
Essential Calculus: Early Transcendentals
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9781133112280
Author: James Stewart
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 13.1, Problem 14E
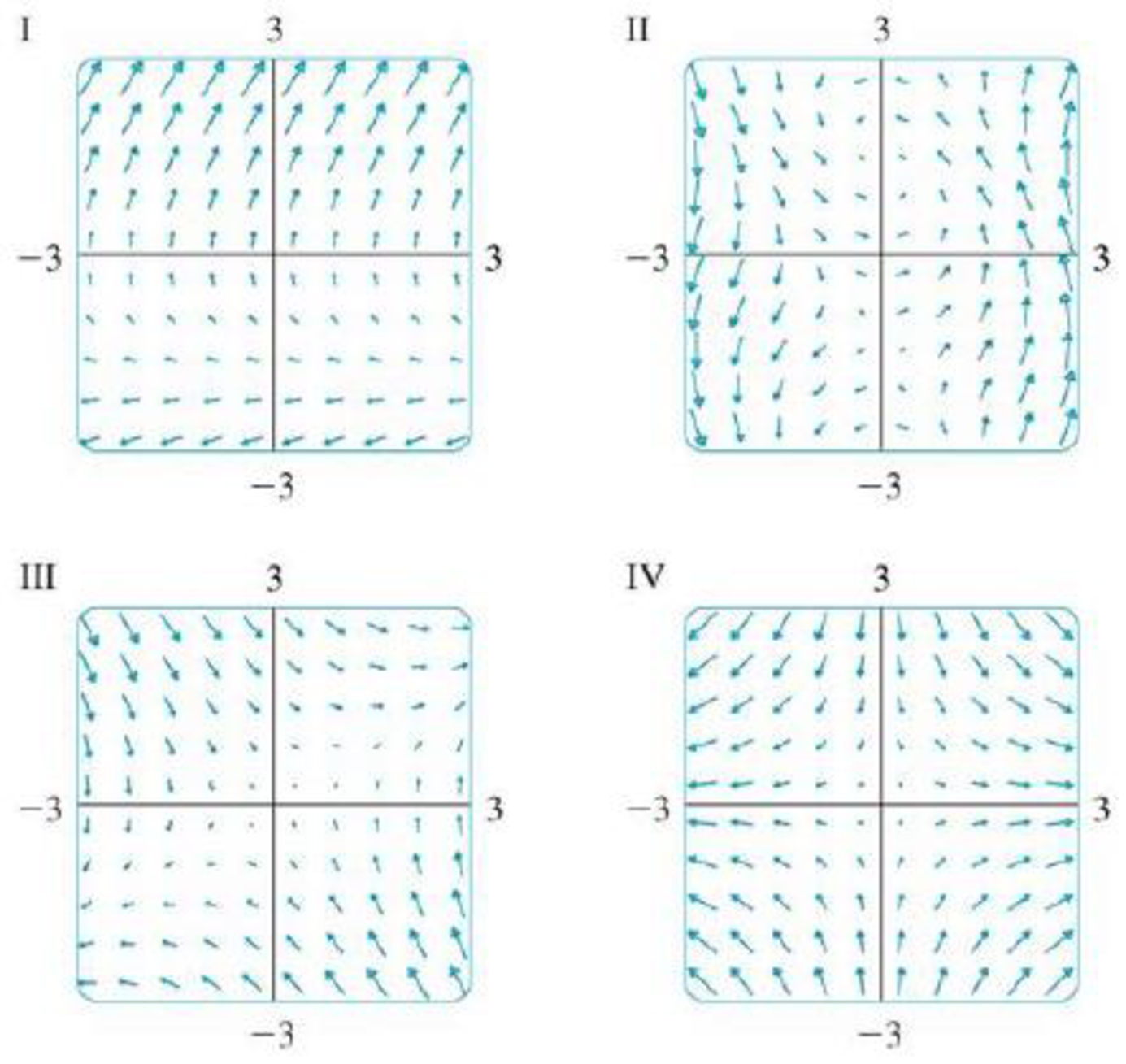
Match the
14. F(x, y) = ⟨cos(x + y), x⟩
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
(b) Find the (instantaneous) rate of change of y at x = 5.
In the previous part, we found the average rate of change for several intervals of decreasing size starting at x = 5. The instantaneous rate of
change of fat x = 5 is the limit of the average rate of change over the interval [x, x + h] as h approaches 0. This is given by the derivative in the
following limit.
lim
h→0
-
f(x + h) − f(x)
h
The first step to find this limit is to compute f(x + h). Recall that this means replacing the input variable x with the expression x + h in the rule
defining f.
f(x + h) = (x + h)² - 5(x+ h)
=
2xh+h2_
x² + 2xh + h² 5✔
-
5
)x - 5h
Step 4
-
The second step for finding the derivative of fat x is to find the difference f(x + h) − f(x).
-
f(x + h) f(x) =
= (x²
x² + 2xh + h² -
])-
=
2x
+ h² - 5h
])x-5h) - (x² - 5x)
=
]) (2x + h - 5)
Macbook Pro
Evaluate the integral using integration by parts.
Sx² cos
(9x) dx
Let f be defined as follows.
y = f(x) = x² - 5x
(a) Find the average rate of change of y with respect to x in the following intervals.
from x = 4 to x = 5
from x = 4 to x = 4.5
from x = 4 to x = 4.1
(b) Find the (instantaneous) rate of change of y at x = 4.
Need Help?
Read It
Master It
Chapter 13 Solutions
Essential Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Ch. 13.1 - Sketch the vector field F by drawing a diagram...Ch. 13.1 - Sketch the vector field F by drawing a diagram...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 3ECh. 13.1 - Prob. 4ECh. 13.1 - Prob. 5ECh. 13.1 - Prob. 6ECh. 13.1 - Prob. 7ECh. 13.1 - Sketch the vector field F by drawing a diagram...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 9ECh. 13.1 - Sketch the vector field F by drawing a diagram...
Ch. 13.1 - Match the vector fields F with the plots labeled...Ch. 13.1 - Match the vector fields F with the plots labeled...Ch. 13.1 - Match the vector fields F with the plots labeled...Ch. 13.1 - Match the vector fields F with the plots labeled...Ch. 13.1 - Match the vector fields F on 3 with the plots...Ch. 13.1 - Match the vector fields F on 3 with the plots...Ch. 13.1 - Match the vector fields F on 3 with the plots...Ch. 13.1 - Match the vector fields F on 3 with the plots...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 21ECh. 13.1 - Prob. 22ECh. 13.1 - Prob. 23ECh. 13.1 - Prob. 24ECh. 13.1 - Find the gradient vector field f of f and sketch...Ch. 13.1 - Find the gradient vector field f of f and sketch...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 29ECh. 13.1 - At time t = 1, a particle is located at position...Ch. 13.1 - The flow lines (or streamlines) of a vector field...Ch. 13.1 - (a) Sketch the vector field F(x, y) = i + x j and...Ch. 13.2 - Evaluate the line integral, where C is the given...Ch. 13.2 - Evaluate the line integral, where C is the given...Ch. 13.2 - Evaluate the line integral, where C is the given...Ch. 13.2 - Evaluate the line integral, where C is the given...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 5ECh. 13.2 - Evaluate the line integral, where C is the given...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 7ECh. 13.2 - Evaluate the line integral, where C is the given...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 9ECh. 13.2 - Evaluate the line integral, where C is the given...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 11ECh. 13.2 - Prob. 12ECh. 13.2 - Prob. 13ECh. 13.2 - Prob. 14ECh. 13.2 - Evaluate the line integral, where C is the given...Ch. 13.2 - Evaluate the line integral, where C is the given...Ch. 13.2 - Let F be the vector field shown in the figure. (a)...Ch. 13.2 - The figure shows a vector field F and two curves...