
a)
The market price by labeling it P1 on the graph.
a)
Explanation of Solution
As supply is perfectly inelastic in the market, then the market price will be shown on the graph as follows:
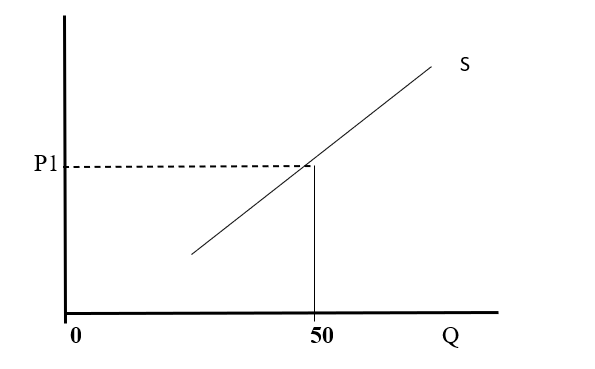
Introduction: The benefits which are obtained by the third party who is not actually buying, selling, or consuming the good are called external benefits such as using a vehicle to travel that reduces the congestion on the road because it provides benefit to other drivers so that they can drive quickly and safely.
b)
MSB, the Socially optimal level of quantity,
b)
Explanation of Solution
- Marginal social benefit is labeled as MSB on the graph and
- Socially optimal level of quantity is labeled as Qs where marginal
social cost and marginal social benefit are equal. - There is a negative externality because hearing music from the concert will not give joy to every person living close to the concert place because they can hate loud music or even it can disturb certain people such as students who study. Therefore, it is a negative externality.
- Yes, there would be a deadweight loss because, in a negative externality, the excessed quantity of output will generate a deadweight loss as the marginal social cost is greater than the marginal social benefit. The shaded area in the graph is a deadweight loss.
Therefore, the graph will be represented as:
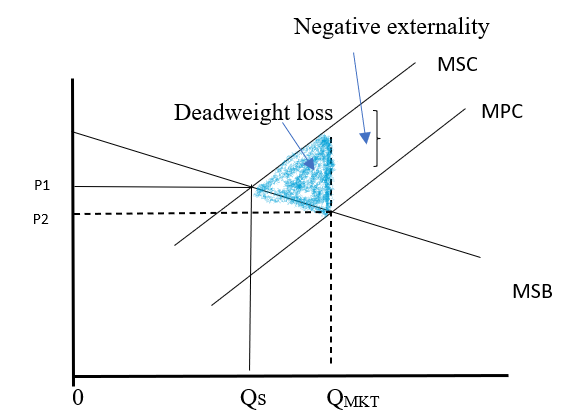
Introduction: Marginal private benefit is the benefit that is obtained by an individual by using an extra unit of the product. And, the marginal social benefit is the benefit that is obtained by the whole society as well as the individual by producing an extra unit of a product.
Marginal private cost is the cost that is incurred by an individual by using an extra unit of the product. And, the marginal social cost is the expense which is incurred by the whole society due to the production of an extra unit of a product.
Chapter 14R Solutions
Krugman's Economics For The Ap® Course

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





