
A square plate with sides 2.0 m in length can rotate around an axle passing through its center of mass (CM) and perpendicular to its surface (Fig. P12.53). There are four forces acting on the plate at different points. The rotational inertia of the plate is 24 kg · m2. Use the values given in the figure to answer the following questions. a. What is the net torque acting on the plate? b. What is the
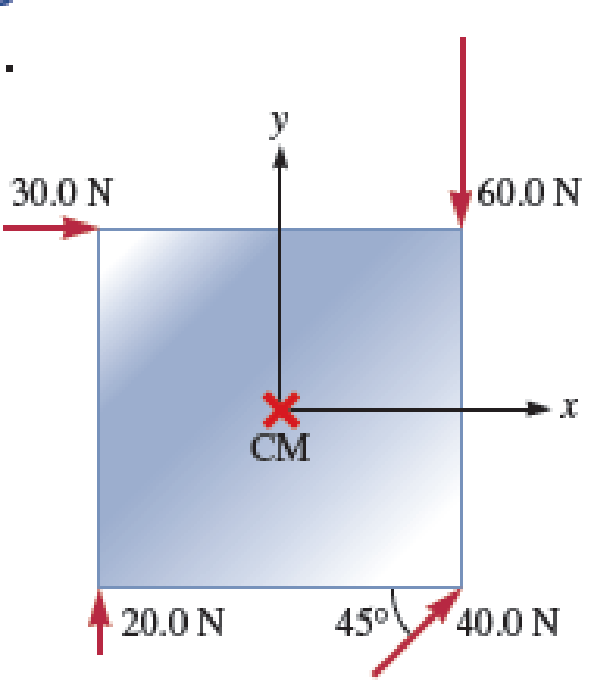
FIGURE P12.53
Problems 53 and 54.
(a)
The net torque acting on the plate.
Answer to Problem 53PQ
The net torque acting on the plate is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the net torque on the plate.
Here,
Write the expression for the torque acting on an object in the cross product form.
Here,
Equation (II) can be solved as,
Conclusion:
For each forces
The diagonal of the square is the square root of the sum of the squares of the two sides of the square which can be found that,
For the torque due to force
The angle between the moment arm and the force is
Substitute
Therefore, the net torque acting on the plate is
(b)
The angular acceleration of the plate.
Answer to Problem 53PQ
The angular acceleration of the plate is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the total torque in terms of rotational inertia.
Here,
Rearrange equation (IV),
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the angular acceleration of the plate is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Webassign Printed Access Card For Katz's Physics For Scientists And Engineers: Foundations And Connections, 1st Edition, Single-term
- A square plate with sides of length 4.0 m can rotate about an axle passing through its center of mass and perpendicular to the plate as shown in Figure P14.36. There are four forces acting on the plate at different points. The rotational inertia of the plate is 24 kgm2. Is the plate in equilibrium? FIGURE P14.36arrow_forwardSuppose you exert a force of 180 N tangential to a 0.280-m-radius, 75.0-kg grindstone (a solid disk). (a) What torque is exerted? (b) What is the angular acceleration assuming negligible opposing friction? (c) What is the angular acceleration if there is an opposing frictional force of 20.0 N exerted 1.50 cm from the axis?arrow_forwardA cam of mass M is in the shape of a circular disk of diameter 2R with an off-center circular hole of diameter R is mounted on a uniform cylindrical shaft whose diameter matches that of the hole (Fig. P1 3.78). a. What is the rotational inertia of the cam and shaft around the axis of the shaft? b. What is the rotational kinetic energy of the cam and shaft if the system rotates with angular speed around this axis?arrow_forward
- The system shown in Figure P13.18 consisting of four particles connected by massless, rigid rods is rotating around the x axis with an angular speed of 2.50 rad/s. The particle masses are m1 = 1.00 kg, m2 = 4.00 kg, m3 = 2.00 kg, and m4 = 3.00 kg. a. What is the rotational inertia of the system around the x axis? b. Using Kr=12I2 (Eq. 13.10), what is the total rotational kinetic energy of the system? c. What is the tangential speed of each of the four particles? d. Considering the system as four particles in motion and using K=i12mvi2, what is the total kinetic energy of the system? How does this value compare with the result obtained in part (b)? FIGURE P13.18arrow_forwardThe fishing pole in Figure P10.22 makes an angle of 20.0 with the horizontal. What is the torque exerted by the fish about an axis perpendicular to the page and passing through the anglers hand if the fish pulls on the fishing line with a force F=100N at an angle 37.0 below the horizontal? The force is applied at a point 2.00 m from the anglers hands. Figure P10.22arrow_forwardA disk with a radius of 4.5 m has a 100-N force applied to its outer edge at two different angles (Fig. P12.55). The disk has arotational inertia of 165 kg m2. a. What is the magnitude of the torque applied to the disk incase 1? b. What is the magnitude of the torque applied to the disk incase 2? c. Assuming the force on the disk is constant in each case,what is the magnitude of the angular acceleration applied tothe disk in each case? d. Which case is a more effective way of spinning the disk?Describe which quantity you are using to determine effectiveness and why you chose that quantity. FIGURE P12.55arrow_forward
- (a) Calculate the angular momentum of Earth in its orbit around the Sun. (b) Compare this angular momentum with the angular momentum of Earth about its axis.arrow_forward(a) Calculate the rotational kinetic energy of Earth on its axis. (b) What is the rotational kinetic energy of Earth in its orbit around the Sun?arrow_forwardA flywheel (l=50kgm2) starting from rest acquires an angular velocity of 200.0 rad/s while subject to a constant torque from a motor for 5 s. (a) What is the angular acceleration of the flywhell? (b) What is the magnitude of the torque?arrow_forward
- A rope of negligible mass is wrapped around a 225 kg solid cylinder of radius 0.400 m. The cylinder is suspended several meters off the ground with its axis oriented horizontally, and turns on that axis without friction, (a) If a 75.0-kg man takes hold of the free end of the rope and falls under the force of gravity, what is his acceleration? (b) What is the angular acceleration of the cylinder? (c) if the mass of the rope were not neglected, what would happen to the angular acceleration of the cylinder as the man falls?arrow_forwardFind the net torque on the wheel in Figure P10.23 about the axle through O, taking a = 10.0 cm and b = 25.0 cm. Figure P10.23arrow_forwardA thin stick of mass 0.2 kg and length L=0.5m is attached to the rim of a metal disk of mass M=2.0kg and radius R=0.3m . The stick is free to rotate around a horizontal axis through its other end (see the following figure). (a) If the combinatin is related with the stick horizontal, what is the speed of the center of the disk when the stick is vertical? (b) What is the acceleration fo the center of the disk at the stick is released? (c) At the instant the stick passes through the vertical?arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





