one possible answer for each given velocity. a. vy = 1.3 m/s b. vy = −1.3 m/s c. vy = 0
Expert Solution & Answer
To determine
The position and acceleration of the rubber disk.
Answer to Problem 1PQ
The table listing position and acceleration for three values of velocity is given in the table given below.
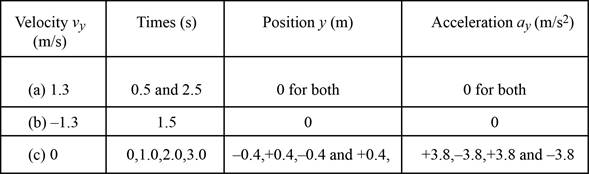
Explanation of Solution
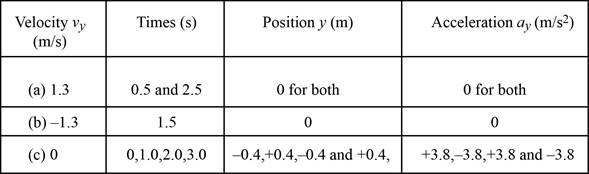
A table listing the velocity, time, position in meter, and acceleration in meter per Second Square is shown in the table below.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Subscribe now to access step-by-step solutions to millions of textbook problems written by subject matter experts!
Students have asked these similar questions
4
3
2
LAssume
-0.5
0.5
1.5
2.5
3.5
4.5
5
55
6
6.5
7.5
8
8.5
9.5
10
-1-
-2
3
4
-5-
the velocity of a person traveling along a straight hiking trail is given by the graph
depicted. The input to the function is time in hours, and the output is velocity in
miles per hour. The trail travels east-west, and the velocity shown is the eastward
velocity.
At time t=10 the displacement of the hiker from time t=0 is:
Negative
Positive
Zero
You cannot determine given the graph of the velocity function.
11. A 32 caliber bullet is shot straight up from a rifle with a muzzle speed of 295 m/s. Approximately; what is the
peak height that could be achieved by the bullet assuming no air resistance?
(295mls) (Sin² (90))
2(97.80m/s²)
1445.5m / ku
1000 m
44.5
0
A) 1.3 miles B) 2.8 miles C) 3.2 miles D) 4440 miles E) none of the above
A child rides a pony on a circular track whoseradius is 5.25 m. (a) Find the distance traveled and the displacement after the child has gone halfway around the track. (b) Doesthe distance traveled increase, decrease, or stay the same whenthe child completes one circuit of the track? Explain. (c) Does thedisplacement increase, decrease, or stay the same when the childcompletes one circuit of the track? Explain. (d) Find the distanceand displacement after a complete circuit of the track.
Chapter 16 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.1CECh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.2CECh. 16.2 - For each expression, identify the angular...Ch. 16.5 - Prob. 16.4CECh. 16.6 - Prob. 16.5CECh. 16.6 - Prob. 16.6CECh. 16 - Case Study For each velocity listed, state the...Ch. 16 - Case Study For each acceleration listed, state the...Ch. 16 - Prob. 3PQCh. 16 - Prob. 4PQ
Ch. 16 - Prob. 5PQCh. 16 - Prob. 6PQCh. 16 - The equation of motion of a simple harmonic...Ch. 16 - The expression x = 8.50 cos (2.40 t + /2)...Ch. 16 - A simple harmonic oscillator has amplitude A and...Ch. 16 - Prob. 10PQCh. 16 - A 1.50-kg mass is attached to a spring with spring...Ch. 16 - Prob. 12PQCh. 16 - Prob. 13PQCh. 16 - When the Earth passes a planet such as Mars, the...Ch. 16 - A point on the edge of a childs pinwheel is in...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16PQCh. 16 - Prob. 17PQCh. 16 - A jack-in-the-box undergoes simple harmonic motion...Ch. 16 - C, N A uniform plank of length L and mass M is...Ch. 16 - Prob. 20PQCh. 16 - A block of mass m = 5.94 kg is attached to a...Ch. 16 - A block of mass m rests on a frictionless,...Ch. 16 - It is important for astronauts in space to monitor...Ch. 16 - Prob. 24PQCh. 16 - A spring of mass ms and spring constant k is...Ch. 16 - In an undergraduate physics lab, a simple pendulum...Ch. 16 - A simple pendulum of length L hangs from the...Ch. 16 - We do not need the analogy in Equation 16.30 to...Ch. 16 - Prob. 29PQCh. 16 - Prob. 30PQCh. 16 - Prob. 31PQCh. 16 - Prob. 32PQCh. 16 - Prob. 33PQCh. 16 - Show that angular frequency of a physical pendulum...Ch. 16 - A uniform annular ring of mass m and inner and...Ch. 16 - A child works on a project in art class and uses...Ch. 16 - Prob. 37PQCh. 16 - Prob. 38PQCh. 16 - In the short story The Pit and the Pendulum by...Ch. 16 - Prob. 40PQCh. 16 - A restaurant manager has decorated his retro diner...Ch. 16 - Prob. 42PQCh. 16 - A wooden block (m = 0.600 kg) is connected to a...Ch. 16 - Prob. 44PQCh. 16 - Prob. 45PQCh. 16 - Prob. 46PQCh. 16 - Prob. 47PQCh. 16 - Prob. 48PQCh. 16 - A car of mass 2.00 103 kg is lowered by 1.50 cm...Ch. 16 - Prob. 50PQCh. 16 - Prob. 51PQCh. 16 - Prob. 52PQCh. 16 - Prob. 53PQCh. 16 - Prob. 54PQCh. 16 - Prob. 55PQCh. 16 - Prob. 56PQCh. 16 - Prob. 57PQCh. 16 - An ideal simple harmonic