
To review:
In the given question, it is asked to identify characteristics of homologous chromosomes synapsis which can be used to distinguish between two plant species. Plant species A (Diploid) possesses
Introduction:
Prophase-1 is a phase in the process of germ cell division (meiosis) in which duplicated chromosome gets condensed and aligns with their homologous chromosome. This pairing between two homologous partners is followed by a crossing over which results in genetic recombination (exchange of genetic material between pair of homologous chromosomes).
The organism which possesses a pair of homologous chromosomes in its somatic cell is termed as a diploid organism. Similarly, the organism possessing three homologous chromosomes in its somatic cell is termed as a triploid organism.
Explanation of Solution
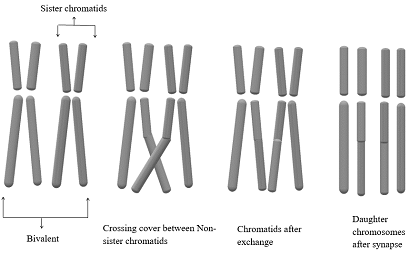
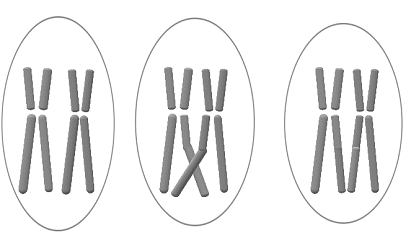
According to the given information, species-A is diploid and possesses
According to the given information, species-B is triploid and possesses
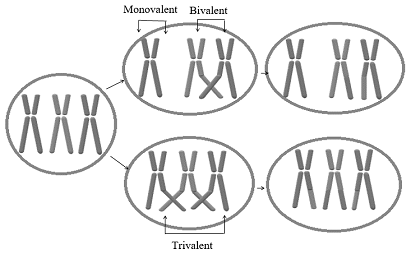 Diagram-Triploid cell with unpaired chromosome, a pair of homologous chromosome, and trivalent.
Diagram-Triploid cell with unpaired chromosome, a pair of homologous chromosome, and trivalent.
In species-A, the possible number of pair of homologous chromosomes is
In species-B, the possible number of triplets could be
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (2nd Edition)
- in the expermient of following chromosomal dna movement through meiosis, how many chromosomes were present when meiosis I started? How many nuclei are present at the end of meiosis ll? How many chromosomes are in each? What is the ploidy of the DNA at the end of meiosis l? What about at the end of meiosis ll? How are meiosis l and meiosis ll different? List two reasonarrow_forwardSuppose that meiosis occurs in the transient diploid stageof the cycle of a haploid organism of chromosome number n. What is the probability that an individual haploidcell resulting from the meiotic division will have a complete parental set of centromeres (that is, a set all fromone parent or all from the other parent)?arrow_forwardIn the moss Polytrichum commune, the haploidchromosome number is 7. A haploid male gametefuses with a haploid female gamete to form a diploid cell that divides and develops into the multicellular sporophyte. Cells of the sporophyte thenundergo meiosis to produce haploid cells calledspores. What is the probability that an individualspore will contain a set of chromosomes all ofwhich came from the male gamete?arrow_forward
- During metaphase I of meiosis, tetrads align along the metaphase plate independently of each other. Therefore, there is a random “shuffle” of maternal and paternal chromosomes in the resulting gametes.The following diagram demonstrates how this works in a diploid cell with four chromosomes . Because there are two pairs of chromosomes and each pair can align in one of two ways during metaphase I, the number of possible variations in the gametes produced is , or .For an organism that is , there are three pairs of chromosomes, so the number of possible variations in the gametes produced due to independent assortment in metaphase I is , or . In an organism with a haploid number of , how many possible combinations of maternal and paternal chromosomes can occur in its gametes? Select one: a. 72=49 b. 27=128 c.17=1 d. 214=16 384arrow_forwardFor a species with a diploid number of 18, indicate how manychromosomes will be present in the somatic nuclei of individualsthat are haploid, triploid, tetraploid, trisomic, and monosomicarrow_forwardA group of naturally occurring diploids of a species has 50 pairsof chromosomes.how many centromeres would you expect in Anaphase (mitosis)?by the end of the telophase (mitosis), what is the chromosome number of the species?in prophase (mitosis), how many chromatids should there be at this stage?arrow_forward
- During zygotene stage of meiosis I, a remarkable pairing of chromosomes occurs. Look at the bottom part of As shown in which “mitosis: growth of the body” has produced cells with four different types of chromosomes. The black ones came from the sperm nucleus. The red ones came from the egg nucleus. If one of these nuclei were to undergo meiosis, which chromosomeswould pair during zygotene (which are homologous)— the long black one with the short black one or the long black one with the long red one?arrow_forwardIn experiment of Following chromosomal DNA movement through meiosis, what is the trial 1 and trial 2 meiotic division beads diagram for prophase l, metaphase l, anapahse l, telophase l, prophase ll, metaphase ll, anaphase ll, telophase ll, and cytokinesis?arrow_forwardIf an organism has a haploid number of three, how many tetrad structures will align on the equatorial plane in metaphase 1 of meiosis?arrow_forward
- A diploid organism produces four gametes from one parent cell through the process of meiosis. Two gametes are found to have 7 chromosomes and two gametes are found to have 5 chromosomes. A) Is this the expected number of chromosomes that would be found in each gamete following a normal cycle of meiosis? If yes, explain why. If no, explain why not and describe how the gamete situation described above occurred. B) Determine the number of homologous chromosome pairs that the original parent cell contained, before meiosis began. Explain how you determined this value.arrow_forwardA diploid species has four chromosomes per set for a total of eightchromosomes in its somatic cells. Draw such a cell as it wouldlook in late prophase of meiosis II and prophase of mitosis. Discuss how prophase of meiosis II and prophase of mitosis differfrom each other, and explain how the difference originates.arrow_forwardThe kidney bean plant, Phaseolus vulgaris, is a diploid speciescontaining a total of 22 chromosomes in somatic cells. Howmany possible types of trisomic individuals could be producedin this species?arrow_forward
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning

