
(a)
Interpretation:
Chemical equation for the conversion of given
Concept Introduction:
The name of the carboxylic acid itself implies that it is acidic. Addition of carboxylic acid to water results in ionization. Hydrogen ion transfer occurs from carboxylic acid to water and hydronium ion is formed. Carboxylate ion is also formed due to the loss of hydrogen ion from carboxylic acid.
Carboxylate ion is the negative ion which is formed when one or more acidic protons are lost from carboxylic acid. Similar to carboxylic acid it reacts with strong base to form carboxylic acid salt and water.
Carboxylic acid salts when treated with a strong acid produces carboxylic acid as the product.
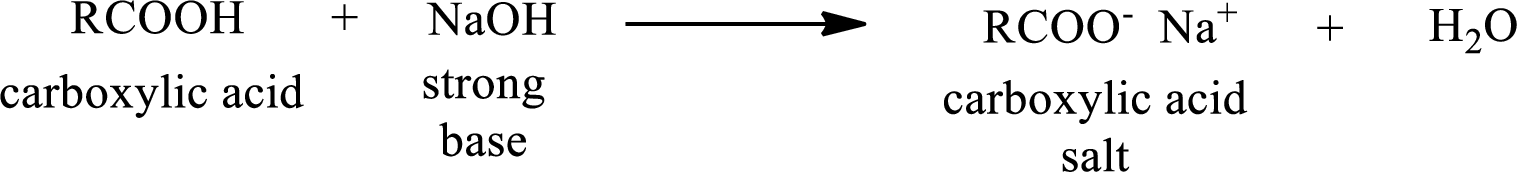
Carboxylic acid forms carboxylic acid salt by reacting with a strong base. The general reaction scheme for the formation of carboxylic acid salt is given as shown below,
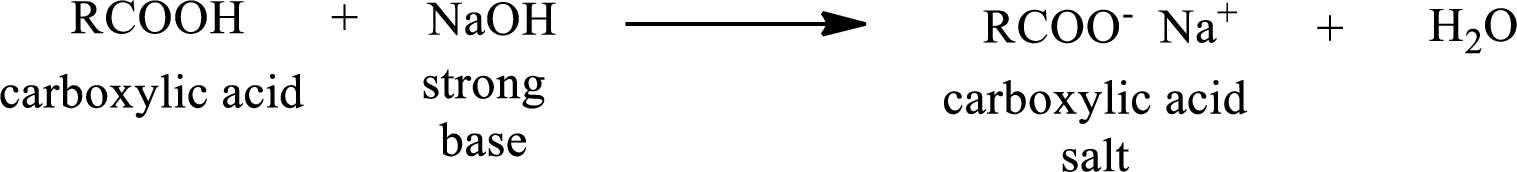
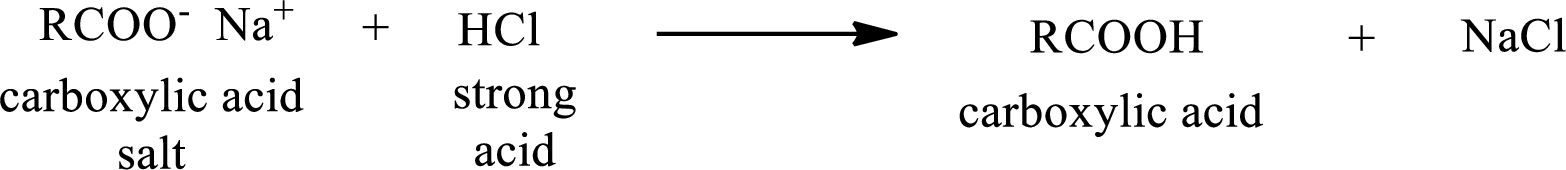
The reverse of the above reaction is conversion of carboxylic acid salt to carboxylic acid. This is accomplished by using strong acid. The scheme is shown below,
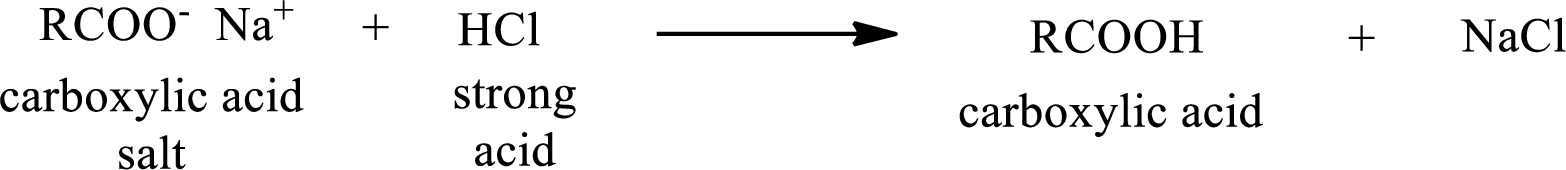