oscillator comprises a...Ch. 16 - Table P16.59 gives the position of a block...Ch. 16 - Use the position data for the block given in Table...Ch. 16 - Consider the position data for the block given in...Ch. 16 - Prob. 62PQCh. 16 - Prob. 63PQCh. 16 - Use the data in Table P16.59 for a block of mass m...Ch. 16 - Consider the data for a block of mass m = 0.250 kg...Ch. 16 - A mass on a spring undergoing simple harmonic...Ch. 16 - A particle initially located at the origin...Ch. 16 - Consider the system shown in Figure P16.68 as...Ch. 16 - Prob. 69PQCh. 16 - Prob. 70PQCh. 16 - Prob. 71PQCh. 16 - Prob. 72PQCh. 16 - Determine the period of oscillation of a simple...Ch. 16 - The total energy of a simple harmonic oscillator...Ch. 16 - A spherical bob of mass m and radius R is...Ch. 16 - Prob. 76PQCh. 16 - A lightweight spring with spring constant k = 225...Ch. 16 - Determine the angular frequency of oscillation of...Ch. 16 - Prob. 79PQCh. 16 - A Two springs, with spring constants k1 and k2,...Ch. 16 - Prob. 81PQCh. 16 - Prob. 82PQ
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Only E, G, and Iarrow_forwardSolve using First Order Ordinary Differential Equationarrow_forwardTo Merge into the highway you need to increase your speed from 50 km/h to 100 km/h. If your car can accelerate at 4.0 m/s2, what should the minimum length of the ramp be? (report your answer in meters) Your Answer: Question 9 options:arrow_forward
- 1.8 kg sits on top of a block with mass M = 5.6 kg which sits on a table. The coefficients of friction (both static A block with mass m= and kinetic) between all surfaces are u, = H = H=1 A string with negligible mass is connected to each mass and wraps halfway around a pulley with negligible mass, as shown in figure. What is the acceleration of the pulley, in m/s, at the instant the force, F= 92.63 N is applied on the pulley horizontally to the right as shown in figure? 9 = 10 m/s alınız) H = 1 F O 21.00 M O 25.20 O 700 O 4.90 O 1050arrow_forward14- 12니 E 10 8. 6. 4 21 F 10 12 14 16 18 20 6. Time (hours) The total distance travelled is km. The net displacement is km. displacement at t=18 hrs is km The distance between points E and F is km. The displacement between points E and F is km Distance (km)arrow_forwardCan you please provide a complete solution set to this problem? A rollercoaster car is traveling on a track and approaching a loopped portion of track. What is the minimum speed needed at the bottom of the loop to clear the loop? The diameter is 15 meters.arrow_forward
- The velocity-time graph that describes the velocity of an object with time is given as in the figure below. if the values of a= 82.3, b=126.9 and c=53.4, Find the average acceleration ( in units of km/h²) of the object over the tie period [0, 2] h. v(km/h) b a t(h) 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 Select one: O A. 98.0 Ов. 106.8 Ос. 67.8 OD. -14.4 O E. -115.6arrow_forwardFor the first part of the problem I got the velocity to be 3.77m/s which I think is correct. The second part I am a bit confused with. From what I think it would be Ki=Kf+Ugf (1/2)(5)(3.77)=(1/2)(5)(?vf?)+(5)(9.8)(H) I want to find the H but I feel I also need the Vf. Would the Vf be 0 because it is at rest at the highest point? but wouldnt it still have a forward velocity. Does that mean I have to split up everything into X and Y components?arrow_forwardRMQ7: please answer all parts and explain stepsarrow_forward
- A soccer player kicks a rock horizontally off a 32 m high cliff into a pool of water. If the player hears the sound of the splash 2.72 s later, what was the initial speed given to the rock (in m/s)? Assume the speed of sound in air is 343 m/s. m/s What If? If the temperature near the cliff suddenly falls to 0°C, reducing the speed of sound to 331 m/s, what would the initial speed of the rock have to be (in m/s) for the soccer player to hear the sound of the splash 2.72 s after kicking the rock? m/sarrow_forwardNeeds Complete typed solution with 100 % accuracy.arrow_forwardAre my calculations right? I never used sin or theta before.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

An Introduction to Physical Science
Physics
ISBN:9781305079137
Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION (Physics Animation); Author: EarthPen;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XjkUcJkGd3Y;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY