
Gerry creates the computational domain sketched in Fig. P1 5-46C to simulate flow through a sudden contraction in a two-dimensional duct. He is interested tithe time-averaged pressure drop and the minor loss coefficient created by the sudden contraction. Gerry generates a grid and calculates the flow with a CFD code, assuming stead, turbulent. incompressible flow (with a turbulence model).
(a) Discuss one way that Gerry could improve his computational domain and grid so that be would get the some results in approximate) half the computer time.
(b) There may be a fundamental flaw in how Germ’ has set up his computational domain. What is ir? Discuss what should be different about Gerry’s setup. 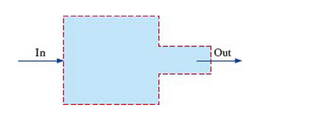 FIGURE P15-46C
FIGURE P15-46C
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 15 Solutions
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
- An incompressible CFD code is used to simulate the flow of gasoline through a two-dimensional rectangular channel in which there is a large circular settling chamber. Flow enters from the left and exits to the right as shown. A time-averaged turbulent flow solution is generated using a turbulence model. Top–bottom symmetry is assumed. Inlet velocity V is known, and outlet pressure Pout is also known. Generate the blocking for a structured grid using four-sided blocks, and sketch a coarse grid using four-sided cells, being sure to cluster cells near walls. Also be careful to avoid highly skewed cells. Label the boundary conditions that should be applied to every edge of every block of your computational domain.arrow_forwardFor the two-dimensional computational domain of Fig, with the given node distribution, sketch a simple structured grid using four-sided cells and sketch a simple unstructured polyhedral grid using at least one of each: 3-sided, 4-sided, and 5-sided cells. Try to avoid large skewness. Compare the cell count for each case and discuss your results.arrow_forwardOil (kinematic viscosity, v = 1.0 x 10-5 m³/s) flows through a pipe of 0.5 m diameter with a velocity of 10 m/s. Water (kinematic viscosity, V = 0.89 x 10-6 m²/s) is flowing through a model pipe of diameter 20 mm. For satisfying the dynamic similarity, the velocity of water (in m/s) is %3D Warrow_forward
- examples, by conering them mer and then trying to draw the paral law, and thiking about how the sine and conine laws re sed to d the mknowns Then before solhing any of the problems, try and sntve some of the Fundamental Problems given on the next page. The solutiuns und answers to these are given in the back of the boik. Doing this throuphout the book will help immensely in developing your problem-solving skills 1%19 |. A 1:-1 lec.2.pdf 2.3 VECTOR ADDITION OF FORCES 27 FUNDAMENTAL PROBLEMS* F2-1. Determine the magnitude of the resultant force acting on the screw eye and its direction measured clockwise from the x axis F2-4. Resolve the 30-lb force into components along the r and raves, and determine the magnitude of each of these components 30 Ib ŽAN 6KN 12-1 F2-4 12-2. Two forces act on the hook. Determine the magnitade F2-5. The foroe = 450 Ih acts on the frame. Resolve this force into eomponents acting along members AB and AC, and determine the magnitude of each component. of the…arrow_forwardThe Russian Typhoon-class submarine is 170 m long, witha maximum diameter of 23 m. Its propulsor can deliverup to 80,000 hp to the seawater. Model the submarine asan 8:1 ellipsoid and estimate the maximum speed, in knots,of this ship.arrow_forwardThe center of mass for a human body can be determined by a segmental method. Using cadavers, it is possible to determine the mass of individual body segments (as a proportion of total body mass) and the center of mass for each segment (often expressed as a distance from one end of the segment). Finding the overall body center of mass can be a complex calculation, involving more than 10 body segments. Below, we will look at a simplified model that uses just six segments: head, trunk, two arms, and two legs. Search y X As a percentage of total body mass, the head is 10%, the two arms are 10%, the trunk is 56%, and the two legs are 24%. The center of mass for each segment is given as an (x,y) coordinate, both units in cm: head = (0, 165), arms = (0, 115), trunk = (0, 95), and legs = (0, 35). Assume the body mass for the individual is 88 kg and their total height is 180 cm. Determine they and y coord 99+ H of massarrow_forward
- A periodic Kármán vortex street is formed when an uniform stream flows over a circular cylinder (Figure Q4). By applying method of repeating variables or Buckingham Pi's Theorem, determine a dimensionless relationship for Kármán vortex shedding frequency (fx.) as a function of free-stream speed (V), fluid density (p), fluid viscosity(u), and cylinder diameter (D). Q4 V D Figure Q4arrow_forwardShip whose full length is 100 m is to travel at 10 m/sec. For dynamical similarity, with what velocity should a 1:25 model of the ship be towed?arrow_forwardBlood of density 1,060 kg/m3 and viscosity 0.0034 Pa/s flows through an aorta with radius 0.013 m. The heart beats at a rate of 73 beats/min. A laboratory model of the aorta, consists of pumping water of density 999 kg/m3 and viscosity 0.0011 Pa/s flowing through a pipe of radius 0.010 m. In order to achieve Womersley number similarity calculate the period of the in-vitro cycle. Give your answer in seconds.arrow_forward
- Q4: Use dimensional analysis to show that in a problem involving shallow water waves (Figure 1), both the Froude number (Fr = and the Reynolds number (Re pch. are relevant dimensionless parameters Fr = f (Re). The wave speed c of %3D waves on the surface of a liquid is a function of depth h, gravitational acceleration g, fluid density p, and fluid viscosity u. P. u Figure 1arrow_forward4. The water velocity at a certain point along a 1:10 scale model of a dam spillway is 5 m/s. What is the corresponding prototype velocity if the model and prototype operate in accordance with Froude number similarity? (Ans: 15.8 m/s)arrow_forwardSolve this pls. Same problem with different values already solved on bartleby. You can use it for reference. Here's the link :arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





