
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781305389892
Author: Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 14, Problem 14TYK
Discuss Concepts During replication, an error uncorrected by proofreading or mismatch repair produces a DNA molecule with a base mismatch at the indicated position:
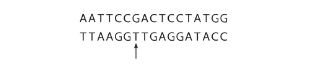
The mismatch results in a mutation. This DNA molecule is received by one of the two daughter cells produced by mitosis. In the next round of replication and division, the mutation appears in only one of the two daughter cells. Develop a hypothesis to explain this observation.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
DNA polymerase occasionally incorporates the wrong nucleotide during DNA
replication. If left unrepaired, the base-pair mismatch that results will lead to
mutation in the next replication. As part of a template strand, the incorporated
wrong base will direct the incorporation of a base complementary to itself, so the
bases on both strands of the DNA at that position will now be different from what
they were before the mismatch event.
The MM-minus strain of yeast does not have a functional mismatch excision repair
system, but it has normal base excision repair and nucleotide excision repair systems.
Which of the following statements is correct about differences in the mutation
spectrum between MMR-minus and wildtype yeast?
More than one answer is correct.
(a) More point mutations will arise in MMR-minus yeast.
Fewer point mutations will arise in MMR-minus yeast as compared with
wildtype.
(b) Of the total point mutations that do occur, the fraction in which G is replaced by
C will be…
You conducted an experiment to determine the mechanism of DNA replication in the hypothetical organism Fungus mungus. Your data shows that synthesis of newly replicated DNA from F. mungus is discontinuous on both strands of the replication fork. Does this result support or not support the hypothesis that F. mungus replicates its DNA by the same mechanism as yeast?
Briefly explain your answer.
DNA repair processes use the old DNA strand as the template to repair mismatched bases on the newly synthesized strand . A yeast strain (yst150) has a mutation on the gene coding for the enzyme responsible for distinguishing between the old and new strand of DNA . How does the mutation rate of strain yst150 compare with the rate of non-mutant (wild-type ) yeast ? Explain your answer .
Chapter 14 Solutions
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Ch. 14.1 - Prob. 1SBCh. 14.2 - Prob. 1SBCh. 14.2 - Prob. 2SBCh. 14.2 - Prob. 3SBCh. 14.2 - Prob. 4SBCh. 14.3 - What is the importance of complementary base...Ch. 14.3 - Why is a primer needed for DNA replication? How is...Ch. 14.3 - DNA polymerase III and DNA polymerase I are used...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 4SBCh. 14.4 - Why is a proofreading mechanism important for DNA...
Ch. 14 - Working on the Amazon River, a biologist isolated...Ch. 14 - Prob. 2TYKCh. 14 - Pyrimidines built from a single carbon ring are:...Ch. 14 - Which of the following statements about DNA...Ch. 14 - Which of the following statements about DNA is...Ch. 14 - Prob. 6TYKCh. 14 - Prob. 7TYKCh. 14 - Prob. 8TYKCh. 14 - Prob. 9TYKCh. 14 - Prob. 10TYKCh. 14 - Discuss Concepts Eukaryotic chromosomes can be...Ch. 14 - Prob. 12TYKCh. 14 - Prob. 13TYKCh. 14 - Discuss Concepts During replication, an error...Ch. 14 - Design an Experiment Design an experiment using...Ch. 14 - Prob. 16TYKCh. 14 - Prob. 1ITDCh. 14 - Prob. 2ITD
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Explain the function of an origin of replication in the replication of DNA, and know how the prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells differ in terms of the number of origins of replication on each chromosome. Explain why replication is different on the two strand at a replication fork, including: how these differences are related to the fact that DNA strands are synthesized in a 5’ to 3’ direction. what is meant by the terms bidirectional replication, and replication bubble. the role of the leading strand, lagging strand, Okazaki fragments, continuous and discontinuous replicationarrow_forwardDNA polymerase occasionally incorporates the wrong nucleotide during DNA replication. If left unrepaired, the base-pair mismatch that results will lead to mutation in the next replication. As part of a template strand, the incorporated wrong base will direct the incorporation of a base complementary to itself, so the bases on both strands of the DNA at that position will now be different from what they were before the mismatch event. The MER-minus strain of yeast does not have a functional mismatch excision repair system, but it has normal base excision repair and nucleotide excision repair systems. Which of the following statements is correct about differences in the mutation spectrum between MER-minus and wildtype yeast? More than one answer is correct. Options: More point mutations will arise in MER-minus yeast. Fewer point mutations will arise in MER-minus yeast as compared with wildtype. Of the total point mutations that…arrow_forwardIn Semi conservative replication: A. After one round of replication of a single molecule of DNA, one DNA molecule will be produced that contains two parental strands of DNA and one DNA molecule will be produced that contains two new (or de novo) strands. B. After one round of replication of a single molecule of DNA, two resulting DNA molecules will be produced both of which contain a mix of both parental and new DNA interspersed on every strand of DNA C. After two rounds of replication of a single molecule of DNA, two resulting DNA molecules will contain both a parental strand and a new strand of DNA and the other two resulting DNA molecules will contain all new (or de novo) DNA D. After two rounds of replication of a single molecule of DNA, one resulting DNA molecule will contain 2 parental strands of DNA and the other three resulting DNA molecules will contain all new (or de novo) DNA E. A and C F. B and Darrow_forward
- DNA repair enzymes preferentially repair mis- matched bases on the newly synthesized DNA strand, using the old DNA strand as a template. If mismatches were instead repaired without regard for which strand served as template, would mismatch repair reduce repli- cation errors? Would such a mismatch repair system result in fewer mutations, more mutations, or the same number of mutations as there would have been without any repair at all? Explain your answers.arrow_forwardConsider Figure 7, which illustrates a point in DNA synthesis for one end of a chromosome, after the lengths of the chromosomes have been replicated, but before telomerase has functioned. (The other end of the chromosome is not shown. A and C mark the midpoint of the chromosome). Each long rectangle represents one strand of DNA. 1. State the locations below as the 5’ or 3’ ends. Location labeled B is: 5’ 3’ Not possible to determine and I have answered below. Location labeled D is: 5’ 3’ None of the above and I have explained my reasoning here.arrow_forwardShown below is a drawing showing the result of an experiment in which an RNA molecule is allowed to mix with genomic DNA that has been denatured by boiling, and the two molecules are allowed to hybridize. The DNA strand is presumed to be the lighter-shaded one on the top. Note that only one strand of DNA is shown. This result was the first evidence for which of the following processes? a Replication b Transcription c Translation d Splicingarrow_forward
- Why is DNA replication is considered a semi-discontinuous process? Explain in detail.arrow_forwardTo promote genetic diversity in bacteria, it has been found that some species have a genetic mechanism that allows them to increase their mutation rate during DNA replication. A scientist hypothesizes that the functions of the following two enzymes would be impacted by this mechanism. In each case, state if you agree and provide a reason for your answer. i) DNA primase ii) DNA polymerase IIIarrow_forwardHuman Fbh1 helicase is important in the process of DNA replication. When a mutation occurs during the production of Fbh1, the result is a mutant Fbh1 that binds at the replication fork and prevents any helicase protein from attaching to the strand. Based on this information and the image shown, what would happen during DNA replication if this mutant helicase were present? A - Topoisomerase would unwind the DNA and an RNA primer would attach to the DNA molecule and initiate replication. The process would then stop at the blue triangle because helicase is needed to separate the strands of DNA. B - Topoisomerase would unwind the DNA, but then the process would stop at the blue triangle because helicase, the RNA primer, would not be able to attach to the DNA molecule and initiate replication. C - The process would begin at the blue triangle when topoisomerase unwinds the DNA and an RNA primer attaches to the DNA molecule and initiates replication. DNA polymerase would begin the synthesis…arrow_forward
- The regulation of replication is essential to genomic stability. Normally, the DNA is replicated just once in every eukaryotic cell cycle (in the S phase). Normal cells produce protein A, which increases in concentration in the S phase. In cells that have a mutated copy of the gene encoding protein A, the protein is not functional, and replication takes place continuously throughout the cell cycle, with the result that cells may have 50 times the normal amount of DNA. Protein B is normally present in G1, but disappears from the cell nucleus during the S phase. In cells with a mutated copy of the gene encoding protein A, the levels of protein B fail to drop in the S phase and, instead, remain high throughout the cell cycle. When the gene for protein B is mutated, noreplication takes place. Propose a mechanism for how protein A and protein B might normally regulate replication so that each cell gets the proper amount of DNA. Explain how mutation of these genes produces the effects just…arrow_forwardWhich of the following statements about the DNA replication is false? a. Synthesis of the new DNA strands is form 39 to 59 b.Synthesis of the new DNA strands is from 59 to 39 c. DNA Unwinds, primase adds RNA primer, DNA polymerases synthesize the new strand and remove the RNA primer d. Many initiation points exist in each eukaryotic chromosome. e. Okazaki fragments are synthesized in the opposite direction from the direction in which the replication for moves.arrow_forwardWhich of the followings statements are true about DNA polymerase? 1.) It can only go in one direction, meaning the lagging strand can't be synthesized continuously. 2.) It cannot start a DNA strand from scratch, so another enzyme is needed to create "primers" as a starting point. 3.) It cannot copy epigenetic marks (such as methyl groups) on its own; these must be "copied" onto the daughter DNA strand by other enzymes after DNA replication. 4.) All of the abovearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning
QCE Biology: Introduction to Gene Expression; Author: Atomi;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a7hydUtCIJk;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY