
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure of wax formed when lauric acid reacts with
Concept Introduction:
Lipids are
Waxes are the type of nonpolar lipids that contain esters and are formed by the reaction of
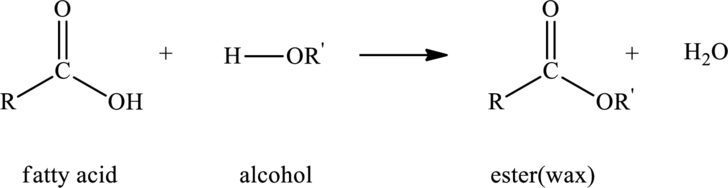
Here,
(b)
Interpretation:
Structure of wax formed from myristic acid and
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 15 Solutions
Principles of General Organic & Biological Chemistry
- Draw the structure of a wax formed from oleic acid and cetyl alcohol (CH3(CH2)14CH2OH).arrow_forwardWhy is it safe for us to consume foods like vinegar that contain acetic acids?arrow_forwardAn unsaturated lipid a. is more soluble in polar solvents than a saturated lipid b. has a lower melting point than a saturated lipid. c. spoils less easily than a saturated lipid. d. is more difficult to digest than a saturated lipid.arrow_forward
- Draw the structure of methyl hexanoatearrow_forwardWhat will happen if you soak your hands in ethyl alcohol or isopropyl alcohol, what will happen? What differentiates the two alcohol? Why does alcohol breaks lipid in the skin of the hand.?arrow_forwardWhy is ethyl alcohol soluble in water?arrow_forward
- safflower oil glyceryl tripalmitate (tripalmitin) beeswax sodium stearate cholesterol ty acid soap triacylalycerol wax GPLarrow_forward17. Match the lipid on the left with its description on the right. 1. lecithin 2. sphingomyelin 3. wax 4. cephalin 5. glycolipid a. An ester of a fatty acid and a high-molecular- weight alcohol other than glycerol. b. A lipid that contains sphingosine, fatty acids, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen-containing compound. I c. A lipid that contains fatty acids, a sugar, and glycerol. d. A lipid that contains glycerol, fatty acids, a phosphate group, and choline. e. A lipid that contains glycerol, fatty acids, a phophate group, and ethanolamine.arrow_forwardPalmitic acid is a(n) _____ fatty acid. a. monounsaturated b. waxy c. saturated d. polyunsaturatedarrow_forward
- Fatty acids are distributed throughout the body, via a time-release/transport molecule created by: a. an esterification reaction with glycerol b. a hydrolytic reaction with methylamine c. an alkylation reaction with butanol d. a carboxylation reaction with lactic acid e. an ether formation reaction with ethylene glycolarrow_forwardAs the number of C=C double bonds in a fatty acid _______, the melting point ____.arrow_forwardThe structure of the fatty acid, palmitoleic acid, is shown below. How would you classify this fatty acid? a. polyunsaturated b. waxy c. monounsaturated d. saturatedarrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning



