
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The spatial arrangement for the
Concept Introduction:
Hydrocarbons are the organic compounds that contain only hydrogen and carbon atoms. Hydrocarbon derivatives are the one in which the compounds contain hydrogen and carbon atoms along with one or more additional elements. The additional elements that can be present in hydrocarbon derivatives are oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, chlorine, bromine etc.
Hydrocarbons are further classified into two categories. They are saturated hydrocarbons and
Saturated hydrocarbons are
Alkane has general molecular formula as
Considering the geometry of carbon atoms, the carbon atoms that have double bonds will have trigonal planar geometry. The carbon atoms that have only single bonds attached to it will have tetrahedral geometry. The carbon atoms that have a triple bond attached to it will have a linear geometry.
(a)
Answer to Problem 13.38EP
The spatial arrangement is identified as tetrahedral.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure is,
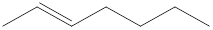
Looking into the left most carbon atom present in the given structure, it is not bonded to any double bonds or triple bond. This carbon atom has only four single bonds (three with hydrogen and one with carbon atom). Therefore, the spatial arrangement of the left-most carbon atom is tetrahedral.
The spatial arrangement of the left-most carbon atom is identified.
(b)
Interpretation:
The spatial arrangement for the chemical bonds in the left‑most carbon atom in the given structure has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Hydrocarbons are the organic compounds that contain only hydrogen and carbon atoms. Hydrocarbon derivatives are the one in which the compounds contain hydrogen and carbon atoms along with one or more additional elements. The additional elements that can be present in hydrocarbon derivatives are oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, chlorine, bromine etc.
Hydrocarbons are further classified into two categories. They are saturated hydrocarbons and unsaturated hydrocarbons. The hydrocarbons that contain single bonds between carbon atoms in the entire molecule is known as saturated hydrocarbon. The hydrocarbons that contain atleast one double or triple bond between two carbon atoms in the entire molecule is known as unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Saturated hydrocarbons are alkanes. Unsaturated hydrocarbons are alkene, alkyne and aromatic hydrocarbons.
Alkane has general molecular formula as
Considering the geometry of carbon atoms, the carbon atoms that have double bonds will have trigonal planar geometry. The carbon atoms that have only single bonds attached to it will have tetrahedral geometry. The carbon atoms that have a triple bond attached to it will have a linear geometry.
(b)
Answer to Problem 13.38EP
The spatial arrangement is identified as tetrahedral.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure is,
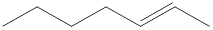
Looking into the left most carbon atom present in the given structure, it is not bonded to any double bonds or triple bond. This carbon atom has only four single bonds (three with hydrogen and one with carbon atom). Therefore, the spatial arrangement of the left-most carbon atom is tetrahedral.
The spatial arrangement of the left-most carbon atom is identified.
(c)
Interpretation:
The spatial arrangement for the chemical bonds in the left‑most carbon atom in the given structure has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Hydrocarbons are the organic compounds that contain only hydrogen and carbon atoms. Hydrocarbon derivatives are the one in which the compounds contain hydrogen and carbon atoms along with one or more additional elements. The additional elements that can be present in hydrocarbon derivatives are oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, chlorine, bromine etc.
Hydrocarbons are further classified into two categories. They are saturated hydrocarbons and unsaturated hydrocarbons. The hydrocarbons that contain single bonds between carbon atoms in the entire molecule is known as saturated hydrocarbon. The hydrocarbons that contain atleast one double or triple bond between two carbon atoms in the entire molecule is known as unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Saturated hydrocarbons are alkanes. Unsaturated hydrocarbons are alkene, alkyne and aromatic hydrocarbons.
Alkane has general molecular formula as
Considering the geometry of carbon atoms, the carbon atoms that have double bonds will have trigonal planar geometry. The carbon atoms that have only single bonds attached to it will have tetrahedral geometry. The carbon atoms that have a triple bond attached to it will have a linear geometry.
(c)
Answer to Problem 13.38EP
The spatial arrangement is identified as trigonal planar.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure is,
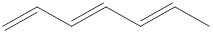
Looking into the left most carbon atom present in the given structure, it is bonded to one double bond. This carbon atom has only two single bonds with hydrogen and a double bond with carbon atom. Therefore, the spatial arrangement of the left-most carbon atom is trigonal planar.
The spatial arrangement of the left-most carbon atom is identified.
(d)
Interpretation:
The spatial arrangement for the chemical bonds in the left‑most carbon atom in the given structure has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Hydrocarbons are the organic compounds that contain only hydrogen and carbon atoms. Hydrocarbon derivatives are the one in which the compounds contain hydrogen and carbon atoms along with one or more additional elements. The additional elements that can be present in hydrocarbon derivatives are oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, chlorine, bromine etc.
Hydrocarbons are further classified into two categories. They are saturated hydrocarbons and unsaturated hydrocarbons. The hydrocarbons that contain single bonds between carbon atoms in the entire molecule is known as saturated hydrocarbon. The hydrocarbons that contain atleast one double or triple bond between two carbon atoms in the entire molecule is known as unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Saturated hydrocarbons are alkanes. Unsaturated hydrocarbons are alkene, alkyne and aromatic hydrocarbons.
Alkane has general molecular formula as
Considering the geometry of carbon atoms, the carbon atoms that have double bonds will have trigonal planar geometry. The carbon atoms that have only single bonds attached to it will have tetrahedral geometry. The carbon atoms that have a triple bond attached to it will have a linear geometry.
(d)
Answer to Problem 13.38EP
The spatial arrangement is identified as tetrahedral.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure is,
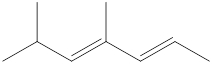
Looking into the left most carbon atom present in the given structure, it is not bonded to any double bonds or triple bond. This carbon atom has only four single bonds (three with hydrogen and one with carbon atom). Therefore, the spatial arrangement of the left-most carbon atom is tetrahedral.
The spatial arrangement of the left-most carbon atom is identified.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
GENERAL,ORGANIC,+BIO.CHEM.-MINDTAP
- The molecular formula for glucose is C6H12O6. What would be the molecular formula for a polymer made by linking ten glucose molecules together by dehydration reactions? Group of answer choices A. C60H120O60 B. C60H102O51 C. C60H100O50 D. C60H111O51 Use the following information to answer the following questions."The native structure of hemoglobin (HB) comprises of two α and two β subunits, each of which carries a heme group. There appear to be no previous studies that report the in-vitro folding and assembly of Hb from highly unfolded α and β globin in a 'one-pot' reaction. One difficulty that has to be overcome for studies of this kind is the tendency of Hb to aggregate during refolding. This work demonstrates that denaturation of Hb in 40% acetonitrile at pH 10.0 is reversible." (J Am Soc Mass Spectrum 2007, 18, 8-16)In sickle-cell disease, as a result of a single amino acid change, the mutant hemoglobin tetramers associate with each other and assemble into large fibers.…arrow_forwardGiven below is the structure of tallose.Answer the following questiona. what is the maximum number of stereoisomers can tallose have?b. how many chiral carbons does it have?c. what is the configuration of tallose is it D or L sugar?d. what type of monosaccharide is it?arrow_forwardConsider olive oil, an oil with a high percentage of fat derived from oleic acid (otherwise known as cis[18:1] fatty acid). a, Explain why such a structure may allow olive oil to be one of the "healthier" oils? b, why such a structure may allow olive oil to be a liquid at room temperature, while butter and lard are solid at room temperature? c, why such a structure may cause olive oil to be prone to oxidative damage upon exposure to air and heat?arrow_forward
- Classify the fatty acid with the following structural formula in the ways indicated.a. What is the type designation (SFA, MUFA, or PUFA) for this fatty acid? b. On the basis of carbon chain length and degree of unsaturation, what is the numerical shorthand designation for this fatty acid?c. To which “omega” family of fatty acids does this fatty acid belong? d. What is the “delta” designation for the carbon chain double-bond location for this fatty acid?arrow_forwardDescribe the structural similarities and differences of the following pairs. Identify which of these is a structural isomer, and how to identify structural isomers. a. Glucose and Mannose b. Galactose and Fructose c. Ribulose and Xylulose d. ribose and glucosearrow_forwardThe polymer chains of glycosaminoglycans are widelyspread apart and bind large amounts of water.a. What two functional groups of the polymer make thisbinding of water possible?b. What type of bonding is involved?arrow_forward
- Classify the fatty acid with the following structural formula in the ways indicated. a. What is the type designation (SFA, MUFA, or PUFA) for this fatty acid? b. On the basis of carbon chain length and degree of unsaturation, what is the numerical shorthand designation for this fatty acid? c. To which "omega" family of fatty acids does this belong? d. What is the "delta" designation for the carbon chain double-bond locations for this fatty acid? Note: There are 2 items in the photo.arrow_forwardWhat is the contribution of dilsulfide bonds in proteins?Which groups or side chain participate in these reactions? Discuss with examples in detail.arrow_forwardConstruct the two enantiomeric forms/structure of the following monosaccharides and designate the handedness of each using D, L system: a. Ribulosearrow_forward
- Which functional groups are present in digitoxin? a. To what lipid family does the complex ring drawn to the right of the structure belong? b. Identify the type of glycosidic bond that joins each of the monosaccharide residue in the molecule c. Draw the open form of the monosaccharide used to produce the trisaccharide portion of digitoxin.arrow_forwardProline provides structural regidity in proteins. What is the consequence of this on protein structure?arrow_forwardDraw a trisaccharide that has TWO different forms of glycosidic bonds via a Hayworth Projection. Also, note the names of each monomer.arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