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 19ECh. 13.2 - Evaluate the line integral CFdr, where C is given...Ch. 13.2 - Evaluate the line integral C F dr, where C is...Ch. 13.2 - Evaluate the line integral C F dr, where C is...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 23ECh. 13.2 - Use a calculator or CAS to evaluate the line...Ch. 13.2 - (a) Find the work done by the force field F(x, y)...Ch. 13.2 - A thin wire is bent into the shape of a semicircle...Ch. 13.2 - A thin wire has the shape of the first-quadrant...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 33ECh. 13.2 - Prob. 34ECh. 13.2 - Prob. 35ECh. 13.2 - Prob. 36ECh. 13.2 - Prob. 37ECh. 13.2 - Prob. 38ECh. 13.2 - Find the work done by the force field F(x, y, z) =...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 40ECh. 13.2 - Prob. 41ECh. 13.2 - Prob. 42ECh. 13.2 - Prob. 43ECh. 13.2 - Prob. 44ECh. 13.2 - (a) Show that a constant force field does zero...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 45ECh. 13.2 - Prob. 46ECh. 13.2 - Experiments show that a steady current I in a long...Ch. 13.3 - The figure shows a curve C and a contour map of a...Ch. 13.3 - A table of values of a function f with continuous...Ch. 13.3 - Determine whether or not F is a conservative...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 4ECh. 13.3 - Prob. 5ECh. 13.3 - Prob. 6ECh. 13.3 - Determine whether or not F is a conservative...Ch. 13.3 - Determine whether or not F is a conservative...Ch. 13.3 - Determine whether or not F is a conservative...Ch. 13.3 - Determine whether or not F is a conservative...Ch. 13.3 - (a) Find a function f such that F = f and (b) use...Ch. 13.3 - (a) Find a function f such that F = f and (b) use...Ch. 13.3 - (a) Find a function f such that F = f and (b) use...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 14ECh. 13.3 - Prob. 15ECh. 13.3 - (a) Find a function f such that F = f and (b) use...Ch. 13.3 - Show that the line integral is independent of path...Ch. 13.3 - Show that the line integral is independent of path...Ch. 13.3 - Find the work done by the force field F in moving...Ch. 13.3 - Find the work done by the force field F in moving...Ch. 13.3 - Is the vector field shown in the figure...Ch. 13.3 - Is the vector field shown in the figure...Ch. 13.3 - Let F = f, where f(x, y) = sin(x 2y). Find...Ch. 13.3 - Show that if the vector field F = P i + Q j + R k...Ch. 13.3 - Use Exercise 25 to show that the line integral...Ch. 13.3 - Determine whether or not the given set is (a)...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 28ECh. 13.3 - Prob. 29ECh. 13.3 - Determine whether or not the given set is (a)...Ch. 13.3 - Let F(x, y) = yi+xjx2+y2 (a) Show that P/y=Q/x....Ch. 13.3 - (a) Suppose that F is an inverse square force...Ch. 13.4 - Evaluate the line integral by two methods: (a)...Ch. 13.4 - Evaluate the line integral by two methods: (a)...Ch. 13.4 - Evaluate the line integral by two methods: (a)...Ch. 13.4 - Evaluate the line integral by two methods: (a)...Ch. 13.4 - Use Greens Theorem to evaluate the line integral...Ch. 13.4 - Use Greens Theorem to evaluate the line integral...Ch. 13.4 - Use Greens Theorem to evaluate the line integral...Ch. 13.4 - Use Greens Theorem to evaluate the line integral...Ch. 13.4 - Use Greens Theorem to evaluate the line integral...Ch. 13.4 - Use Greens Theorem to evaluate the line integral...Ch. 13.4 - Use Greens Theorem to evaluate C F dr. (Check the...Ch. 13.4 - Use Greens Theorem to evaluate C F dr. (Check the...Ch. 13.4 - Use Greens Theorem to evaluate C F dr. (Check the...Ch. 13.4 - Use Greens Theorem to evaluate C F dr. (Check the...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 17ECh. 13.4 - A particle starts at the point (2, 0), moves along...Ch. 13.4 - Use one of the formulas in (5) to find the area...Ch. 13.4 - If a circle C with radius 1 rolls along the...Ch. 13.4 - (a) If C is the line segment connecting the point...Ch. 13.4 - Let D be a region bounded by a simple closed path...Ch. 13.4 - Use Exercise 22 to find the centroid of a...Ch. 13.4 - Use Exercise 22 to find the centroid of the...Ch. 13.4 - A plane lamina with constant density (x, y) = ...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 26ECh. 13.4 - Use the method of Example 5 to calculate C F dr,...Ch. 13.4 - Calculate C F dr, where F(x, y) = x2 + y, 3x y2...Ch. 13.4 - If F is the vector field of Example 5, show that C...Ch. 13.4 - Complete the proof of the special case of Greens...Ch. 13.4 - Use Greens Theorem to prove the change of...Ch. 13.5 - Find (a) the curl and (b) the divergence of the...Ch. 13.5 - Find (a) the curl and (b) the divergence of the...Ch. 13.5 - Find (a) the curl and (b) the divergence of the...Ch. 13.5 - Find (a) the curl and (b) the divergence of the...Ch. 13.5 - Find (a) the curl and (b) the divergence of the...Ch. 13.5 - Find (a) the curl and (b) the divergence of the...Ch. 13.5 - Find (a) the curl and (b) the divergence of the...Ch. 13.5 - The vector field F is shown in the xy-plane and...Ch. 13.5 - The vector field F is shown in the xy-plane and...Ch. 13.5 - Let f be a scalar field and F a vector field....Ch. 13.5 - Determine whether or not the vector field is...Ch. 13.5 - Determine whether or not the vector field is...Ch. 13.5 - Determine whether or not the vector field is...Ch. 13.5 - Determine whether or not the vector field is...Ch. 13.5 - Determine whether or not the vector field is...Ch. 13.5 - Determine whether or not the vector field is...Ch. 13.5 - Is there a vector field G on 3 such that curl G =...Ch. 13.5 - Prob. 18ECh. 13.5 - Prob. 19ECh. 13.5 - Prob. 20ECh. 13.5 - Prove the identity, assuming that the appropriate...Ch. 13.5 - Prove the identity, assuming that the appropriate...Ch. 13.5 - Prob. 23ECh. 13.5 - Prob. 24ECh. 13.5 - Prob. 25ECh. 13.5 - Prob. 26ECh. 13.5 - Prob. 27ECh. 13.5 - Prob. 28ECh. 13.5 - Prob. 29ECh. 13.5 - Let r = x i + y j + z k and r = |r|. 32. If F =...Ch. 13.5 - Prob. 31ECh. 13.5 - Prob. 32ECh. 13.5 - Prob. 33ECh. 13.5 - Prob. 34ECh. 13.5 - Prob. 35ECh. 13.5 - Maxwells equations relating the electric field E...Ch. 13.6 - Identify the surface with the given vector...Ch. 13.6 - Identify the surface with the given vector...Ch. 13.6 - Prob. 3ECh. 13.6 - Prob. 4ECh. 13.6 - Match the equations with the graphs labeled IIV...Ch. 13.6 - Match the equations with the graphs labeled IIV...Ch. 13.6 - Prob. 13ECh. 13.6 - Match the equations with the graphs labeled IIV...Ch. 13.6 - Find a parametric representation for the surface....Ch. 13.6 - Prob. 16ECh. 13.6 - Find a parametric representation for the surface....Ch. 13.6 - Find a parametric representation for the surface....Ch. 13.6 - Find a parametric representation for the surface....Ch. 13.6 - Find a parametric representation for the surface....Ch. 13.6 - Find a parametric representation for the surface....Ch. 13.6 - Find a parametric representation for the surface....Ch. 13.6 - Find parametric equations for the surface obtained...Ch. 13.6 - Find parametric equations for the surface obtained...Ch. 13.6 - The surface with parametric equations...Ch. 13.6 - Find an equation of the tangent plane to the given...Ch. 13.6 - Prob. 30ECh. 13.6 - Prob. 31ECh. 13.6 - Prob. 32ECh. 13.6 - Find the area of the surface. 39. The part of the...Ch. 13.6 - Prob. 34ECh. 13.6 - Find the area of the surface. 41. The part of the...Ch. 13.6 - Find the area of the surface. 42. The part of the...Ch. 13.6 - Prob. 37ECh. 13.6 - Prob. 38ECh. 13.6 - Prob. 39ECh. 13.6 - Prob. 41ECh. 13.6 - Find the area of the surface. 40.The part of the...Ch. 13.6 - Find the area of the surface. 48.The helicoid (or...Ch. 13.6 - Find the area of the surface. 43.The surface with...Ch. 13.6 - Find the area of the surface. 50.The part of the...Ch. 13.6 - If the equation of a surfaceSis z =f(x,y),...Ch. 13.6 - Find the area of the surface correct to four...Ch. 13.6 - Find the area of the surface correct to four...Ch. 13.6 - Find, to four decimal places, the area of the part...Ch. 13.6 - Find the area of the surface with vector equation...Ch. 13.6 - (a) Show that the parametric equations x...Ch. 13.6 - (a) Show that the parametric equationsx = acosh u...Ch. 13.6 - Find the area of the part of the spherex2+y2+ z2=...Ch. 13.6 - The figure shows the surface created when the...Ch. 13.6 - Use Definition 6 and the parametric equations for...Ch. 13.6 - Use Formula 10 to find the area of the surface...Ch. 13.6 - Use Formula 10 to find the area of the surface...Ch. 13.7 - Let S be the boundary surface of the box enclosed...Ch. 13.7 - A surface S consists of the cylinderx2+ y2=1, 1 z...Ch. 13.7 - Prob. 3ECh. 13.7 - Suppose that f(x,y,z)=g(x2+y2+z2), where g is a...Ch. 13.7 - Evaluate the surface integral. 5. s (x + y + z)...Ch. 13.7 - Evaluate the surface integral. 6. s xyz dS, Sis...Ch. 13.7 - Evaluate the surface integral. 7. s y dS,Sis the...Ch. 13.7 - Evaluate the surface integral. 8.s (x2+ y2)dS, Sis...Ch. 13.7 - Evaluate the surface integral. 9. s x2yz dS, Sis...Ch. 13.7 - Evaluate the surface integral. 10. s xz dS, S is...Ch. 13.7 - Evaluate the surface integral. 11. s x dS, S is...Ch. 13.7 - Evaluate the surface integral. 12. s y dS, S is...Ch. 13.7 - Evaluate the surface integral. Sx2z2dS, S is the...Ch. 13.7 - Evaluate the surface integral. SzdS, S is the...Ch. 13.7 - Evaluate the surface integral. 15. SydS, S is the...Ch. 13.7 - Evaluate the surface integral. 16. Sy2dS, S is the...Ch. 13.7 - Evaluate the surface integral. 17. s (x2z +...Ch. 13.7 - Evaluate the surface integral. 19. S(z+x2y)dS, S...Ch. 13.7 - Evaluate the surface integral. 19. s xz dS, S is...Ch. 13.7 - Evaluate the surface integral. 20. s (x2 + y2 +...Ch. 13.7 - Evaluate the surface integral s F dS for the...Ch. 13.7 - Evaluate the surface integral s F dS for the...Ch. 13.7 - Evaluate the surface integral s F dS for the...Ch. 13.7 - Evaluate the surface integral s F dS for the...Ch. 13.7 - Evaluate the surface integral SFdS for the given...Ch. 13.7 - Evaluate the surface integral SFdS for the given...Ch. 13.7 - Evaluate the surface integral sFdS for the given...Ch. 13.7 - Evaluate the surface integral SFdS for the given...Ch. 13.7 - Evaluate the surface integral sFdS for the given...Ch. 13.7 - Evaluate the surface integral SFdS for the given...Ch. 13.7 - Evaluate the surface integral SFdS for the given...Ch. 13.7 - Evaluate the surface integral SFdS for the given...Ch. 13.7 - Find the value of Sx2y2z2dS correct to four...Ch. 13.7 - Find a formula for s F dS similar to Formula 10...Ch. 13.7 - Find a formula for s F dS similar to Formula 10...Ch. 13.7 - Find the center of mass of the hemisphere x2 + y2...Ch. 13.7 - Find the mass of a thin funnel in the shape of a...Ch. 13.7 - (a) Give an integral expression for the moment of...Ch. 13.7 - Let S be the part of the sphere x2 + y2 + z2 = 25...Ch. 13.7 - Prob. 41ECh. 13.7 - Prob. 42ECh. 13.7 - Use Gausss Law to find the charge contained in the...Ch. 13.7 - Use Gausss Law to find the charge enclosed by the...Ch. 13.7 - The temperature at the point (x, y, z) in a...Ch. 13.7 - Prob. 46ECh. 13.7 - Let F be an inverse square field, that is, |F(r) =...Ch. 13.8 - Use Stokes Theorem to evaluate ScurlFdS. 1....Ch. 13.8 - Use Stokes Theorem to evaluate ScurlFdS. 2....Ch. 13.8 - Use Stokes Theorem to evaluate s curl F dS. 4....Ch. 13.8 - F(x, y, z) = xyz i + xy j + x2yz k. S consists of...Ch. 13.8 - Use Stokes Theorem to evaluate c F dr. In each...Ch. 13.8 - Use Stokes Theorem to evaluate c F dr. In each...Ch. 13.8 - Use Stokes Theorem to evaluate CFdr. In each case...Ch. 13.8 - Use Stokes Theorem to evaluate CFdr. In each case...Ch. 13.8 - (a) Use Stokes Theorem to evaluate c F dr, where...Ch. 13.8 - (a) Use Stokes Theorem to evaluate c F dr, where...Ch. 13.8 - Prob. 11ECh. 13.8 - Verify that Stokes Theorem is true for the given...Ch. 13.8 - Verify that Stokes Theorem is true for the given...Ch. 13.8 - Let C be a simple closed smooth curve that lies in...Ch. 13.8 - A particle moves along line segments from the...Ch. 13.8 - Evaluate c (y + sin x) dx + (z2 + cos y) dy + x3...Ch. 13.8 - Prob. 17ECh. 13.8 - Prob. 18ECh. 13.9 - Verify that the Divergence Theorem is true for the...Ch. 13.9 - Verify that the Divergence Theorem is true for the...Ch. 13.9 - Verify that the Divergence Theorem is true for the...Ch. 13.9 - Prob. 4ECh. 13.9 - Prob. 5ECh. 13.9 - Prob. 6ECh. 13.9 - Use the Divergence Theorem to calculate the...Ch. 13.9 - Use the Divergence Theorem to calculate the...Ch. 13.9 - Use the Divergence Theorem to calculate the...Ch. 13.9 - Prob. 10ECh. 13.9 - Use the Divergence Theorem to calculate the...Ch. 13.9 - Use the Divergence Theorem to calculate the...Ch. 13.9 - Prob. 13ECh. 13.9 - Prob. 14ECh. 13.9 - Use the Divergence Theorem to evaluate s F dS,...Ch. 13.9 - Prob. 18ECh. 13.9 - Prob. 19ECh. 13.9 - Prob. 20ECh. 13.9 - Prob. 21ECh. 13.9 - Prob. 22ECh. 13.9 - Prob. 23ECh. 13.9 - Prob. 24ECh. 13.9 - Prob. 25ECh. 13.9 - Prob. 26ECh. 13.9 - Prob. 27ECh. 13.9 - Prob. 28ECh. 13.9 - Prob. 29ECh. 13.9 - Prob. 30ECh. 13 - Prob. 1RCCCh. 13 - Prob. 2RCCCh. 13 - Prob. 3RCCCh. 13 - (a) Define the line integral of a vector field F...Ch. 13 - Prob. 5RCCCh. 13 - Prob. 6RCCCh. 13 - Prob. 7RCCCh. 13 - Prob. 8RCCCh. 13 - Prob. 9RCCCh. 13 - Prob. 10RCCCh. 13 - Prob. 11RCCCh. 13 - Prob. 12RCCCh. 13 - Prob. 13RCCCh. 13 - Prob. 14RCCCh. 13 - State the Divergence Theorem.Ch. 13 - In what ways are the Fundamental Theorem for Line...Ch. 13 - Prob. 1RQCh. 13 - Prob. 2RQCh. 13 - Prob. 3RQCh. 13 - Prob. 4RQCh. 13 - Prob. 5RQCh. 13 - Prob. 6RQCh. 13 - Prob. 7RQCh. 13 - Prob. 8RQCh. 13 - Prob. 9RQCh. 13 - Prob. 10RQCh. 13 - Prob. 11RQCh. 13 - Prob. 12RQCh. 13 - A vector field F, a curve C, and a point P are...Ch. 13 - Prob. 2RECh. 13 - Prob. 3RECh. 13 - Prob. 4RECh. 13 - Prob. 5RECh. 13 - Prob. 6RECh. 13 - Prob. 7RECh. 13 - Prob. 8RECh. 13 - Prob. 9RECh. 13 - Find the work done by the force field F(x, y, z) =...Ch. 13 - Prob. 11RECh. 13 - Show that F is a conservative vector field. Then...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13RECh. 13 - Show that F is a conservative and use this fact to...Ch. 13 - Verify that Greens Theorem is true for the line...Ch. 13 - Prob. 16RECh. 13 - Prob. 17RECh. 13 - Prob. 18RECh. 13 - Prob. 19RECh. 13 - Prob. 20RECh. 13 - Prob. 21RECh. 13 - If f and g are twice differentiable functions,...Ch. 13 - If f is a harmonic function, that is, 2f = 0, show...Ch. 13 - Prob. 24RECh. 13 - Find the area of the part of the surface z = x2 +...Ch. 13 - (a) Find an equation of the tangent plane at the...Ch. 13 - Prob. 27RECh. 13 - Prob. 28RECh. 13 - Prob. 29RECh. 13 - Prob. 30RECh. 13 - Prob. 31RECh. 13 - Prob. 32RECh. 13 - Prob. 33RECh. 13 - Prob. 34RECh. 13 - Verify that the Divergence Theorem is true for the...Ch. 13 - Compute the outward flux of F(x, y, z) =...Ch. 13 - Let F(x, y) = (2x3+2xy22y)i+(2y3+2x2y+2x)jx2+y2...Ch. 13 - Prob. 38RECh. 13 - If the components of F have continuous second...Ch. 13 - Prob. 39RE
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, calculus and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Velocity of a Ball Thrown into the Air The position function of an object moving along a straight line is given by s = f(t). The average velocity of the object over the time interval [a, b] is the average rate of change of f over [a, b]; its (instantaneous) velocity at t = a is the rate of change of f at a. A ball is thrown straight up with an initial velocity of 128 ft/sec, so that its height (in feet) after t sec is given by s = f(t) = 128t - 16t². (a) What is the average velocity of the ball over the following time intervals? [3,4] [3, 3.5] [3, 3.1] ft/sec ft/sec ft/sec (b) What is the instantaneous velocity at time t = 3? ft/sec (c) What is the instantaneous velocity at time t = 7? ft/sec Is the ball rising or falling at this time? O rising falling (d) When will the ball hit the ground? t = sec Need Help? Read It Watch Itarrow_forwardpractice problem please help!arrow_forwardpractice problem please help!arrow_forward
- Find the slope of the tangent line to the graph of the function at the given point. m = 8 f(x) = 7x at (1,3) Determine an equation of the tangent line. y = Need Help? Read It Watch Itarrow_forwardFind the slope of the tangent line to the graph of the function at the given point. f(x) = -4x + 5 at (-1, 9) m Determine an equation of the tangent line. y = Need Help? Read It Watch It SUBMIT ANSWERarrow_forwardFind the slope of the tangent line to the graph of the function at the given point. f(x) = 5x-4x² at (-1, -9) m Determine an equation of the tangent line. y = Need Help? Read It Master It SUBMIT ANSWERarrow_forward
- For what value of A and B the function f(x) will be continuous everywhere for the given definition?..arrow_forward2. [-/1 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES SESSCALCET2 6.4.006.MI. Use the Table of Integrals to evaluate the integral. (Remember to use absolute values where appropriate. Use C for the constant of integration.) 7y2 y² 11 dy Need Help? Read It Master It SUBMIT ANSWER 3. [-/1 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES SESSCALCET2 6.4.009. Use the Table of Integrals to evaluate the integral. (Remember to use absolute values where appropriate. Use C for the constant of integration.) tan³(12/z) dz Need Help? Read It Watch It SUBMIT ANSWER 4. [-/1 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES SESSCALCET2 6.4.014. Use the Table of Integrals to evaluate the integral. (Use C for the constant of integration.) 5 sinб12x dx Need Help? Read Itarrow_forwardPlease refer belowarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Cengage
01 - What Is an Integral in Calculus? Learn Calculus Integration and how to Solve Integrals.; Author: Math and Science;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BHRWArTFgTs;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY