
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The missing reagents for each step in Your Turn 13.6 are to be supplied.
Concept introduction:
In order to identify the missing reagents in the given reaction sequence, it is important to identify if the reaction involves a
Under basic conditions, the nucleophile attacks the
Answer to Problem 13.1P
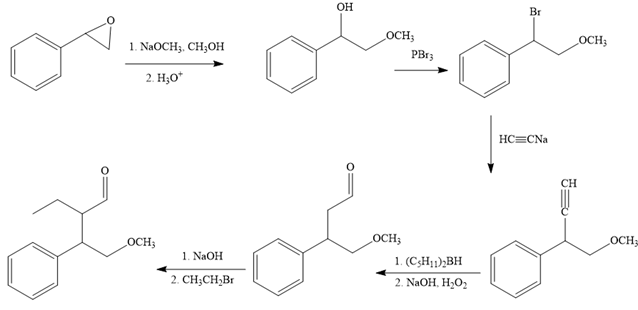
The missing reagents for each step in the given reaction sequence are given below:
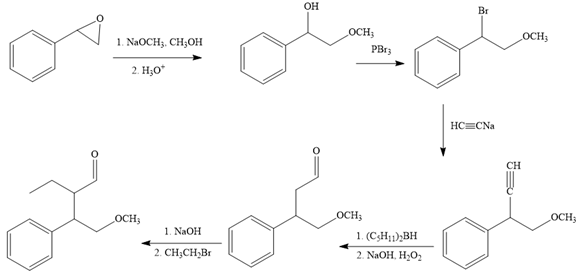
Explanation of Solution
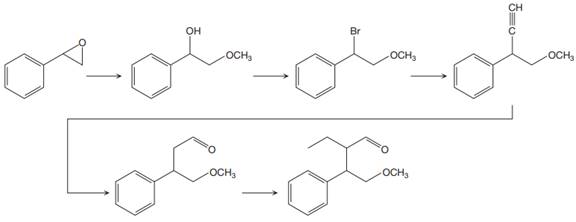
The reaction sequence given in Your Turn 13.6 is:
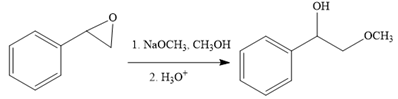
The first reaction is the conversion of an epoxide to alcohol. Thus, it is a functional group transformation reaction in which the nucleophile,
The first reaction and the missing reagents for it are shown below:
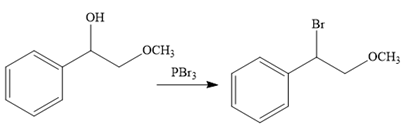
The second reaction also involves functional group transformation. The alcoholic (
In the third reaction, the bromine atom is replaced by an acetylene group (
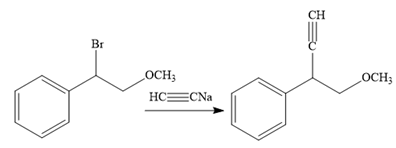
The fourth reaction in the given reaction sequence is a reaction involving a functional group transformation. Terminal alkynes undergo a hydroboration-oxidation reaction which leads to the formation of an aldehyde. The reagents used in the hydroboration-oxidation reaction are disiamylborane [
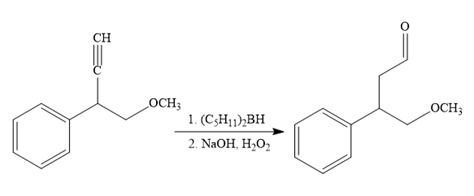
The fifth reaction involves the alteration of the carbon skeleton. The alpha hydrogen attached to an alpha carbon in aldehydes is weakly acidic. A strong base abstracts this alpha hydrogen to form an enolate ion. This enolate serves as a nucleophile and reacts with an alkyl halide via
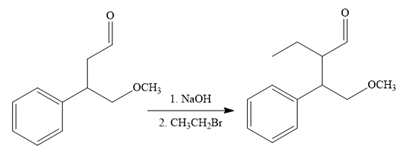
The complete reaction sequence with appropriate reagents for each are given below:
In order to identify the missing reagents in the given reaction sequence, it is important to identify if the reaction involves a functional group transformation or it is a reaction that alters the carbon skeleton.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles And Mechanisms
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
