
Concept explainers
a)
Profit maximizing price quantity combination and corresponding profits for the monopolist
a)
Explanation of Solution
Demand curve,
Therefore, profits are,
Differentiating the profit equation with respect to
Second order condition, proves that this price and quantity maximizes the profits for a monopolist.
And profits given this price and quantity is,
b)
Nash equilibrium output for two firms operating in Cournot model. Also to compute
market output, price and firms profits.
b)
Explanation of Solution
From the demand function, we get,
Also,
So, profit for the firm 1 ,
Differentiating with respect to
And similarly, profit equation of the firm 2 reveals,
Solving 1 and 2 we get,
Market output will be,
And market price is,
So, at
The profits for firm 1 is,
The profit for firm 2 is,
c)
To find Nash
c)
Explanation of Solution
In case of a Bertrand model, undercutting of prices by both the firms leads to price becoming approximately nil in the given scenario. Hence the price will tend to zero, and quantity will become tending to 150 .
So, price
And Quantity
As there are no cost to production so firms will undercut to a level that at the end of the day both firms will be willing to provide the quantity at price 0 .
Profits for the firm
And market output is,
However the maximum demand is only for 150 units, therefore market output is 150 .
d)
To graph the demand curve for cases in parts (a), (b), (c).
d)
Explanation of Solution
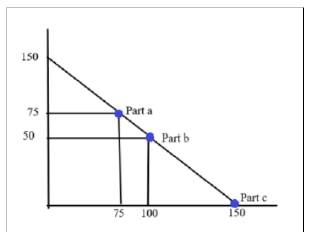
In the above diagram, Price is measured on
In part
In part c, the two firms follows Bertand equilibrium model, quantity produced is 150 units with 0 price per unit.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
- answerarrow_forwardDiscuss the preferred deterrent method employed by the Zambian government to combat tax evasion, monetary fines. As noted in the reading the potential penalty for corporate tax evasion is a fine of 52.5% of the amount evaded plus interest assessed at 5% annually along with a possibility of jail time. In general, monetary fines as a deterrent are preferred to blacklisting of company directors, revoking business operation licenses, or calling for prison sentences. Do you agree with this preference? Should companies that are guilty of tax evasion face something more severe than a monetary fine? Something less severe? Should the fine and interest amount be set at a different rate? If so at why? Provide support and rationale for your responses.arrow_forwardNot use ai pleasearrow_forward
- For the statement below, argue in position for both in favor or opposed to the statement. Incompetent leaders can't be ethical leaders. Traditional leadership theories and moral standards are not adequate to help employees solve complex organizational issues.arrow_forwardpresentation on "Dandelion Insomnia." Poemarrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- "Whether the regulator sells or gives away tradeable emission permits free of charge, the quantities of emissions produced by firms are the same." Assume that there are n identical profit-maximising firms where profit for each firm is given by π(e) with л'(e) > 0; π"(e) < 0 and e denotes emissions. Individual emissions summed over all firms gives E which generates environmental damages D(E). Show that the regulator achieves the optimal level of total pollution through a tradeable emission permit scheme, where the permits are distributed according to the following cases: Case (i) the firm purchases all permits; Case (ii) the firm receives all permits free; and Page 3 of 5 ES30031 Case (iii) the firm purchases a portion of its permits and receives the remainder free of charge.arrow_forwardcompare and/or contrast the two plays we've been reading, Antigone and A Doll's House.arrow_forwardPlease answer step by steparrow_forward
- Suppose there are two firms 1 and 2, whose abatement costs are given by c₁ (e₁) and C2 (е2), where e denotes emissions and subscripts denote the firm. We assume that c{(e) 0 for i = 1,2 and for any level of emission e we have c₁'(e) # c₂' (e). Furthermore, assume the two firms make different contributions towards pollution concentration in a nearby river captured by the transfer coefficients ε₁ and 2 such that for any level of emission e we have C₂'(e) # The regulator does not know the resulting C₁'(e) Τι environmental damages. Using an analytical approach explain carefully how the regulator may limit the concentration of pollution using (i) a Pigouvian tax scheme and (ii) uniform emissions standards. Discuss the cost-effectiveness of both approaches to control pollution.arrow_forwardBill’s father read that each year a car’s value declines by 10%. He also read that a new car’s value declines by 12% as it is driven off the dealer’s lot. Maintenance costs and the costs of “car problems” are only $200 per year during the 2-year warranty period. Then they jump to $750 per year, with an annual increase of $500 per year.Bill’s dad wants to keep his annual cost of car ownership low. The car he prefers cost $30,000 new, and he uses an interest rate of 8%. For this car, the new vehicle warranty is transferrable.(a) If he buys the car new, what is the minimum cost life? What is the minimum EUAC?(b) If he buys the car after it is 2 years old, what is the minimum cost life? What is the minimum EUAC?(c) If he buys the car after it is 4 years old, what is the minimum cost life? What is the minimum EUAC?(d) If he buys the car after it is 6 years old, what is the minimum cost life? What is the minimum EUAC?(e) What strategy do you recommend? Why? Please show each step and formula,…arrow_forwardO’Leary Engineering Corp. has been depreciating a $50,000 machine for the last 3 years. The asset was just sold for 60% of its first cost. What is the size of the recaptured depreciation or loss at disposal using the following depreciation methods?(a) Straight-line with N = 8 and S = 2000(b) Double declining balance with N = 8(c) 40% bonus depreciation with the balance using 7-year MACRS Please show every step and formula, don't use excel. The answer should be (a) $2000 loss, (b) $8000 deo recap, (c) $14257 dep recap, thank you.arrow_forward
 Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an...EconomicsISBN:9781305506381Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. HarrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an...EconomicsISBN:9781305506381Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. HarrisPublisher:Cengage Learning






