
Managerial Accounting
17th Edition
ISBN: 9781260247787
Author: Ray H. Garrison, Eric W. Noreen, Peter C. Brewer
Publisher: RENT MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 13, Problem 22P
PROBLEM 12-22 Special Order Decisions LO12-4
Polaski Company manufactures and sells a single product called a Ret. Operating at capacity, the company can produce and sell 30,000 Rets per year. Costs associated with this level of production and sales are given below:
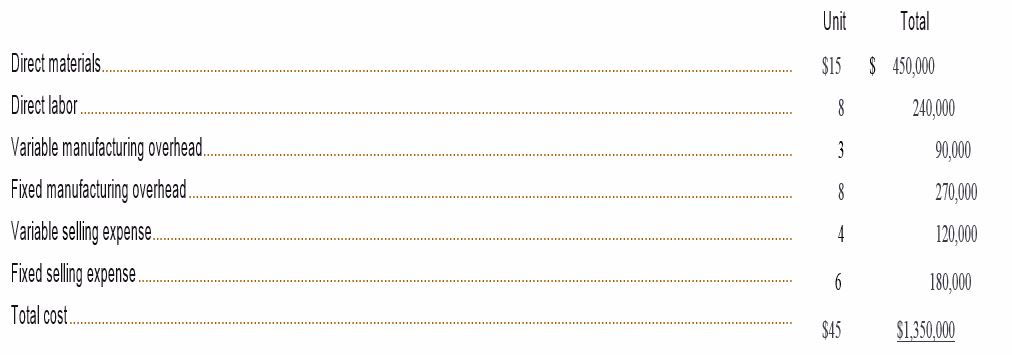
The Rets normally sell for $50 each. Fixed manufacturing
Required:
- Assume that due to a recession, Polaski Company expects to sell only 25,000 Rets through regular channels next year. A large retail chain has offered to purchase 5,000 Rets if Polaski is willing to accept a 16% discount off the regular price. There would be no sales commissions on this order: thus, variable selling expenses would be slashed by 75%. However, Polaski Company would have to purchase a special machine to engrave the retail chain’s name on the 5,000 units. This machine would cost $10,000. Polaski Company has no assurance that the retail chain will purchase additional units in the future. What is the financial advantage (disadvantage) of accepting the special order?
- Refer to the original data. Assume again that Polaski Company expects to sell only 25,000 Rets through regular channels next year. The U.S. Army would like to make a one-time-only purchase of 5,000 Rets. The Army would pay a fixed fee of SI.80 per Ret and it would reimburse Polaski Company for all costs of production (variable and fixed) associated with the units. Because the army would pick up the Rets with its own trucks, there would be no variable selling expenses associated with this order. What is the financial advantage (disadvantage) of accepting the U.S. Army’s special order?
- Assume the same situation as described in (2) above, except that the company expects to sell 30,000 Rets through regular channels next year. Thus, accepting the U.S. Army’s order would require giving up regular sales of 5,000 Rets. Given this new information, what is the financial advantage (disadvantage) of accepting the U.S. Army’s special order?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Question 6
Amundsen Company makes 60,000 units per year of a part it uses in the products it manufactures. The unit product cost of
this part is computed as follows:
Direct Materials
Direct Labor
Variable Manufacturing Overhead
Fixed Manufacturing Overhead
Variable Selling
Fixed Selling
Total
$ 10.10
$17.40
$ 2.70
$15.00
$ 2.75
$ 3.25
$51.20
An outside supplier has offered to sell the company all of these parts it needs. If the company accepts this offer, the facilities
now being used to make the part would be idle and fixed manufacturing overhead would be reduced by 80% of current cost.
The variable selling costs would be reduced to 40% of current cost.
Required:
What is the maximum amount the company should be willing to pay an outside supplier per unit for the part?
12
Division P of the Nyers Company makes a part that can either be sold to outside customers or transferred internally to Division Q for
further processing. Annual data relating to this part are as follows:
Annual production capacity
80,000
units
Selling price of the item to outside customers
$35
Variable cost per unit
$23
Fixed cost per unit
$5
Division Q of the Nyers Company requires 15,000 units per year and is currently paying an outside supplier $33 per unit. If outside
customers demand only 50,000 units per year, then what is the lowest acceptable transfer price from the viewpoint of the selling
division?