From the above chemical equation it is found that the carboxylic acid salt reacts with strong acid to form carboxylic acid.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given carboxylic acid salt is calcium propanoate. The structure of calcium propanoate can be given as shown below,
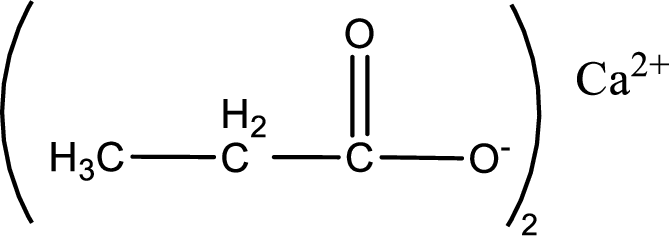
Carboxylic acid sat is converted to carboxylic acid by reaction with strong acid. In the problem statement it is given that the strong acid is
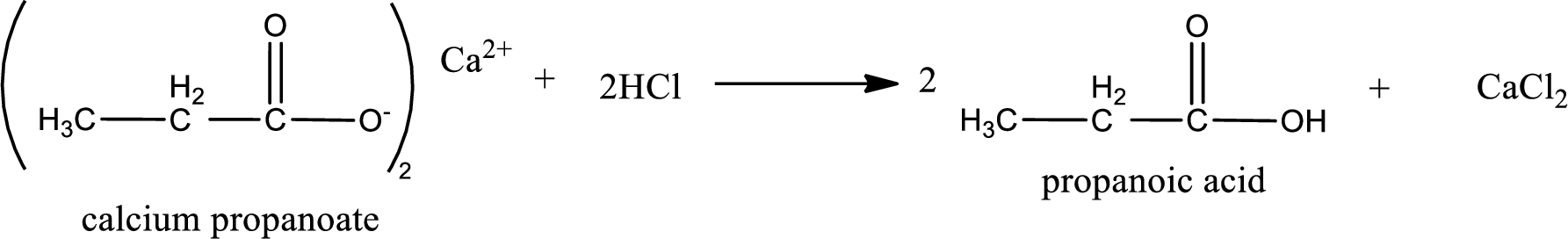
Chemical equation for the conversion of given carboxylic acid salt to carboxylic acid using hydrochloric acid is written.
(b)
Interpretation:
Chemical equation for the conversion of given carboxylic acid salt to its parent carboxylic acid using
Concept Introduction:
The name of the carboxylic acid itself implies that it is acidic. Addition of carboxylic acid to water results in ionization. Hydrogen ion transfer occurs from carboxylic acid to water and hydronium ion is formed. Carboxylate ion is also formed due to the loss of hydrogen ion from carboxylic acid.
Carboxylate ion is the negative ion which is formed when one or more acidic protons are lost from carboxylic acid. Similar to carboxylic acid it reacts with strong base to form carboxylic acid salt and water.
Carboxylic acid salts when treated with a strong acid produces carboxylic acid as the product.
Carboxylic acid forms carboxylic acid salt by reacting with a strong base. The general reaction scheme for the formation of carboxylic acid salt is given as shown below,
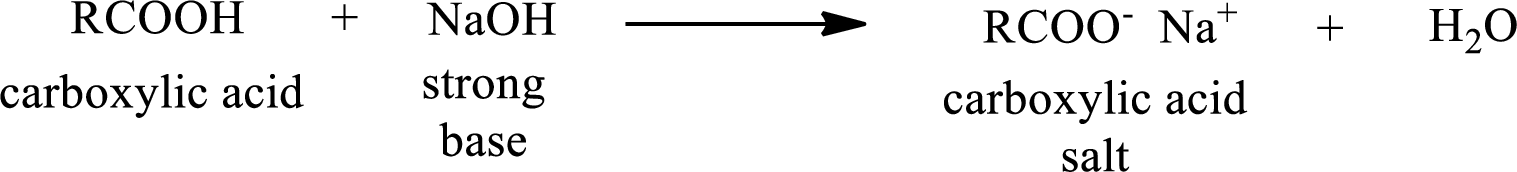
The reverse of the above reaction is conversion of carboxylic acid salt to carboxylic acid. This is accomplished by using strong acid. The scheme is shown below,
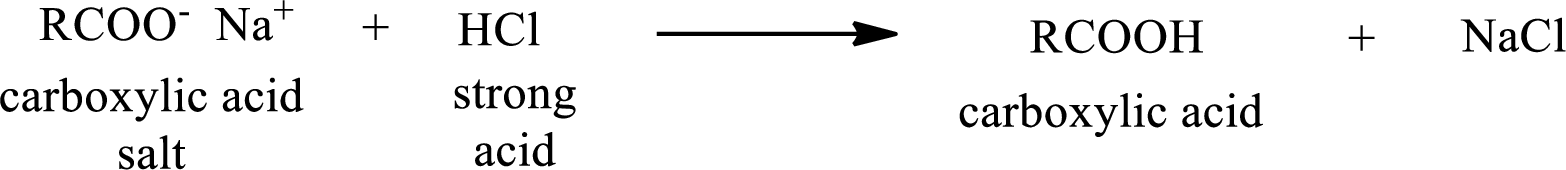
From the above chemical equation it is found that the carboxylic acid salt reacts with strong acid to form carboxylic acid.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Given carboxylic acid salt is sodium lactate. The structure of sodium lactate can be given as shown below,
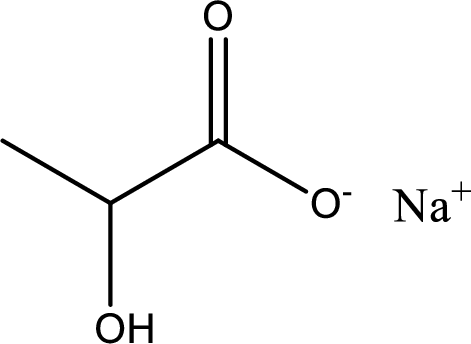
Carboxylic acid sat is converted to carboxylic acid by reaction with strong acid. In the problem statement it is given that the strong acid is
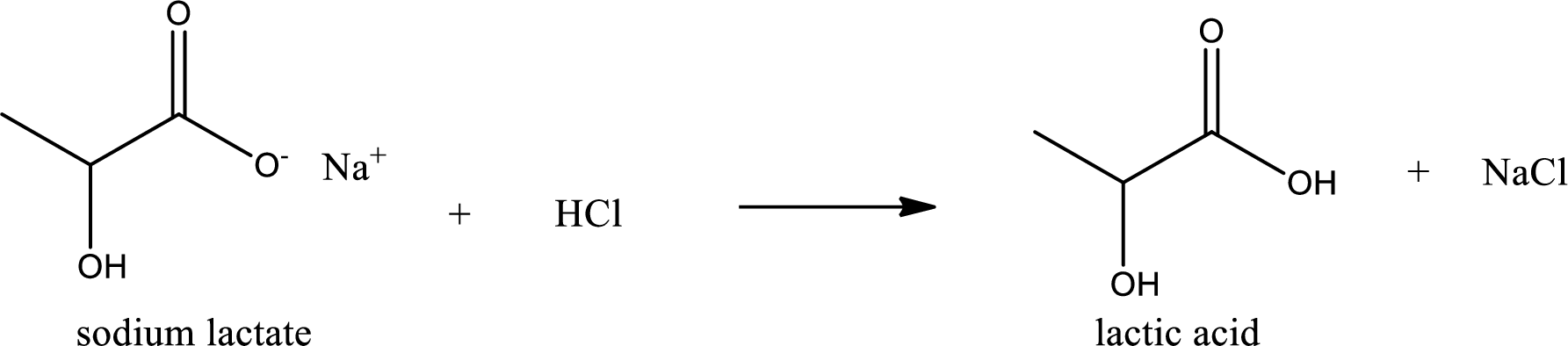
Chemical equation for the conversion of given carboxylic acid salt to carboxylic acid using hydrochloric acid is written.
(c)
Interpretation:
Chemical equation for the conversion of given carboxylic acid salt to its parent carboxylic acid using
Concept Introduction:
The name of the carboxylic acid itself implies that it is acidic. Addition of carboxylic acid to water results in ionization. Hydrogen ion transfer occurs from carboxylic acid to water and hydronium ion is formed. Carboxylate ion is also formed due to the loss of hydrogen ion from carboxylic acid.
Carboxylate ion is the negative ion which is formed when one or more acidic protons are lost from carboxylic acid. Similar to carboxylic acid it reacts with strong base to form carboxylic acid salt and water.
Carboxylic acid salts when treated with a strong acid produces carboxylic acid as the product.
Carboxylic acid forms carboxylic acid salt by reacting with a strong base. The general reaction scheme for the formation of carboxylic acid salt is given as shown below,
The reverse of the above reaction is conversion of carboxylic acid salt to carboxylic acid. This is accomplished by using strong acid. The scheme is shown below,
From the above chemical equation it is found that the carboxylic acid salt reacts with strong acid to form carboxylic acid.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Given carboxylic acid salt is magnesium succinate. The structure of magnesium succinate can be given as shown below,
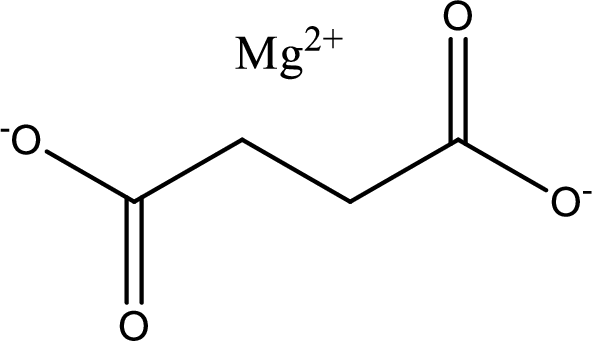
Carboxylic acid sat is converted to carboxylic acid by reaction with strong acid. In the problem statement it is given that the strong acid is
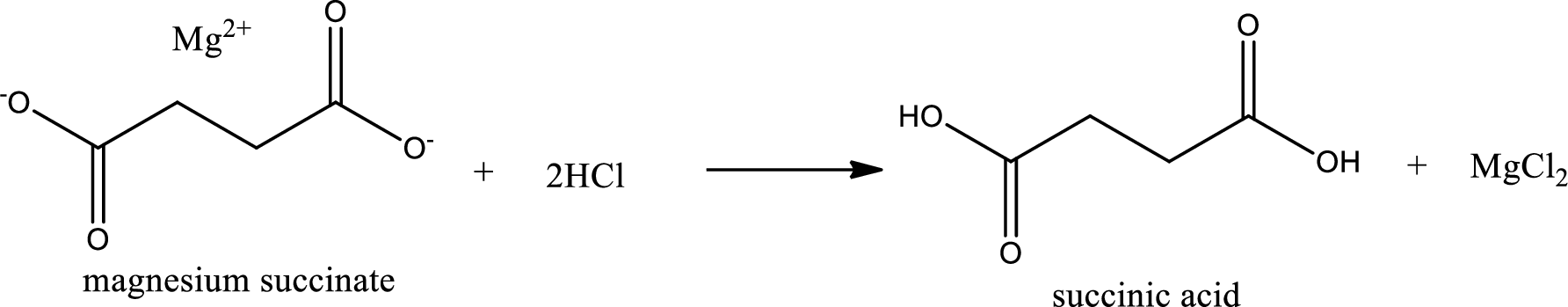
Chemical equation for the conversion of given carboxylic acid salt to carboxylic acid using hydrochloric acid is written.
(d)
Interpretation:
Chemical equation for the conversion of given carboxylic acid salt to its parent carboxylic acid using
Concept Introduction:
The name of the carboxylic acid itself implies that it is acidic. Addition of carboxylic acid to water results in ionization. Hydrogen ion transfer occurs from carboxylic acid to water and hydronium ion is formed. Carboxylate ion is also formed due to the loss of hydrogen ion from carboxylic acid.
Carboxylate ion is the negative ion which is formed when one or more acidic protons are lost from carboxylic acid. Similar to carboxylic acid it reacts with strong base to form carboxylic acid salt and water.
Carboxylic acid salts when treated with a strong acid produces carboxylic acid as the product.
Carboxylic acid forms carboxylic acid salt by reacting with a strong base. The general reaction scheme for the formation of carboxylic acid salt is given as shown below,
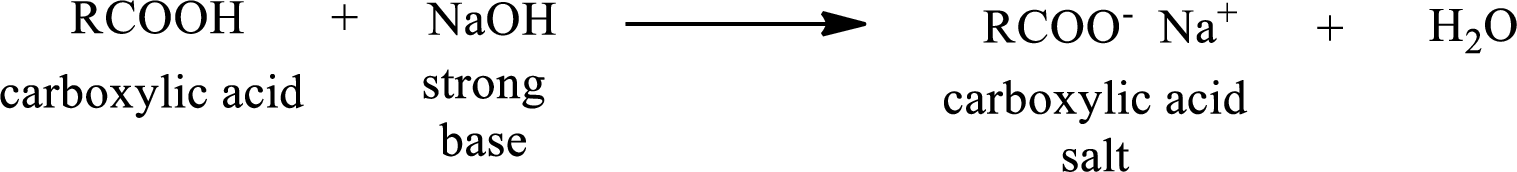
The reverse of the above reaction is conversion of carboxylic acid salt to carboxylic acid. This is accomplished by using strong acid. The scheme is shown below,
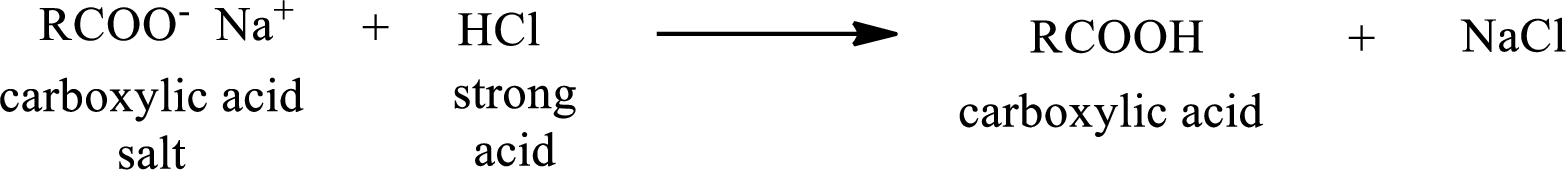
From the above chemical equation it is found that the carboxylic acid salt reacts with strong acid to form carboxylic acid.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Given carboxylic acid salt is potassium benzoate. The structure of potassium benzoate can be given as shown below,
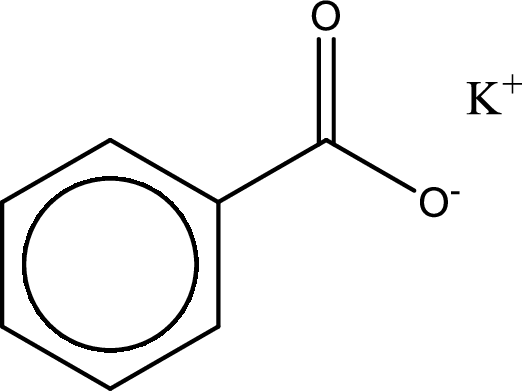
Carboxylic acid sat is converted to carboxylic acid by reaction with strong acid. In the problem statement it is given that the strong acid is
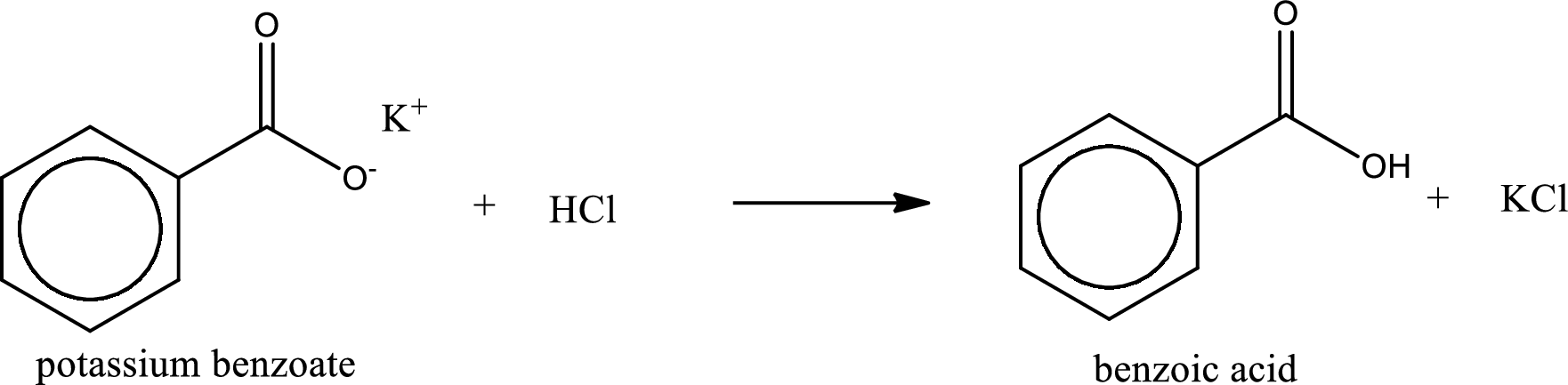
Chemical equation for the conversion of given carboxylic acid salt to carboxylic acid using hydrochloric acid is written.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Bundle: General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry, 7th + OWLv2 Quick Prep for General Chemistry, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
- Consider a buffer solution that contains 0.55 M NH2CH2CO2H and 0.35 M NH2CH2CO2Na. pKa(NH2CH2CO2H)=9.88. a. Calculate its pH. b. Calculate the change in pH if 0.155 g of solid NaOH is added to 250 mL of this solution. c. If the acceptable buffer range of the solution is ±0.10 pH units, calculate how many moles of H3O+ can be neutralized by 250 mL of the initial buffer.arrow_forwardGive full explanation The physcian orders ascorbic acid 0.25mg IM for your patient admitted with an alcohol problem. You have ascorbic acid 500mg/mL. How many milliliters will you administer?arrow_forwardA prescription came in for 34% salicylic acid. The pharmacy has 95% salicylic and 10%salicylic acid available. Write a recipe for 500mg of 34% salicylic acid.arrow_forward
