
The beam is fabricated from four boards nailed together as shown. Determine the shear force each nail along the sides C and the top D must resist if the nails are uniformly spaced at s = 3 in. The beam is subjected to a shear of V = 4.5 kip.
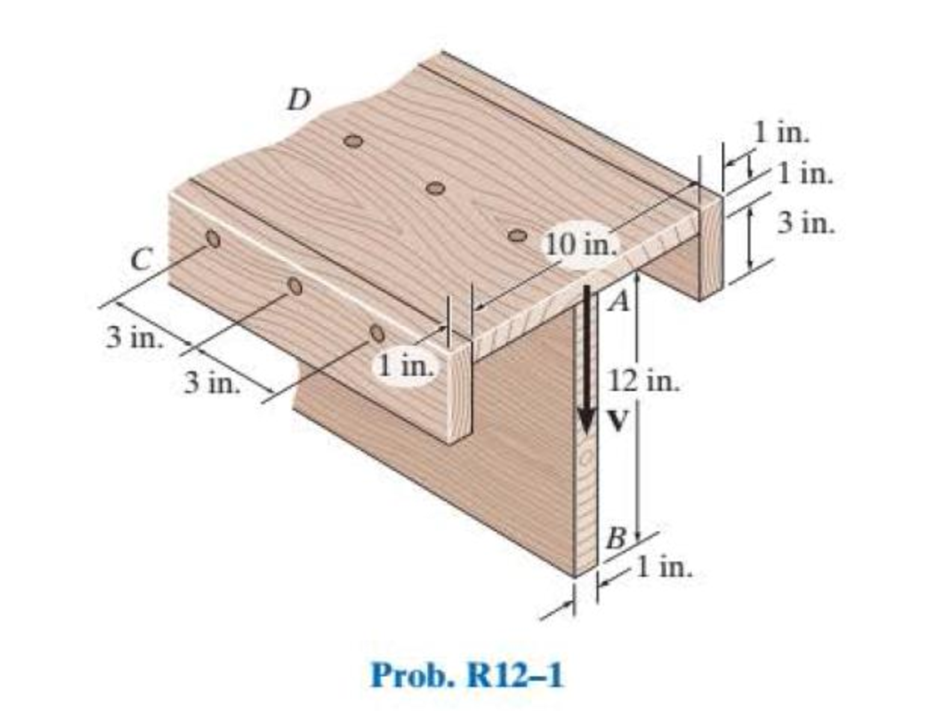
The shear force
The shear force
Answer to Problem 1RP
The shear force
The shear force
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The shear force is
The uniform nail spacing is 3 in.
Calculation:
Sketch the diagram of the T section as shown in Figure 1.
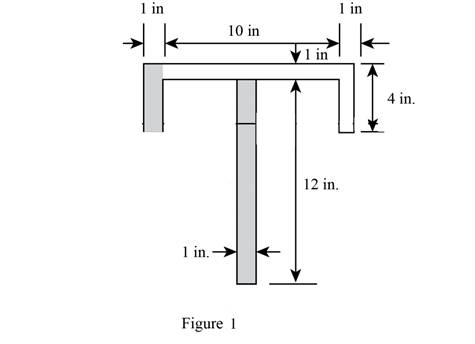
The area of the beam is the sum of area of three rectangles 1, 2, and 3.
The dimensions of rectangle 1 as width
The dimensions of rectangle 2 as width
The dimensions of rectangle 2 as width
Find the value of area section 1 as shown below:
Substitute 10 in. for
Find the value of area section 2 as shown below:
Substitute 4 in. for
Find the value of area section 3 as shown below:
Substitute 12 in. for
Calculate the centroid of
Here,
Substitute
Sketch the diagram of
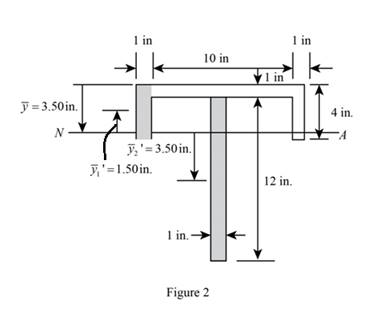
Calculate the moment of inertia of the beam (I) as follows:
Refer to Figure 2:
The value of
The value of
The value of
Substitute 10 in. for
Calculate the first moment area
Here,
Refer to Figure 2.
The value of
Substitute
Calculate the first moment area
Here,
Refer to Figure 2.
The value of
Substitute
Show the formula for shear flow
Here, V is the shear force and I is the moment of inertia
Substitute4.5 kip for V,
Show the formula for shear flow
Substitute4.5 kip for V,
Calculate the shear force
Here, s is the spacing and
Substitute
Hence, the shear force
Calculate the shear force
Here, s is the spacing and
Substitute
Hence, the shear force
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Statics and Mechanics of Materials, Student Value Edition (5th Edition)
- The beam is constructed from two boards fastened together at the top and bottom with three rows of nails spaced every 8 in. If an internal shear force of V = 800 lb is applied to the boards, determine the shear force resisted by each nail.arrow_forward20 mm 20 mm 4. The simply supported beam on the right is built up from three boards by nailing them together as shown. If P = 12 kN, determine the maximum allowable spacing s of the nails to support the load, if each nail can resist a shear force of 1.5 kN. 1 m m B 100 mm 25 mm- 25 mm 200 mm 25 mmarrow_forward1. The wide-flange beam is subjected to a shear force of V = 20 kN. Determine the shear stress distribution in the beam.arrow_forward
- A beam is constructed from three boards bolted together as shown. Determine the shear force in each bolt if the bolts are spaced s = 250 mm apart and the shear is V = 35 kN.arrow_forwardThe beam is constructed from three boards. Determine the maximum loads P that it can support if the allowable shear stress for the wood is tallow = 400 psi. What is the maximum allowable spacing s of the nails used to holdthe top and bottom flanges to the web if each nail can resist a shear force of 400 lb?arrow_forwardBelow is the shear diagram and the cross-section of a built-up beam. The allowable shear load on the bolts is 1000 N. Dimension a is 50 mm. Determine the largest allowable spacing of the bolts. Sheardiagram: 400 N Cross-section: bolt a -600N NZ.arrow_forward
- A |100 lb B +2+ 4 ft - 180 lb с - 3 -arrow_forwardIf the T-beam is subjected to a vertical shear of V=90kN , determine the maximum shear stress in the beam. Also, compute the shear-stress jump at the flange- web junction AB. 100 mm 100 mm A 100 mm B 75 mm 150 mmarrow_forwardPlease help mearrow_forward
- The structure shown consists of a single member ABCDE with a pin support at A and a roller support at E. Points B and D are at the midpoints of their respective segments. Determine the internal shear force acting on I which are located immediately to the left of C. Take N = 1 kN, O = 3 kN, and P = 4 kN.arrow_forward1 Determine the location e of the shear center, point O, for the thin-walled member having the cross section shown. The member segments have the same thickness t-5 mm (b30 mm, d=100 mm). |45° 0. 45°arrow_forwardQ1) For the beam loaded as shown, find the magnitude and the location of the maximum shearing stress due to the shearing force. skN 80 2 kN in 100 60 4•M36KN.m R = R = 17KN 4in 6im 4in - +120mmarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