A. $35
В. $33
C. $28
D. $23
E. None of the above
QUESTION 7
Quiet Corp. currently makes 2000 subcomponents a year in one of its factories. The unit costs to produce are:
Description
Per unit
Direct materials
Direct labor
Variable manufacturing overhead
Fixed manufacturing overhead
$4
4
2
IMI
An outside supplier has offered to provide Quiet Corp. with the 2000 subcomponents at a $17 per unit price. Fixed overhead is not avoidable. If Quiet Corp. decides to
buy from the outside supplier, the impact to net income will be ?
If positive, enter the number, if negative, place a-sign before your number
Chapter 13 Solutions
Managerial Accounting
Ch. 13.A - EXERCISE 12A-1 Absorption Costing Approach to...Ch. 13.A - EXERCISE 12A-2 Customer Latitude and Pricing...Ch. 13.A - Prob. 3ECh. 13.A - Prob. 4ECh. 13.A - Prob. 5ECh. 13.A - EXERCISE 12A-6 Value-Based Pricing; Absorption...Ch. 13.A - Prob. 7ECh. 13.A - Prob. 8PCh. 13.A - Prob. 9PCh. 13.A - Prob. 10P
Ch. 13.A - Prob. 11PCh. 13.A -
PROBLEM 12A-12 Absorption Costing Approach to...Ch. 13.A - PROBLEM 12A-13 Value-Based Pricing LO12-10 The...Ch. 13 - Prob. 1QCh. 13 - Prob. 2QCh. 13 - Prob. 3QCh. 13 - Prob. 4QCh. 13 - “Variable costs and differential costs mean the...Ch. 13 - 12-6 "All future costs are relevant in decision...Ch. 13 - Prentice Company is considering dropping one of...Ch. 13 - Prob. 8QCh. 13 - 12-9 What is the danger in allocating common fixed...Ch. 13 - 12-10 How does opportunity cost enter into a make...Ch. 13 - 12-11 Give at least four examples of possible...Ch. 13 - 12-12 How will relating product contribution...Ch. 13 - Define the following terms: joint products, joint...Ch. 13 - 12-14 From a decision-making point of view, should...Ch. 13 - What guideline should be used in determining...Ch. 13 - Prob. 16QCh. 13 - Prob. 1AECh. 13 - Prob. 2AECh. 13 - Cane Company manufactures two products called...Ch. 13 - (
Alpha Beta
$30
$...Ch. 13 - Prob. 3F15Ch. 13 - Prob. 4F15Ch. 13 - Prob. 5F15Ch. 13 - (
Alpha Beta
$30
$...Ch. 13 - Prob. 7F15Ch. 13 -
Cane Company manufactures two products called...Ch. 13 - Prob. 9F15Ch. 13 - (
Alpha Beta
$30
$...Ch. 13 - Prob. 11F15Ch. 13 - Prob. 12F15Ch. 13 - (
Alpha ...Ch. 13 - (
Alpha Beta
$30
$...Ch. 13 - (
Alpha Beta
$30
$...Ch. 13 -
EXERCISE 12-1 Identifying Relevant Costs...Ch. 13 -
EXERCISE 12-2 Dropping or Retaining a Segment...Ch. 13 -
EXERCISE 12-3 Make or Buy Decision LO12-3
Troy...Ch. 13 -
EXERCISE 12-4 Special Order Decision...Ch. 13 -
EXERCISE 12-5 Volume Trade-Off Decisions...Ch. 13 - Prob. 6ECh. 13 - Prob. 7ECh. 13 - Prob. 8ECh. 13 - Prob. 9ECh. 13 - Prob. 10ECh. 13 - (
$3.60
10.00
2.40
9.00
$25.00
)
EXERCISE 12-11...Ch. 13 - Prob. 12ECh. 13 - EXERCISE 12-13 Sell or Process Further Decision...Ch. 13 - en
r
Ch. 13 - Prob. 15ECh. 13 - (
$150
31
20
29
3
24
15
$272
$34
)
EXERCISE...Ch. 13 - Prob. 17ECh. 13 - Prob. 18PCh. 13 - PROBLEM 12-19 Dropping or Retaining a Segment...Ch. 13 -
PROBLEM 12-20 Sell or Process Further Decision...Ch. 13 - Prob. 21PCh. 13 - PROBLEM 12-22 Special Order Decisions LO12-4...Ch. 13 -
PROBLEM 12-23 Make or Buy Decision LO12-3
Silven...Ch. 13 - Prob. 24PCh. 13 - Prob. 25PCh. 13 - Prob. 26PCh. 13 - Prob. 27PCh. 13 - Prob. 28PCh. 13 - CASE 12-29 Sell or Process Further Decision LO12-7...Ch. 13 -
CASE 12-30 Ethics and the Manager; Shut Dora or...Ch. 13 - CASE 12-31 Integrative Case: Relevant Costs;...Ch. 13 -
CASE 12-32 Make or Buy Decisions; Volume...Ch. 13 - Prob. 33C
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- PROBLEMS Problem 1 The Norman Company predicts that 64,000 units of material will be used during the year. The materials are expected to cost P20.00 per unit. It is anticipated that it will cost P 40.00 to place each order. The annual carrying cost is P 2.00 . Determine: a. The most economical order quantity b. The total cost of ordering and carrying at the EOQ pointarrow_forwardQUESTION 1 B Limited produces and sells the following three products: Product X Y Z Selling price per unit (N$) 16 20 10 Variable cost per unit(N$) 5 15 7 Contribution per unit(N$) 11 5 3 Budgeted Sales Volume (units) 50,000 10,000 100,000 The company expects the fixed costs to be N$300000, for the coming year. Assume that sales arise throughout the year in a constant mix. Required: (a) Draw a multiproduct profit volume chart assuming the budget is achieved.arrow_forwardQUESTION 1 B Limited produces and sells the following three products: Product X Y Z Selling price per unit (N$) 16 20 10 Variable cost per unit(N$) 5 15 7 Contribution per unit(N$) 11 5 3 Budgeted Sales Volume (units) 50,000 10,000 100,000 The company expects the fixed costs to be N$300000, for the coming year. Assume that sales arise throughout the year in a constant mix. Required: (a)Calculate the weighted average contribution sales ratio (C/S ratio) of the products? (b)Calculate the break-even sales revenue required AND Calculate the margin of safety. (c)Calculate the amount of sales revenue required to generate a profit of N$600000. (d)Draw a multiproduct profit volume chart assuming the budget is achieved.arrow_forward
- Question 9.2 Vision Limited manufactures a product that has the following costs: Per unit Per year Direct materials $6.00 Direct labour 5.00 Variable manufacturing overhead 4.00 Fixed manufacturing overhead $360,000 Variable SG&A expenses 5.00 Fixed SG&A expenses 120,000 The company applies the absorption costing approach to cost-plus pricing. The calculations are based on budgeted production and sales of 30,000 units per year.The company has spent $600,000 on this product and expects a return on investment of 15%.Required:a) Calculate the markup on absorption cost.b) Compute the target selling price of the product using the absorption costing approach.arrow_forwardQuestion 21 Fox Company has just received an unexpected order from a customer for 1,000 units of a new product. The product will have total variable costs of $15.00 per unit. Fox Company will have to rent a machine for $10,000, pay overtime amounting to $5,000 to a supervisor to handle this order, and fixed packaging and shipping costs of $2,000 for this order. The minimum (floor) price per unit that Fox Company should charge for this order is: Select one: a. $15 b. $30 c. $32 d. $25arrow_forwardTB Problem 07-171 Tullius Corporation has received a request... Tullius Corporation has received a request for a special order of 8,300 units of product C64 for $45.20 each. The normal selling price of this product is $50.30 each, but the units would need to be modified slightly for the customer. The normal unit product cost of product C64 is computed as follows: Direct materials $ 16.00 Direct labor 5.30 Variable manufacturing overhead 2.50 Fixed manufacturing overhead 5.40 Unit product cost $ 29.20 Direct labor is a variable cost. The special order would have no effect on the company's total fixed manufacturing overhead costs. The customer would like some modifications made to product C64 that would increase the variable costs by $4.90 per unit and that would require a one-time investment of $44,700 in special molds that would have no salvage value. This special order would have no effect on the company's other sales. The company…arrow_forward
- QUESTION 7 Daffy Duct, Inc., has the capacity to produce 12,000 cases of duct tape per year but only produces and sells 10,000 cases at $50 per case. The direct materials equals $130,000, direct labor equals $110,000, and overhead equals $100,000. Sixty percent of the manufacturing overhead is variable. The forty percent of fixed overhead is allocated equally to all products. Dewey, Cheatum & Howe has offered to purchase 1,000 cases but at a reduced price of $40 per case. What is the additional operating income (loss) of accepting this offer? ENTER NEGATIVE NUMBERS WITH A "-" SIGN. DO NOT USE PARENTHESES. EXAMPLE: -1,000arrow_forwardQUESTION 10 Randall has received a special order for 4300 units of its product at a special price of $20. The product normally sells for $34 and has the following manufacturing costs: AZ Direct materials Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead Fixed manufacturing overhead Per unit 2 3 3 2 Assume that Randall has sufficient capacity to fill the order. If Randall accepts the order, what effect will the order have on the company's short-term profit? *** If a decrease, place a sign before your answer. For example, a decrease of $1,000 would be answered -1,000.arrow_forward12 Our company currenty makes and sells two products: A and B. The relative number of production and sales between A and B is 2:3. In other words, each time the company produces and sells two units of product A, it produces and sells three units of product B. The following cost information is available: Company A В Unit Selling Price $11 $15 Unit Varible Cost $5 $7 Total fixed expenses $15,000 How much sales volume does the company need to make from Product B if it wants to achieve $3,000 profits? (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round the final answer to the nearest units.) А. 1,500 units В. 1,340 units C. 893 units D. 1,000 units Е. None of the abovearrow_forward
- 15 es [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Diego Company manufactures one product that is sold for $77 per unit in two geographic regions-East and West. The following information pertains to the company's first year of operations in which it produced 59,000 units and sold 54,000 units. Variable costs per unit: Manufacturing: Direct materials. Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead Variable selling and administrative Fixed costs per year: Fixed manufacturing overhead Fixed selling and administrative expense $27 $ 10 $2 $3 The company sold 41,000 units in the East region and 13,000 units in the West region. It determined that $330,000 of its fixed selling and administrative expense is traceable to the West region, $280,000 is traceable to the East region, and the remaining $52,000 is a common fixed expense. The company will continue to incur the total amount of its fixed manufacturing overhead costs as long as it continues to produce any amount of…arrow_forwardQuestion 20 Bell Company sells several products. Information of average revenue and costs is as follows: Selling price per unit $33.00 Variable costs per unit. Direct material $6.00 Direct manufacturing labor $1.50 $0.25 Manufacturing overhead Selling costs $2.00 Annual fixed costs $111,000 The company sells 12,000 units. The contribution margin per unit is $23.25 $25.50 $14.00 $25.25arrow_forwardProblem 11 (Cost-Plus and Market-Based Pricing) Temps, a large labor contractor, supplies contract labor to building construction companies. For 20X1, Temps has budgeted to supply 80,000 hours of contract labor. Its variable cost is P120 per hour and its fixed costs are P2,400,000. Roger Mason, the general manager, has proposed a cost-plus approach for pricing labor at full cost plus 20%. Required: 1. Calculate the price per hour that Temps should charge based on Mason's proposal. 2. Sheila Ragos, the marketing manager, has supplied the following information on demand levels at different prices: Demand (Hours) 120,000 100,000 80,000 70,000 Price per Hour P160 170 180 190 200 60,000 Temps can meet any of these demand levels. Fixed costs will remain unchanged for all the preceding demand levels. On the basis of this additional information, what price per hour should Temps charge? 3. Comment on your answers to Requirements 1 and 2. Why are they the same or not the same?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...
Accounting
ISBN:9781337115773
Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Revenue recognition explained; Author: The Finance Storyteller;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=816Q6pOaGv4;License: Standard Youtube License