- Which of the following liquid substances exhibit the highest viscosity at 25 ºC? A. H3C−(CH2)4−CH2OH (hexanol) B. H3C−(CH2)3−CH2OH (pentanol) C. H3C−(CH2)4−COOH (hexanoic acid) D. All of the above have equal viscosities.arrow_forwardWhat is the isoelectric point of casein? Please choose one correct answer only. A. pH 6.6 B. pH 5.6 C. pH 4.6 D. pH 3.6 E. None of the given optionsarrow_forwardDefine the following terms briefly as they relate to the experiments Cite an example for each using the Fischer/Haworth projection formula a. Aldohexose b. Reducing Sugar c. Hemiacetalarrow_forward
- Shown below is the titration curve for phosphoric acid. At what pH is the solution entirely in the H3PO4 form? 0-0.5 14 12.5 O2.1 NICHarrow_forwardCalcium containing antacid differ from aluminium containing antacid: A. Depend upon their basic property B. Don't have any amphoteric effect C. Don't cause systemic alkalosis D. All of thesearrow_forwardFor the treatment of his indigestion, Tin must drink a salt solution with a pH between 8.00 to 8.50. Tan, Tin's friend, wanted to give Tin a 0.895 mM solution of a water-soluble salt generated from the ions K+ and C3H2O42-. a. Write the chemical formula of the salt offered by Tan. b. What is the hydrolysis reaction for the salt solution offered by Tan. c. What is the pH of the salt solution? (2 decimal places)arrow_forward
- Trans-oleic acid (18:1,D9) has a melting temperature of (44.5C) and cis-oleic acid (18:1,D9) has a melting point of (13.4C). Briefly explain the difference in melting points between the two. tw.arrow_forwardThe amount of calcium in physiologic fluids can be determined by a complexometric titration with EDTA. In one such analysis, a 0.100-mL sample of blood serum was made basic by adding 2 drops of NaOH and titrated with 0.001 M EDTA, requiring 0.238 mL to reach the end point. Report the concentration of calcium in the sample as miligrams of Ca per 100 mL. (Ca = 40.078 amu).arrow_forwardIdentify the Lewis acid in the following reaction: A. BF3 B. F C. BF4 D. None of these is an acid. B OD O A O Carrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





