
Concept explainers
During the month of October 20--, The Pink Petal flower shop engaged in the following transactions:

Selected account balances as of October 1 were as follows:
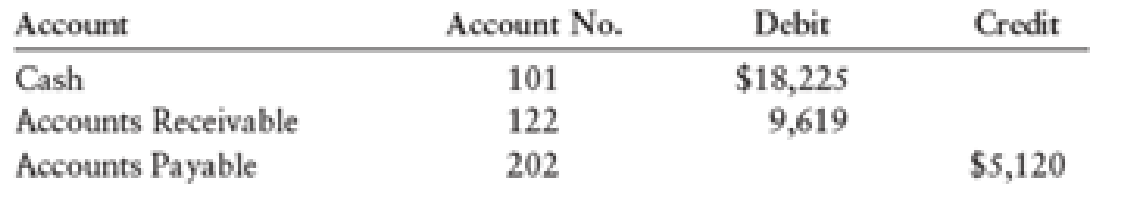
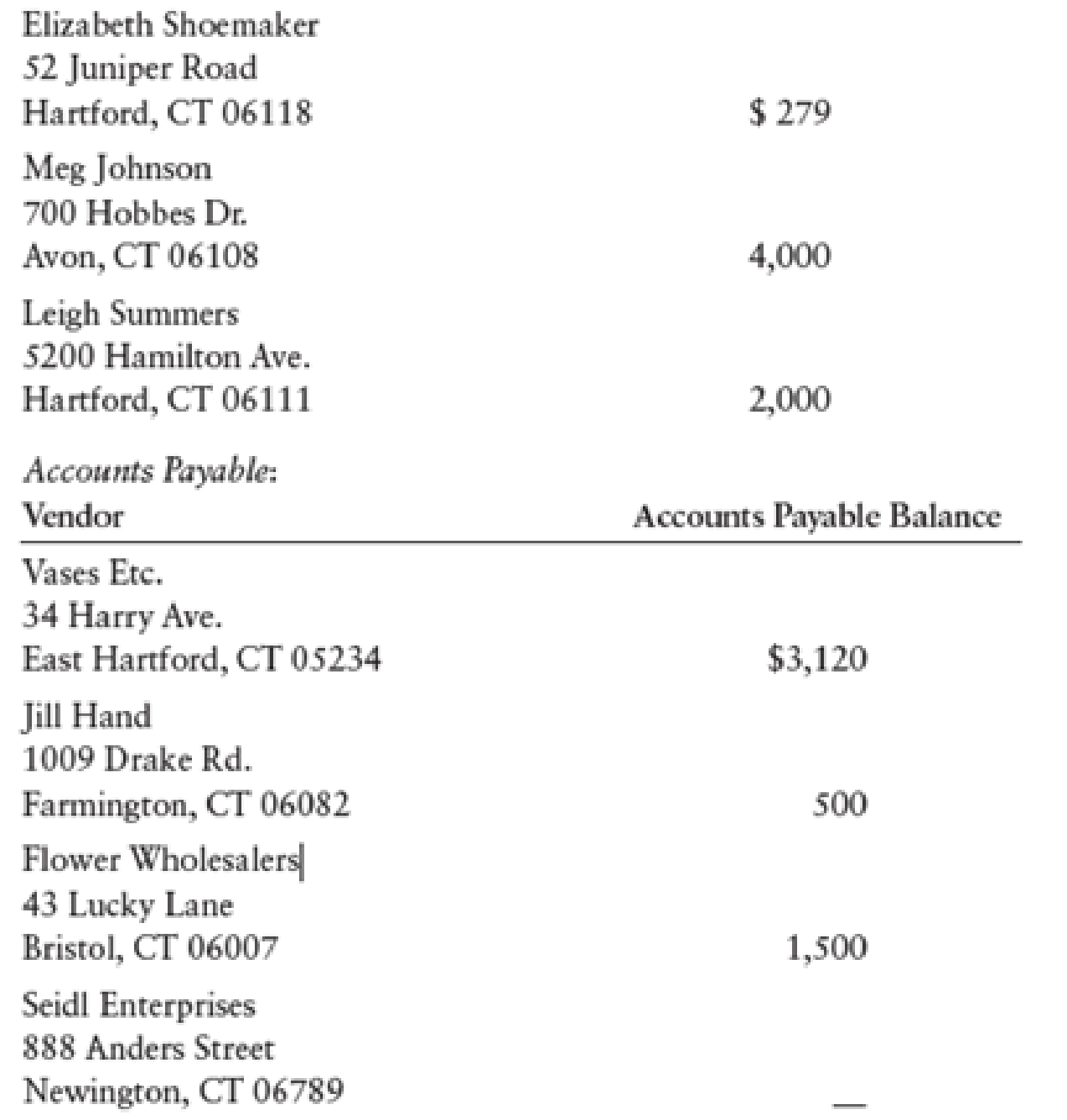
The Pink Petal also had the following subsidiary ledger balances as of October 1:

REQUIRED
- 1. Record the transactions in a sales journal (page 7), cash receipts journal (page 10), purchases journal (page 6), cash payments journal (page 11), and general journal (page 5). Total, verify, and rule the columns where appropriate at the end of the month.
- 2. Post from the journals to the general ledger,
accounts receivable ledger, and accounts payable ledger accounts. Use account numbers as shown in the chapter.
1.
Prepare the given transaction in the sales journal, cash receipts journal, purchase journal, cash payment journal, and general journal and verify the total column and rule the column.
Explanation of Solution
Sales Journal:
Sales journal is one form of special journal book, which records all the sales transactions that are sold to customers on credit. In a single column sales journal, debit aspect of accounts receivable and credit aspect of inventory are recorded, and then posted to individual subsidiary customer account.
Prepare the given transaction in a sales journal and verify the total column and rule the column:
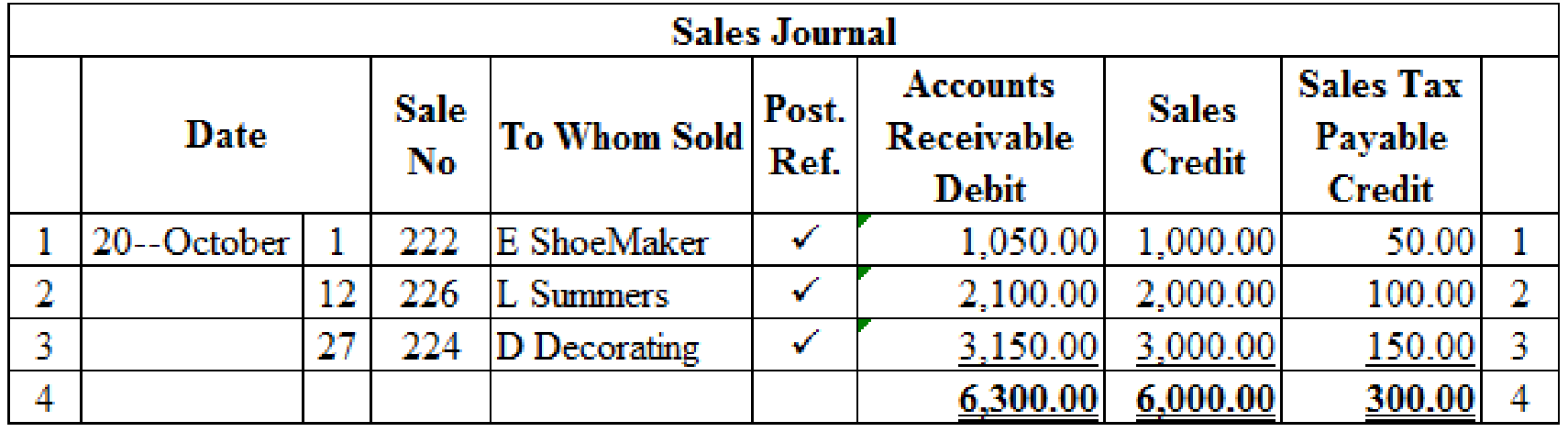
Table (1)
Verification of total debit and credit column:
Cash Receipts Journal: It is a special book where only cash receipts transactions that are received from customers, merchandise sales and service made in cash and collection of accounts receivable are recorded.
The following are the some examples of transactions that would be recorded in the Other Accounts credit column of the cash receipts journal:
- • Cash received as interest on notes payable
- • Interest revenue received from debtors
- • Cash receipts from bank loans
- • Cash receipts for capital investments
Prepare the given transactions in the cash receipts journal and verify the total column and rule the column:
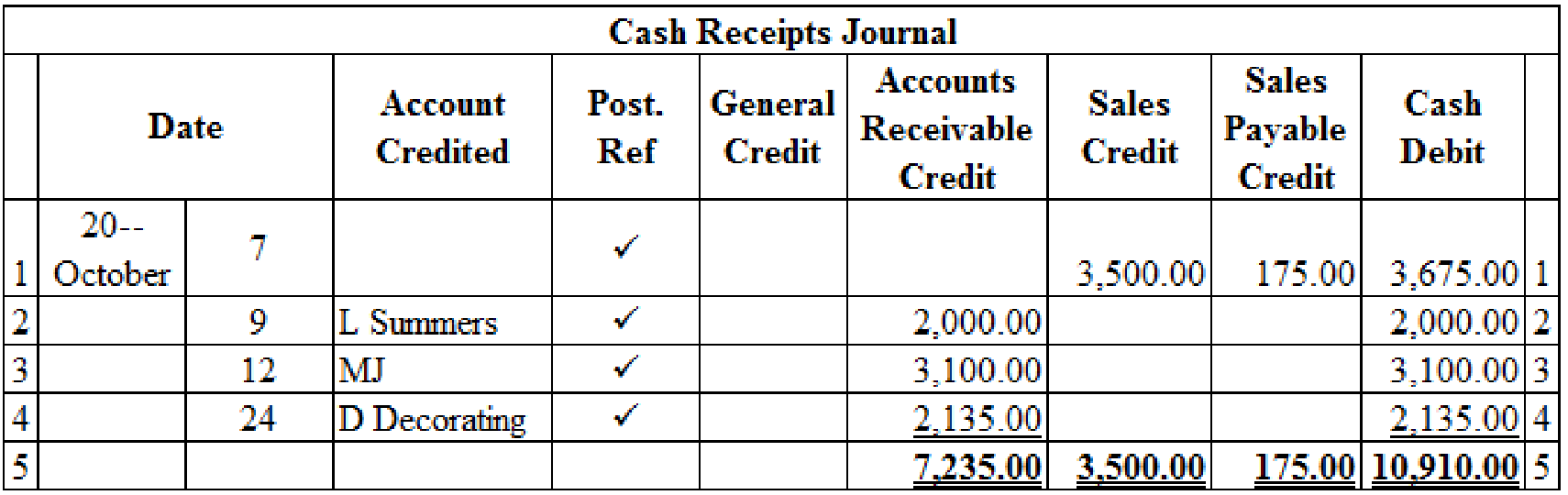
Table (2)
Verification of total debit and credit column:
Purchase Journal: Purchase journal records all the merchandise purchase on credit. In a single column purchase journal, debit aspect of inventory and credit aspect of accounts payable are recorded, and then posted to individual subsidiary supplier account.
Prepare the transactions in the purchase journal:
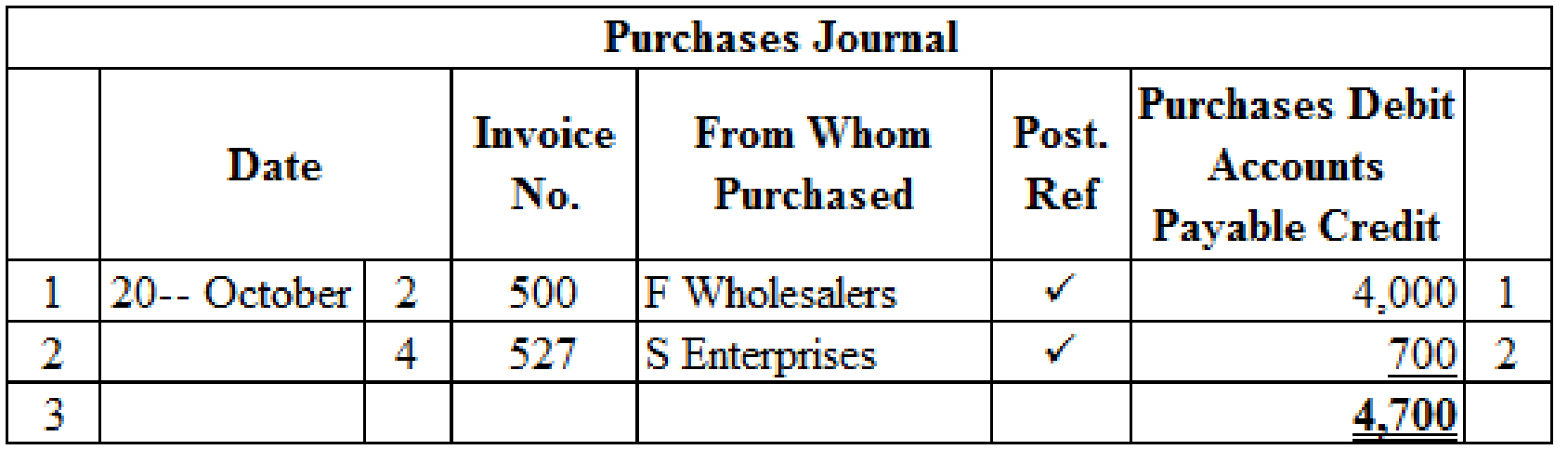
Table (3)
Cash payments journal: Cash payments journal refers to the journal that is used to record the all transaction which is involve the cash payments. For example, the business paid cash to employees (salary paid to employees).
Cash payments journal is used to record merchandise purchases made in cash and payments of accounts payable. It also records all other cash payments to various purposes. To include all these transactions, companies use multi-column cash payments journal.
Prepare the transactions in a cash payments journal and total the each column of cash payments journal:
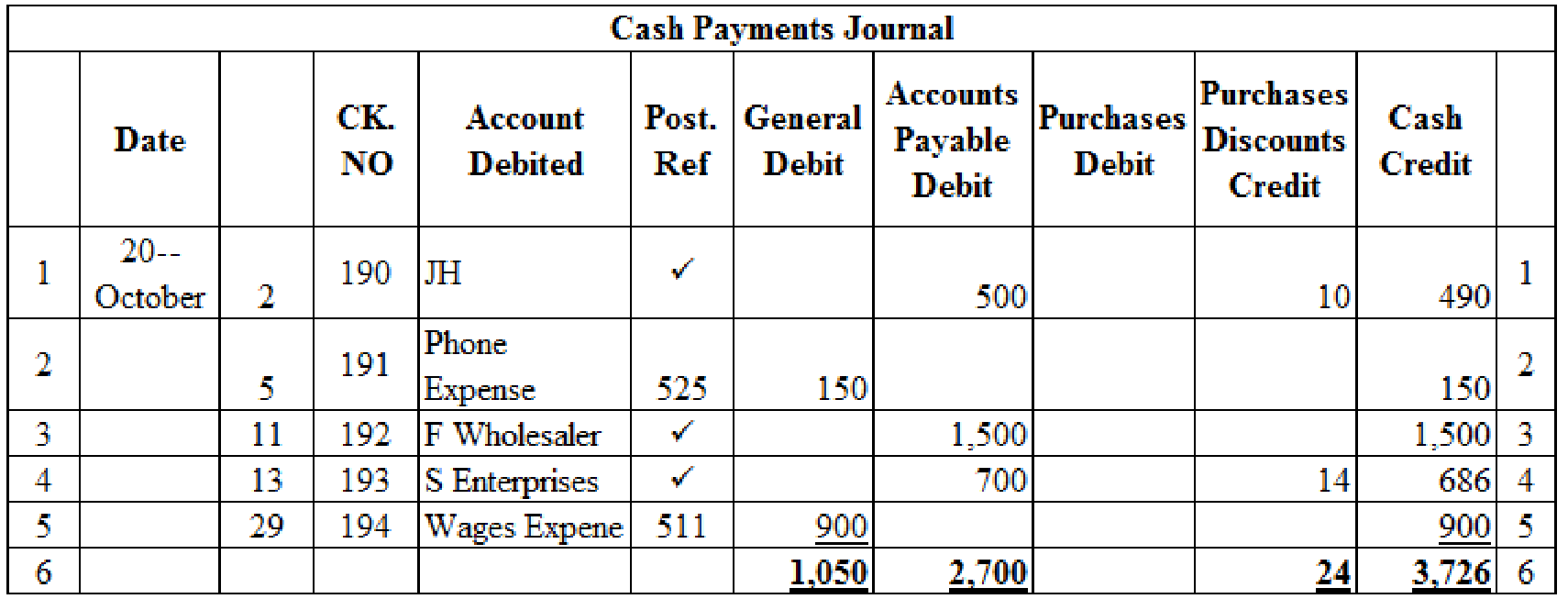
Table (4)
Use the general journal to record the sales returns and allowances:
General Journal: It is a book where all the monetary transactions are recorded in the form of journal entries on the date of their occurrence in a chronological order.
Transaction on October 14:
| General Journal | ||||||
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 20-- | ||||||
| October | 14 | Sales Returns and Allowances | 401.1 | 300.00 | ||
| Sales Tax Payable | 231 | 15.00 | ||||
| Accounts Receivable, MJ | 122/✓ | 315.00 | ||||
| (Record merchandise returned) | ||||||
Table (5)
Description:
- ■ Sales Returns and Allowances is a contra-revenue account, and contra-revenue accounts decrease the equity value, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- ■ Sales Tax Payable is a liability account. Since the payable decreased due to returns, the liability decreased, and a decrease in liability is debited.
- ■ Accounts Receivable, MJ Company is an asset account. Since inventory is returned, amount to be received has decreased, asset account is decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Transaction on October 17:
| Page: 3 | ||||||
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 20-- | ||||||
| October | 17 | Accounts Payable, V Etc. | 202/✓ | 900 | ||
| Purchases Returns and Allowances | 501.1 | 900 | ||||
| (Record merchandise returned) | ||||||
Table (6)
Description:
- ■ Accounts Payable, V Etc, is a liability account. Since inventory is returned, amount to be paid has decreased, liability account is decreased, and a decrease in liability is debited.
- ■ Purchases Returns and Allowances is a contra-cost account, and contra-cost accounts increase the equity value, and an increase in equity is credited.
2.
Post the prepared journals to the general ledger, accounts receivable ledger and accounts payable ledger accounts.
Explanation of Solution
Posting transactions: The process of transferring the journalized transactions into the accounts of the ledger is known as posting the transactions.
Post the prepared journals to the general ledger:
| ACCOUNT Cash ACCOUNT NO. 101 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20-- | |||||||
| October | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 18,225 | |||
| 31 | CR10 | 10,910 | 29,135 | ||||
| 31 | CP11 | 3,726 | 25,409 | ||||
Table (7)
| ACCOUNT Accounts Receivable ACCOUNT NO. 122 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20-- | |||||||
| October | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 9,619 | |||
| 14 | J5 | 315 | 9,304 | ||||
| 31 | S7 | 6,300 | 15,604 | ||||
| 31 | CR10 | 7,235 | 8,369 | ||||
Table (8)
| ACCOUNT Accounts Payable ACCOUNT NO. 202 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20-- | |||||||
| October | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 5,120 | |||
| 17 | J5 | 900 | 4,220 | ||||
| 31 | P6 | 4,700 | 8,920 | ||||
| 31 | CP11 | 2,700 | 6,220 | ||||
Table (9)
| ACCOUNT Sales Tax Payable ACCOUNT NO. 231 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20-- | |||||||
| October | 14 | J5 | 15 | 15 | |||
| 31 | S7 | 300 | 285 | ||||
| 31 | CR10 | 175 | 460 | ||||
Table (10)
| ACCOUNT Sales ACCOUNT NO. 401 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20-- | |||||||
| October | 31 | S7 | 6,000 | 6,000 | |||
| 31 | CR10 | 3,500 | 9,500 | ||||
Table (11)
| ACCOUNT Sales Returns and Allowances ACCOUNT NO. 401.1 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20-- | |||||||
| October | 14 | J5 | 300.00 | 300.00 | |||
Table (12)
| ACCOUNT Purchases ACCOUNT NO. 501 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20-- | |||||||
| October | 31 | P6 | 4,700 | 4,700 | |||
Table (13)
| ACCOUNT Purchases Return and Allowances ACCOUNT NO. 501.1 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20-- | |||||||
| October | 17 | J5 | 900 | 900 | |||
Table (14)
| ACCOUNT Purchases Discounts ACCOUNT NO. 501.2 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20-- | |||||||
| October | 31 | CP11 | 24 | 24 | |||
Table (15)
| ACCOUNT Wages Expense ACCOUNT NO. 511 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20-- | |||||||
| October | 29 | CP11 | 900 | 900 | |||
Table (16)
| ACCOUNT Phone Expense ACCOUNT NO. 5125 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20-- | |||||||
| October | 5 | CP11 | 150 | 150 | |||
Table (17)
Post the prepared journals to the accounts receivable ledger:
| NAME D Decorating | ||||||
| ADDRESS 12 J Lane, H, CT 06117 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| 20-- | ||||||
| October | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 3,340 | ||
| 24 | CR10 | 2,135 | 1,205 | |||
| 27 | S7 | 3,150 | 4,355 | |||
Table (18)
| NAME MJ | ||||||
| ADDRESS 700 H DR., AVON, CT 06108 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| 20-- | ||||||
| October | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 4,000 | ||
| 12 | CR10 | 3,100 | 900 | |||
| 14 | J5 | 315 | 585 | |||
Table (19)
| NAME E Shoe Maker | ||||||
| ADDRESS 52 J Road, H, CT 06118 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| 20-- | ||||||
| October | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 279 | ||
| 1 | S7 | 1,050 | 1,329 | |||
Table (20)
| NAME L Summers | ||||||
| ADDRESS 5200 H Avenue., H CT 06111 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| 20-- | ||||||
| October | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 2,000 | ||
| 9 | CR10 | 2,000 | ||||
| 12 | S7 | 2,100 | 2,100 | |||
Table (21)
Post the journals to the accounts payable ledger:
| NAME F Wholesalers | ||||||
| ADDRESS 43 L Lane., B CT 06007 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| 20-- | ||||||
| October | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 1,500 | ||
| 2 | P6 | 4,000 | 5,500 | |||
| 11 | CP11 | 1,500 | 4,000 | |||
Table (22)
| NAME J Hand | ||||||
| ADDRESS 1009 D Rd., F CT 06082 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| 20-- | ||||||
| October | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 500 | ||
| 2 | CP11 | 500 | 0 | |||
Table (23)
| NAME S Enterprises | ||||||
| ADDRESS 88 A Street, N, CT 06789 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| 20-- | ||||||
| October | 4 | P6 | 700 | 700 | ||
| 13 | CP11 | 700 | 0 | |||
Table (24)
| NAME V Etc. | ||||||
| ADDRESS 34 h Avenue., East H, CT 05234 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| 20-- | ||||||
| October | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 3,120 | ||
| 17 | J5 | 900 | 2,220 | |||
Table (25)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27
- i need correct options accountingarrow_forwardCan you help me with accounting questionsarrow_forwardDuring its first year, Yutsang Enterprises showed a $22 per-unit profit under absorption costing but would have reported a total profit of $20,000 less under variable costing. Suppose production exceeded sales by 600 units and an average contribution margin of 58% was maintained. a. What is the fixed cost per unit? b. What is the sales price per unit? c. What is the variable cost per unit? d. What is the unit sales volume if total profit under absorption costing was $240,000?arrow_forward
- Wood Manufacturing uses a job-order costing system and a predetermined overhead rate based on direct labor-hours to apply manufacturing overhead to jobs. Manufacturing overhead cost and direct labor hours were estimated at $120,000 and 50,000 hours, respectively, for the year. In August, Job #527 was completed at a cost of $6,200 in direct materials and $3,000 in direct labor. The labor rate is $7 per hour. By the end of the year, Wood had worked a total of 55,000 direct labor-hours and had incurred $130,500 in actual manufacturing overhead cost. If Job #527 contained 250 units, the unit product cost on the completed job cost sheet would be___. Answerarrow_forwardchoose best answerarrow_forwardGolydyodyodoyxoarrow_forward
- What is the gross profit rate?arrow_forwardplease solve this problemarrow_forwardA B C D 8 After analyzing expenses, the company has determined the following cost patterns. 9 Cost of Goods Sold (per unit) 10 Sales Commissions (per dollar of sales) 11 Administrative Salaries (per quarter) 12 Rent Expense (per quarter) 13 Depreciation Expense (per quarter) 14 $29.00 9.50% $45,000 $27,000 $36,000 15 Shipping has been determined to be a mixed cost with the following to tal costs and units: E F G H 16 17 2022 18 Quarter 1 19 Quarter2 20 Quarter 3 21 Quarter 4 22 2023 23 Quarter 1 24 Quarter2 25 Quarter 3 26 Quarter 4 27 28 Use the data to answer the following. 29 30 31 Total Cost Units $67,000 12,500 $94,000 21,000 $89,800 13,800 $92,600 20,000 $72,500 13,700 $80,000 14,000 $84,000 14,300 $100,000 22,500 (Use cells A4 to C26 from the given Information to complete this question. All answers should be input and displayed as positive values.) 321. Using the high-low method, determine a cost formula for shipping costs. 33 34 35 High level of activity 36 Low level of…arrow_forward
 Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





