
Statistical Techniques in Business and Economics
18th Edition
ISBN: 9781260579611
Author: Douglas Lind; William Marchal; Samuel Wathen
Publisher: MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 12, Problem 12E
The following are six observations collected from treatment 1, ten observations collected from treatment 2, and eight observations collected from treatment 3. Test the hypothesis that the treatment
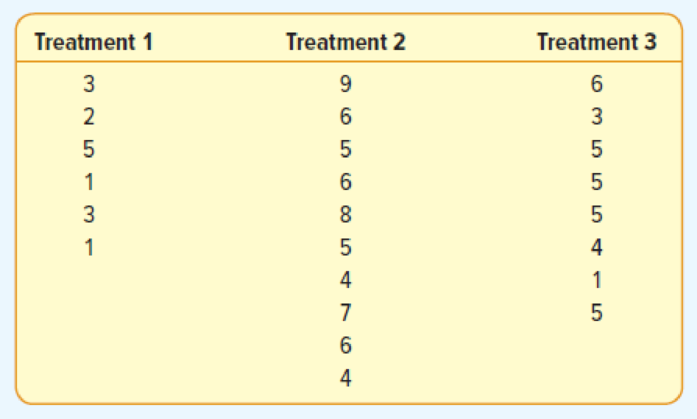
- a. State the null hypothesis and the alternate hypothesis.
- b. What is the decision rule?
- c. Compute SST, SSE, and SS total.
- d. Complete an ANOVA table.
- e. State your decision regarding the null hypothesis.
- f. If H0 is rejected, can we conclude that treatment 2 and treatment 3 differ? Use the 95% level of confidence.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
During busy political seasons, many opinion polls are conducted. In apresidential race, how do you think the participants in polls are generally selected?Discuss any issues regarding simple random, stratified, systematic, cluster, andconvenience sampling in these polls. What about other types of polls, besides political?
Please could you explain why 0.5 was added to each upper limpit of the intervals.Thanks
28. (a) Under what conditions do we say that two random variables X and Y are
independent?
(b) Demonstrate that if X and Y are independent, then it follows that E(XY) =
E(X)E(Y);
(e) Show by a counter example that the converse of (ii) is not necessarily true.
Chapter 12 Solutions
Statistical Techniques in Business and Economics
Ch. 12 - Steele Electric Products Inc. assembles cell...Ch. 12 - What is the critical F value when the sample size...Ch. 12 - Prob. 2ECh. 12 - Prob. 3ECh. 12 - Prob. 4ECh. 12 - Prob. 5ECh. 12 - Prob. 6ECh. 12 - Prob. 2SRCh. 12 - Prob. 7ECh. 12 - Prob. 8E
Ch. 12 - Prob. 9ECh. 12 - Prob. 10ECh. 12 - Prob. 3SRCh. 12 - Prob. 11ECh. 12 - The following are six observations collected from...Ch. 12 - Prob. 13ECh. 12 - Prob. 14ECh. 12 - Prob. 4SRCh. 12 - Prob. 15ECh. 12 - For exercises 15 and 16, conduct a test of...Ch. 12 - Prob. 17ECh. 12 - Prob. 18ECh. 12 - Prob. 5SRCh. 12 - Prob. 19ECh. 12 - Prob. 20ECh. 12 - Prob. 21ECh. 12 - Prob. 22ECh. 12 - Prob. 23CECh. 12 - Prob. 24CECh. 12 - Prob. 25CECh. 12 - Prob. 26CECh. 12 - In an ANOVA table, the MSE is equal to 10. Random...Ch. 12 - Prob. 28CECh. 12 - Prob. 29CECh. 12 - Prob. 30CECh. 12 - Prob. 31CECh. 12 - Prob. 32CECh. 12 - Prob. 33CECh. 12 - Prob. 34CECh. 12 - Prob. 35CECh. 12 - Prob. 36CECh. 12 - Prob. 37CECh. 12 - Prob. 38CECh. 12 - Prob. 39CECh. 12 - Prob. 40CECh. 12 - Prob. 41CECh. 12 - Prob. 42CECh. 12 - Prob. 43CECh. 12 - Prob. 44CECh. 12 - Prob. 45CECh. 12 - Prob. 46CECh. 12 - Prob. 47CECh. 12 - Prob. 48CECh. 12 - Prob. 50DACh. 12 - Prob. 51DACh. 12 - Prob. 1PCh. 12 - Prob. 2PCh. 12 - Prob. 3PCh. 12 - Prob. 4PCh. 12 - Prob. 5PCh. 12 - Prob. 6PCh. 12 - Prob. 7PCh. 12 - Prob. 1CCh. 12 - Prob. 2CCh. 12 - Prob. 1.1PTCh. 12 - The likelihood of rejecting a true null hypothesis...Ch. 12 - Prob. 1.3PTCh. 12 - Prob. 1.4PTCh. 12 - Prob. 1.5PTCh. 12 - Prob. 1.6PTCh. 12 - In a two-tailed test, the rejection region is...Ch. 12 - Prob. 1.8PTCh. 12 - Prob. 1.9PTCh. 12 - Prob. 1.10PTCh. 12 - Prob. 2.1PTCh. 12 - Prob. 2.2PTCh. 12 - Prob. 2.3PT
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 19. Let X be a non-negative random variable. Show that lim nE (IX >n)) = 0. E lim (x)-0. = >arrow_forward(c) Utilize Fubini's Theorem to demonstrate that E(X)= = (1- F(x))dx.arrow_forward(c) Describe the positive and negative parts of a random variable. How is the integral defined for a general random variable using these components?arrow_forward
- 26. (a) Provide an example where X, X but E(X,) does not converge to E(X).arrow_forward(b) Demonstrate that if X and Y are independent, then it follows that E(XY) E(X)E(Y);arrow_forward(d) Under what conditions do we say that a random variable X is integrable, specifically when (i) X is a non-negative random variable and (ii) when X is a general random variable?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...
Algebra
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:McGraw Hill

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:9781305652231
Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Hypothesis Testing using Confidence Interval Approach; Author: BUM2413 Applied Statistics UMP;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Hq1l3e9pLyY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Hypothesis Testing - Difference of Two Means - Student's -Distribution & Normal Distribution; Author: The Organic Chemistry Tutor;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UcZwyzwWU7o;License: Standard Youtube License