
Concept explainers
To prove: △HFS≅ △FST≅ △STH
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
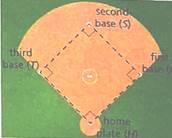
The distances between consecutive bases on a softball field are the same. The distance from home plate to second base is the same as the distance from first base to third base. The angles created at each base are 90∘.
Formula used:
The Hypotenuse-Leg Congruence Theorem
If the hypotenuse and a leg of a right triangle are congruent to the hypotenuse and a leg of a second right triangle , then the two triangles are congruent.
Calculation:
According to the question,
We have,
1. The distances between consecutive bases on a softball field are the same.
HF≅FS≅ST≅TH.
2. The distance from home plate to second base is the same as the distance from first base to third base.
Joining home plate (H) and second base (S), we get two triangles △HFS and △STH.
Joining first base (F) and second base (S), we get two triangles △FST and △THF.
3. The angles created at each base are 90∘.
∠H=∠F=∠S=∠T=90∘
Now, proving the triangles are congruent:-
First, consider two triangles:- △HFS and △FST.

| Statements | Reasons |
| H 1. ¯HS=¯FT 2. ∠F and ∠S are right angles. 3. △HFS and △FST are right triangles. | 1.Given
2. Given. 3. Definition of a right triangle. |
| L 4. ¯FS=¯FS 5. △HFS≅ △FST | 4. Reflexive Property of Congruence
5. HL Congruence Theorem |
Second, consider two triangles:- △FST and △STH.

| Statements | Reasons |
| H 1. ¯SH=¯FT 2. ∠T and ∠S are right angles. 3. △FST and △STH are right triangles. | 1.Given
2. Given. 3. Definition of a right triangle. |
| L 4. ¯ST=¯ST 5. △FST≅ △STH | 4. Reflexive Property of Congruence
5. HL Congruence Theorem |
Third, consider two triangles:- △HFS and △STH
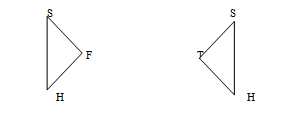
| Statements | Reasons |
| H 1. ¯SH=¯HS 2. ∠T and ∠F are right angles. 3. △HFS and △STH are right triangles. | 1.Given
2. Given. 3. Definition of a right triangle. |
| L 4. ¯HS=¯SH 5. △HFS≅ △STH | 4. Reflexive Property of Congruence
5. HL Congruence Theorem |
Therefore, the three triangles are congruent.
△HFS≅ △FST≅ △STH.
Hence Proved.
Chapter 12 Solutions
BIG IDEAS MATH Integrated Math 1: Student Edition 2016
- CVE, AVM, AC, ¬SA¬ME A Fitch Style proof for this argumentarrow_forward13:26 ... ← Robert F. Blitzer - Thinkin... 0,04 61 KB/d 目 polygons to create a fraudulent tessellation with discrepancies that are too subtle for the eye to notice. In Exercises 45-46, you will use mathematics, not your eyes, to observe the irregularities. B A 45. Find the sum of the angle measures at vertex A. Then explain why the tessellation is a fake. 46. Find the sum of the angle measures at vertex B. Then explain why the tessellation is a fake. =et at If se Fic SECTION 10.3 Polygons, Perimeter, and Tessellations 645 61. I find it helpful to think of a polygon's perimeter as the length of its boundary. 62. If a polygon is not regular, I can determine the sum of the measures of its angles, but not the measure of any one of its angles. 63. I used floor tiles in the shape of regular pentagons to completely cover my kitchen floor. In Exercises 64-65, write an algebraic expression that represents the perimeter of the figure shown. is be 64. le a b C 2/ If se nyarrow_forwardnot use ai please don'tarrow_forward
- pls helparrow_forwardUse the formulas developed in this section to find the area of the figure. A= (Simplify your answer.) 8.5 m 7 T 13 m 7.7 m m 21 marrow_forwardFind the circumference and area of the circle. Express answers in terms of and then round to the nearest tenth. Find the circumference in terms of C = (Type an exact answer in terms of л.) 9 cmarrow_forward
- Find the area of the figure. A = 4 m 11 m 13 m 5 marrow_forwardFind the exact values of sin(2u), cos(2u), and tan(2u) given 2 COS u where д < u < π. 2arrow_forward(1) Let R be a field of real numbers and X=R³, X is a vector space over R, let M={(a,b,c)/ a,b,cE R,a+b=3-c}, show that whether M is a hyperplane of X or not (not by definition). متکاری Xn-XKE 11Xn- Xmit (2) Show that every converge sequence in a normed space is Cauchy sequence but the converse need not to be true. EK 2x7 (3) Write the definition of continuous map between two normed spaces and write with prove the equivalent statement to definition. (4) Let be a subset of a normed space X over a field F, show that A is bounded set iff for any sequence in A and any sequence in F converge to zero the sequence converge to zero in F. އarrow_forward
 Discrete Mathematics and Its Applications ( 8th I...MathISBN:9781259676512Author:Kenneth H RosenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Discrete Mathematics and Its Applications ( 8th I...MathISBN:9781259676512Author:Kenneth H RosenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Mathematics for Elementary Teachers with Activiti...MathISBN:9780134392790Author:Beckmann, SybillaPublisher:PEARSON
Mathematics for Elementary Teachers with Activiti...MathISBN:9780134392790Author:Beckmann, SybillaPublisher:PEARSON
 Thinking Mathematically (7th Edition)MathISBN:9780134683713Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Thinking Mathematically (7th Edition)MathISBN:9780134683713Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Discrete Mathematics With ApplicationsMathISBN:9781337694193Author:EPP, Susanna S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Discrete Mathematics With ApplicationsMathISBN:9781337694193Author:EPP, Susanna S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Pathways To Math Literacy (looseleaf)MathISBN:9781259985607Author:David Sobecki Professor, Brian A. MercerPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Pathways To Math Literacy (looseleaf)MathISBN:9781259985607Author:David Sobecki Professor, Brian A. MercerPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





