
Concept explainers
Find the total impedance of the parallel networks of Fig. 1663 in rectangular and polar form.
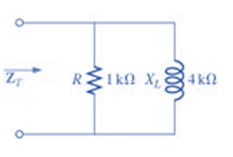
Fig. 1663
(a)
Total impedance of the given network.
Answer to Problem 1P
Rectangular form: ZT=(941.17+j235.29)Ω
Polar form: ZT=970.14Ω∠14.03°
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given network is:

Calculation:
We can see from the given circuit that the resistor R and the inductive reactance XL are in parallel. Therefore, the total resistance of the network will be:
ZT=R∥(jXL)ZT=(1000)(j4000)1000+j4000ZT=j40000001000+j4000ZT=(941.17+j235.29)ΩZT=970.14Ω∠14.03°
(b)
Total impedance of the given network.
Answer to Problem 1P
Rectangular form: ZT=(5679.23−j1153.85)Ω
Polar form: ZT=5883.48Ω∠−11.31°
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given network is:
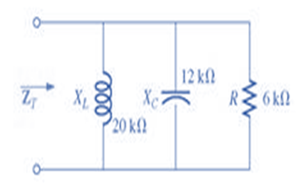
Calculation:
We can see from the given circuit that the resistor R, capacitive reactance XC and the inductive reactance XL are in parallel. Therefore, the total resistance of the network will be:
ZT=R∥(jXL)∥(−jXC)ZT=11jXL+1−jXC+1RZT=1120000∠90°+112000∠−90°+16000ZT=150×10−6∠−90°+83.33×10−6∠90°+166.67×10−6ZT=(5679.23−j1153.85)ΩZT=5883.48Ω∠−11.31°
(c)
Total impedance of the given network.
Answer to Problem 1P
Rectangular form: ZT=j1224.32Ω
Polar form: ZT=1224.32Ω∠90°
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given network is:
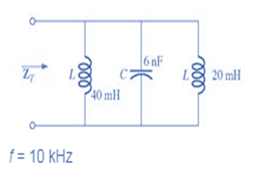
Calculation:
We can see from the given circuit that two inductors and one capacitor are connected in parallel.
Therefore, we need to calculate their equivalent reactance first:
Inductive reactance of 40mH inductor:
XL1=2πfL1XL1=(2π)(10×103)(40×10−3)XL1=2513.27Ω
Inductive reactance of 20mH inductor:
XL1=2πfL2XL1=(2π)(10×103)(20×10−3)XL1=1256.64Ω
Capacitive reactance of 6nF inductor:
XC=12πfCXC=1(2π)(10×103)(6×10−9)XC=2652.58Ω
Therefore, the total resistance of the network will be:
ZT=(jXL1)∥(jXL2)∥(−jXC)ZT=11jXL1+1jXL2+1−jXCZT=112513.27∠90°+11256.63∠90°+12652.58∠−90°ZT=1398×10−6∠−90°+377×10−6∠90°+795.78×10−6∠−90°ZT=1816.78×10−6∠−90°ZT=j1224.32ΩZT=1224.32Ω∠90°
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Starting Out with C++: Early Objects (9th Edition)
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures (4th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
- NO AI PLEASE WILL REJECTarrow_forwardNO AI PLEASE WILL REJECTarrow_forwardCalculate A, B, C, and D constants, sending end voltage and sending end current of a 3-phase, 50-Hz overhead transmission line 100 km long has the following constants Resistance/km/phase = 0.1, Inductive reactance/km/phase 0.20, Capacitive susceptance/km/phase = 0.04 x 10 siemen. when supplying a balanced load of 10,000 kW at 66 kV, p.f. 0-8 lagging. Use nominal T method. andarrow_forward
- Don't use ai to answer I will report you answer. Please give explanation for both correct options and incorrectarrow_forward14:00 APP Voi) 5G 鼷浴醵郯興47% atheva.cc/index/index/index.html The Most Trusted, Secure, Fast, Reliable Cryptocurrency Exchange Get started with the easiest and most secure platform to buy, sell, trade, and earn Cryptocurrency Balance:1000.00 Recharge Withdraw Message About us BTC/USDT ETH/USDT EOS/USDT 83259.00 1841.46 83259.00 +1.02% +0.08% +1.02% Operating norms Symbol B BTC/USDT Latest price 24hFluctuation 83259.00 +1.02% ETH/USDT 1841.46 +0.08% B BTC/USD illı 83259.00 +1.02% Home Markets Trade Record Mine О <arrow_forwardPastner Brands is a calendar-year firm with operations in several countries. As part of its executive compensation plan, at January 1, 2024, the company issued 480,000 executive stock options permitting executives to buy 480,000 shares of Pastner stock for $38 per share. One-fourth of the options vest in each of the next four years beginning at December 31, 2024 (graded vesting). Pastner elects to separate the total award into four groups (or tranches) according to the year in which they vest and measures the compensation cost for each vesting date as a separate award. The fair value of each tranche is estimated at January 1, 2024, as follows: Vesting Date Amount Fair Value Vesting per Option: December 31, 2024 25% $ 3.90 December 31, 2025 25% $ 4.40 25% $ 4.90 25% $ 5.40 December 31, 2026 December 31, 2027 Required: 1. Determine the compensation expense related to the options to be recorded each year 2024-2027, assuming Pastner allocates the compensation cost for each of the four…arrow_forward
- JOB UPDATE Apply on- Jobswood.com OR Search "Jobswood.com" on Google COMPANY JOB PROFILE JOB LOCATION WEB ENGINEER GOOGLE MULTIPLE CITIES (FRESHERS) AMAZON SOFTWARE DEV ENGG MULTIPLE CITIES COGNIZANT SYSTEMS ENGINEER CHENNAI ZENSAR FRONTEND DEVELOPER BENGALURU ORACLE AUTOMATION ENGINEER BENGALURU DIGITAL OCEAN SUPPORT ENGINEER HYDERABAD IBM APPLICATION DEVELOPER HYDERABAD INDIAMART WORK FROM HOME MULTIPLE CITIES AMAZON RECRUITER HYDERABAD GE HEALTHCARE TRAINEE ENGINEER BENGALURUarrow_forwardJOB UPDATE Apply on Vinkjobs.com OR Search "VinkJobs.com" on Google Company Name Job Profile Job Location CISCO Software Engineer Bengaluru Accenture Associate (Freshers) Chennai Trellix Developer Bengaluru Verizon SDET Bengaluru Allerin Test Engineer Mumbai Sutherland SQL/.Net Developer Chennai Bottomline DevOps Engineer Multiple Cities IQVIA HRIS Specialist Bengaluru BYJU's Associate Multiple Cities Spring Works Executive WFH (Remote)arrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forward
 Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
