
To determine:
a) Calculate the rate constant for the given reaction.
b) Determine the rate of the reaction at 23oC and PCH3CO3NO2=10.5 torr.
c) Draw a graph showing PPAN as a function of time from 0 to 200 h.
Answer to Problem 13.138QA
Solution:
d) The rate constant for the given second order reactionis k=9.52×10-4torr-1h-1.
a) The rate of the reaction at 23oC and PCH3CO3NO2=10.5 torr is 0.10 torr/h.
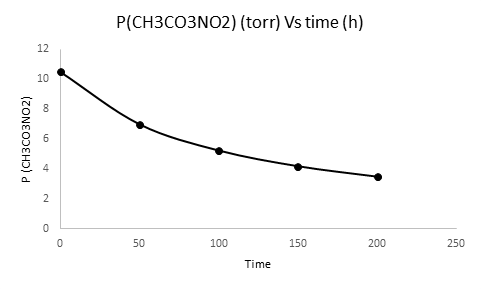
b) A graph showing PPAN as a function of time from 0 to 200 h is given below.
Explanation of Solution
1) Concept:
The given process is second order in peroxyacetyl nitrate, so write rate law for the reaction. From given data and formula for half-life period for second order
2) Given:
The given reaction is second order in peroxyacetyl nitrate.
t1/2=100 h
PCH3CO3NO2=10.5 torr
3) Formulae:
t12=1k[X]0
t12= half-life period
k = rate constant
[X]0= initial pressure
1[X]t=kt+ 1[X]0
[X]t= pressure after time t.
4) Calculations:
a) The half-life of the second order reaction, that is,100 h and initial pressure of CH3CO3NO2 is 10.5 torr.
t12=1k[PCH3CO3NO2]
k=1t12[PCH3CO3NO2]
k=1(100 h)(10.5 torr)
Rate constant
k=9.52×10-4torr-1h-1
b) We can write the general rate law equation for the given second order reaction as
rate=k[PCH3CO3NO2]2
rate=(9.52×10-4torr-1h-1)(10.5 torr)2
rate=0.10 torr/h.
c) To draw the graph, we have to first find the values of [PCH3CO3NO2]t at different time intervals from 0 to 200 h. For that, we can use the integrated rate law equation of second order reaction.
1[PCH3CO3NO2]t=kt+1[PCH3CO3NO2]0
So at 0 h[PCH3CO3NO2]t=10.5 torr
1. At 50 h
1[PCH3CO3NO2]50=(9.52×10-4torr-1h-1)(50 h)+110.5 torr
1[PCH3CO3NO2]50=0.1428
[PCH3CO3NO2]50=7.000 torr
2. At 100 h
1[PCH3CO3NO2]100=(9.52×10-4torr-1h-1)(100 h)+110.5 torr
1[PCH3CO3NO2]100=0.1904
[PCH3CO3NO2]100=5.2510 torr
3. At 150 h
1[PCH3CO3NO2]150=(9.52×10-4torr-1h-1)(150 h)+110.5 torr
1[PCH3CO3NO2]150=0.2380
[PCH3CO3NO2]150=4.2010 torr
4. At 200 h
1[PCH3CO3NO2]200=(9.52×10-4torr-1h-1)(200 h)+110.5 torr
1[PCH3CO3NO2]200=0.3273
[PCH3CO3NO2]200=3.500 torr
Now we have to plot the graph of [PCH3CO3NO2]t versus time
| Time (h) | [PCH3CO3NO2]t(torr) |
| 0 | 10.5 |
| 50 | 7.000 |
| 100 | 5.2510 |
| 150 | 4.2010 |
| 200 | 3.500 |

We have plotted time on X-axis and [PCH3CO3NO2]t(torr) on Y-axis.
Conclusion:
a) The rate constant for the given second order reaction is,k=9.52×10-4torr-1h-1.
b) The rate of the reaction at 23oC and PCH3CO3NO2=10.5 torr is,0.10 torr/h.
c) A graph showing PPAN as a function of time from 0 to 200 h is plotted.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Chemistry: An Atoms-Focused Approach (Second Edition)
- Shown below is the major resonance structure for a molecule. Draw the second best resonance structure of the molecule. Include all non-zero formal charges. H. H. +N=C H H H Cl: Click and drag to start drawing a structure. : ? g B S olo Ar B Karrow_forwardDon't used hand raitingarrow_forwardS Shown below is the major resonance structure for a molecule. Draw the second best resonance structure of the molecule. Include all non-zero formal charges. H H = HIN: H C. :0 H /\ H H Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ×arrow_forward
- Part II. two unbranched ketone have molecular formulla (C8H100). El-ms showed that both of them have a molecular ion peak at m/2 =128. However ketone (A) has a fragment peak at m/2 = 99 and 72 while ketone (B) snowed a fragment peak at m/2 = 113 and 58. 9) Propose the most plausible structures for both ketones b) Explain how you arrived at your conclusion by drawing the Structures of the distinguishing fragments for each ketone, including their fragmentation mechanisms.arrow_forwardPart V. Draw the structure of compound tecla using the IR spectrum Cobtained from the compound in KBr pellet) and the mass spectrum as shown below. The mass spectrum of compound Tesla showed strong mt peak at 71. TRANSMITTANCE LOD Relative Intensity 100 MS-NW-1539 40 20 80 T 44 55 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 m/z D 4000 3000 2000 1500 1000 500 HAVENUMBERI-11arrow_forwardTechnetium is the first element in the periodic chart that does not have any stable isotopes. Technetium-99m is an especially interesting and valuable isotope as it emits a gamma ray with a half life ideally suited for medical tests. It would seem that the decay of technetium should fit the treatment above with the result In(c/c) = -kt. The table below includes data from the two sites: http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/druginfo.cfm?id=7130 http://wiki.medpedia.com/Clinical: Neutrospec_(Technetium_(99m Tc)_fanolesomab). a. b. C. Graph the fraction (c/c.) on the vertical axis versus the time on the horizontal axis. Also graph In(c/c.) on the vertical axis versus time on the horizontal axis. When half of the original amount of starting material has hours fraction remaining disappeared, c/c = ½ and the equation In(c/c.) = -kt becomes In(0.5) = -kt1/2 where t₁₂ is the half life (the time for half of the material to decay away). Determine the slope of your In(c/c.) vs t graph and…arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





