
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
8th Edition
ISBN: 9780073398174
Author: Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 13.3, Problem 50P
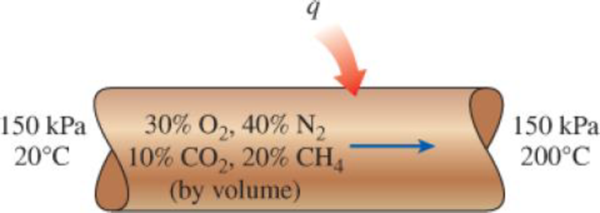
The volumetric analysis of a mixture of gases is 30 percent oxygen, 40 percent nitrogen, 10 percent carbon dioxide, and 20 percent methane. This mixture is heated from 20°C to 200°C while flowing through a tube in which the pressure is maintained at 150 kPa. Determine the heat transfer to the mixture per unit mass of the mixture.
FIGURE P13–52
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
-6-
8 من 8
Mechanical vibration
HW-prob-1
lecture 8 By: Lecturer Mohammed O. attea
The 8-lb body is released from rest a distance xo
to the right of the equilibrium position.
Determine the displacement x as a function of time t,
where t = 0 is the time of release.
c=2.5 lb-sec/ft
wwwww
k-3 lb/in.
8 lb
Prob. -2
Find the value of (c) if the system is critically
damping.
Prob-3
Find Meq and Ceq at point B, Drive eq. of
motion for the system below.
Ш
H
-7~
+
目
T T & T
тт
+
Q For the following plan of building foundation, Determine
immediate settlement at points (A) and (B) knowing that: E,-25MPa,
u=0.3, Depth of foundation (D) =1m, Depth of layer below base level
of foundation (H)=10m.
3m
2m
100kPa
A
2m
150kPa
5m
200kPa
B
W
PE
2
43
R² 80 + 10 + kr³ Ø8=0 +0
R²+J+ kr200
R² + J-) + k r² = 0
kr20
kr20
8+
W₁ =
= 0
R²+1)
R²+J+)
4
lec 8.pdf
Mechanical vibration
lecture 6
By: Lecturer Mohammed C. Attea
HW1 (Energy method)
Find equation of motion and natural frequency for the system shown in fig. by energy
method.
m. Jo
000
HW2// For the system Fig below find
1-F.B.D
2Eq.of motion
8 wn
4-0 (1)
-5-
m
Chapter 13 Solutions
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Ch. 13.3 - Consider a mixture of several gases of identical...Ch. 13.3 - Somebody claims that the mass and mole fractions...Ch. 13.3 - The sum of the mole fractions for an ideal-gas...Ch. 13.3 - Consider a mixture of two gases. Can the apparent...Ch. 13.3 - What is the apparent molar mass for a gas mixture?...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 6PCh. 13.3 - Consider a mixture of two gases A and B. Show that...Ch. 13.3 - The composition of moist air is given on a molar...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 9PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 10P
Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 11PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 12PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13PCh. 13.3 - Is a mixture of ideal gases also an ideal gas?...Ch. 13.3 - Express Daltons law of additive pressures. Does...Ch. 13.3 - Express Amagats law of additive volumes. Does this...Ch. 13.3 - How is the P-v-T behavior of a component in an...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 18PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 19PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 20PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 21PCh. 13.3 - Consider a rigid tank that contains a mixture of...Ch. 13.3 - Is this statement correct? The volume of an...Ch. 13.3 - Is this statement correct? The temperature of an...Ch. 13.3 - Is this statement correct? The pressure of an...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 26PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 27PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 28PCh. 13.3 - 13–29 A gas mixture at 350 K and 300 kPa has the...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 30PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 31PCh. 13.3 - A rigid tank that contains 2 kg of N2 at 25C and...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 33PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 34PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 35PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 36PCh. 13.3 - A 30 percent (by mass) ethane and 70 percent...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 38PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 39PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 40PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 41PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 42PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 43PCh. 13.3 - Is the total internal energy of an ideal-gas...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 45PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 46PCh. 13.3 - 13–47C Is the total internal energy change of an...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 48PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 49PCh. 13.3 - The volumetric analysis of a mixture of gases is...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 52PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 53PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 54PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 55PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 56PCh. 13.3 - An insulated tank that contains 1 kg of O2at 15C...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 59PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 60PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 61PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 62PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 63PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 64PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 66PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 67PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 69PCh. 13.3 - A pistoncylinder device contains 6 kg of H2 and 21...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 71PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 72PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 73PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 74PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 75PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 76PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 77PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 78PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 80PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 81PCh. 13.3 - Fresh water is obtained from seawater at a rate of...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 83PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 84RPCh. 13.3 - The products of combustion of a hydrocarbon fuel...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 89RPCh. 13.3 - Prob. 91RPCh. 13.3 - Prob. 92RPCh. 13.3 - A spring-loaded pistoncylinder device contains a...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 94RPCh. 13.3 - Reconsider Prob. 1395. Calculate the total work...Ch. 13.3 - A rigid tank contains a mixture of 4 kg of He and...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 97RPCh. 13.3 - Prob. 100RPCh. 13.3 - An ideal-gas mixture whose apparent molar mass is...Ch. 13.3 - 13–102 An ideal-gas mixture consists of 2 kmol of...Ch. 13.3 - An ideal-gas mixture consists of 2 kmol of N2and 4...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 104FEPCh. 13.3 - Prob. 105FEPCh. 13.3 - An ideal-gas mixture consists of 3 kg of Ar and 6...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 107FEPCh. 13.3 - Prob. 108FEPCh. 13.3 - Prob. 109FEPCh. 13.3 - Prob. 110FEP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The hose supplying the cylinder operating the bucket of a large excavator has fluid at 1000 psi flowing at 5 gpm. What is theavailable power in the line?arrow_forwardQ For the following plan of building foundation, Determine immediate settlement at points (A) and (B) knowing that: E,-25MPa, u=0.3, Depth of foundation (D) =1m, Depth of layer below base level of foundation (H)=10m. 3m 2m 100kPa A 2m 150kPa 5m 200kPa Barrow_forwardGiven the following data for crack rocker mechanism. If θ2 = 4π/3 and ω2 = 1 rad/s, Determine all possible values of ω4 and ω3 analytically. The lengths of links are a = 2, b = 8, c = 7 and d = 9 in cm.arrow_forward
- Q6] (20 Marks) Select the most suitable choice for the following statements: modo digi -1A 10 af5 1 -The copper-based alloy which is responded to age hardening is a) copper-nickel b) aluminum bronze c) copper - beryllium d) brass besincaluy 2- Highly elastic polymers may experience elongations to greater than.... b) 500% bromsia-P c) 1000%. d) 1200% 15m or -2 a)100% 3- The cooling rate of quenching the steel in saltwater will be ......the cooling rate of quenching ir c) faster than sold) none of them a) slower than 4- Adding of a) Cr b) the same as ...... Will lead to stabilize the b) Mo 10 austenite in steel. c) Nimble avolls 1d) Sized loloin nl 5- The adjacent linear chains of crosslinked polymers are joined one to another at various positic DIR... by.........bonds c) covalent noisqo gd) ionic lg 120M 6- For the ceramic with coordination number 6 the cation to anion radius ratio will be a) Van der Waals a) 0.155-0.225 a) linear b) hydrogen (b) 0.225-0.414 c) 0.414 0.732 ..polymers.…arrow_forwardExamine Notes: Attempt Six Questions Only. rever necessa , Q1] (20 Marks) Answer with true (T) or false (F), corrects the wrong phrases, and gives sho reasons for correct and corrected statements: 1- High chromium irons are basically grey cast irons alloyed with 12 to 30 % Cr. yous board-19qgo orT-1 2- The drawbacks of Al- Li alloys are their high young modulus and high density.&M 0) (0 3- Vulcanized rubbers are classified under thermoplastic polymers. 4- Diamond is a stable carbon polymorph at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. ( 5- The metallic ions of ceramic are called anions, and they are positively charged. yldgiH-S 69001(6arrow_forwardH.W 5.4 Calculate the load that will make point A move to the left by 6mm, E-228GPa. The diameters of the rods are as shown in fig. below. 2P- PA 50mm B 200mm 2P 0.9m 1.3marrow_forward
- d₁ = = Two solid cylindrical road AB and BC are welded together at B and loaded as shown. Knowing that 30mm (for AB) and d₂ 50mm (for BC), find the average normal stress in each road and the total deformation of road AB and BC. E=220GPa H.W 5.3 60kN A For the previous example calculate the value of force P so that the point A will not move, and what is the total length of road AB at that force? P◄ A 125kN 125kN 0.9m 125kN 125kN 0.9m B B 1.3m 1.3marrow_forwardClass: B Calculate the load that will make point A move to the left by 6mm, E-228GPa The cross sections of the rods are as shown in fig. below. 183 P- Solution 1.418mm 200mm 80mm 3P- 18.3 A 080mm B 200mm 3P- 0.9m إعدادات العرض 1.3m 4.061mmarrow_forwardH.W6 Determine the largest weight W that can be supported by two wires shown in Fig. P109. The stress in either wire is not to exceed 30 ksi. The cross- sectional areas of wires AB and AC are 0.4 in2 and 0.5 in2, respectively. 50° 30° Warrow_forward
- Find equation of motion and natural frequency for the system shown in fig. by energy method. H.W2// For the system Fig below find 1-F.B.D 2-Eq.of motion 8wn 4-0 (5) m. Jo marrow_forward2. Read the following Vernier caliper measurements. (The scales have been enlarged for easier reading.) The Vernier caliper is calibrated in metric units. (a) 0 1 2 3 4 5 سلسلسله (b) 1 2 3 4 5 6 سلسل (c) 1 23456 (d) 1 2 3 4 5 6 سلسلسarrow_forwardExplain why on the interval 0<x<1000 mm and 1000<x<2000mm, Mt is equal to positive 160 Nm, but at x= 0mm and x=1000mm Mt is equal to -160 Nm (negative value!). What is the reason for the sign change of Mt?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Thermodynamics - Chapter 3 - Pure substances; Author: Engineering Deciphered;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bTMQtj13yu8;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY